Namespaces | |
| namespace | gpu |
Classes | |
| class | Array |
| Array class, helper to manipulate 2D float array with "(i, j)" indexing. More... | |
| class | ArrayControlFunction |
| class | ArrayFunction |
| Array (x, y) function class. More... | |
| struct | AssertResults |
| class | BiquadFunction |
| Biquad (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | BumpFunction |
| Bump (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | Cloud |
| Represents a collection of unordered points in 2D space. More... | |
| struct | ColorAdjust |
| struct | ComputeMode |
| class | CoordFrame |
| class | CraterFunction |
| Crater (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | DiskFunction |
| DiskFunction (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | DiskLruTileStorage |
| class | DiskSequentialTileStorage |
| class | DrainageBasins |
| class | Edge |
| Represents a line segment in 2D space. More... | |
| class | FbmFunction |
| Fractional Brownian Motion (FBM) function class. More... | |
| class | FbmIqFunction |
| IQ layering function class. More... | |
| class | FbmJordanFunction |
| Jordan layering function class. More... | |
| class | FbmPingpongFunction |
| Pingpong layering function class. More... | |
| class | FbmRidgedFunction |
| Ridged layering function class. More... | |
| class | FbmSwissFunction |
| Swiss layering function class. More... | |
| class | FieldFunction |
| Field function class. More... | |
| class | Function |
| A class that wraps a callable entity taking three floats and returning a float. More... | |
| class | GaussianPulseFunction |
| GaussianPulse (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | GenericFractalFunction |
| A class for generating fractal noise functions based on an underlying noise function. More... | |
| class | Graph |
| Graph class, to manipulate graphs in 2D. More... | |
| class | Interpolator1D |
| A class for performing 1D interpolation using the GSL library. More... | |
| class | InterpolatorCurve |
| Class for performing curve interpolation on a set of points. More... | |
| struct | IVec4Eq |
| struct | IVec4Hash |
| struct | LruTileEntry |
| class | LruTileStorage |
| struct | Mat |
| Mat class for basic manipulation of 2D matrices. More... | |
| class | NoiseFunction |
| A class for generating noise functions. More... | |
| class | ParberryFunction |
| Parberry (x, y) function class. More... | |
| struct | Particle |
| class | Path |
| Represents an ordered set of points in 2D, forming a polyline (open or closed). More... | |
| class | PerlinBillowFunction |
| Perlin 'billow' (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | PerlinFunction |
| Perlin (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | PerlinHalfFunction |
| Perlin 'half' (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | PerlinMixFunction |
| Perlin 'mix' (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | Point |
| A class to represent and manipulate 2D points that can carry a value. More... | |
| struct | Pos |
| class | PyramidDecomposition |
| Pyramid decomposition class, to handle low-pass pyramids (like Laplacian pyramid). More... | |
| class | RamTileStorage |
| struct | Recorder |
| The Recorder class is responsible for recording timing information for individual events. More... | |
| class | RectangleFunction |
| RectangleFunction (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | RiftFunction |
| Rift (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | Simplex2Function |
| OpenSimplex2 (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | Simplex2SFunction |
| OpenSimplex2S (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | SlopeFunction |
| Slope (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | StepFunction |
| Step (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | Tensor |
| A class to represent a multi-dimensional tensor. More... | |
| struct | TileKey |
| struct | TileKeyHash |
| struct | TileRegion |
| class | TileStorage |
| class | Timer |
| The Timer class is a singleton that manages multiple Recorders and provides an interface for timing events. More... | |
| class | ValueCubicNoiseFunction |
| Value Cubic noise (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | ValueDelaunayNoiseFunction |
| ValueDelaunayNoise (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | ValueLinearNoiseFunction |
| ValueLinearNoiseFunction (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | ValueNoiseFunction |
| Value noise (x, y) function class. More... | |
| struct | Vec2 |
| struct | Vec2< float > |
| struct | Vec2< int > |
| struct | Vec3 |
| struct | Vec3< float > |
| struct | Vec3< int > |
| struct | Vec4 |
| struct | Vec4< float > |
| struct | Vec4< int > |
| struct | VirtualArray |
| class | VirtualTexture |
| struct | VirtualTextureStorage |
| Storage manager for VirtualTexture. More... | |
| class | WaveDuneFunction |
| Wave dune (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | WaveSineFunction |
| Wave sine (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | WaveSquareFunction |
| Wave square (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | WaveTriangularFunction |
| Wave triangular (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | WorleyDoubleFunction |
| Worley (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | WorleyFunction |
| Worley (x, y) function class. More... | |
| class | XyControlFunction |
Functions | |
| glm::vec4 | adjust (const glm::vec4 &v, float dx, float dy, float dz, float dw) |
| Array | cv_mat_to_array (const cv::Mat &mat, bool remap_values=true, bool flip_j=false) |
Converts an OpenCV cv::Mat to a 2D Array with optional value scaling to [0, 1]. | |
| template<typename Fn > | |
| void | for_each_cell (Array &a, Fn &&fn) |
| Apply a function to every cell (mutable). | |
| template<typename Fn > | |
| void | for_each_cell (const Array &a, Fn &&fn) |
| Apply a function to every cell (read-only). | |
| template<typename T , typename Fn , typename Reduce > | |
| T | reduce_cells (const Array &a, T init, Fn &&fn, Reduce &&reduce) |
| Reduce all cells to a single value. | |
| template<typename T , typename Fn , typename Reduce > | |
| T | reduce_cells (const Array &a, T init, Reduce &&reduce) |
| Reduce all cells to a single value. | |
| void | alter_elevation (Array &array, const Cloud &cloud, int ir, float footprint_ratio=1.f, glm::vec2 shift={0.f, 0.f}, glm::vec2 scale={1.f, 1.f}) |
| Point-wise alteration: locally enforce a new elevation value while maintaining the 'shape' of the heightmap. | |
| Array | base_elevation (glm::ivec2 shape, const std::vector< std::vector< float > > &values, float width_factor=1.f, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generate a heightmap from a coarse grid of control points with defined elevation values. | |
| Array | flatbed_carve (glm::ivec2 shape, const Path &path, float bottom_extent=32.f, float vmin=0.1f, float depth=0.05f, float falloff_distance=128.f, float outer_slope=0.1f, bool preserve_bedshape=true, RadialProfile radial_profile=RadialProfile::RP_GAIN, float radial_profile_parameter=2.f, Array *p_falloff_mask=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_r=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Carves a flatbed shape along a path. | |
| void | flatbed_carve (Array &z, const Path &path, float bottom_extent=32.f, float vmin=0.1f, float depth=0.05f, float falloff_distance=128.f, float outer_slope=0.1f, bool preserve_bedshape=true, RadialProfile radial_profile=RadialProfile::RP_GAIN, float radial_profile_parameter=2.f, Array *p_falloff_mask=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_r=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Blends a flatbed carve into an existing heightmap. | |
| Array | reverse_midpoint (const Array &array, uint seed, float noise_scale=1.f, float threshold=0.f) |
| Apply the reverse midpoint displacement algorithm to the input array. | |
| Array | ridgelines (glm::ivec2 shape, const std::vector< float > &xr, const std::vector< float > &yr, const std::vector< float > &zr, float slope, float k_smoothing=1.f, float width=0.1f, float vmin=0.f, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox_array={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generate a heightmap based on a set of ridgelines and a specified slope. | |
| Array | ridgelines_bezier (glm::ivec2 shape, const std::vector< float > &xr, const std::vector< float > &yr, const std::vector< float > &zr, float slope, float k_smoothing=1.f, float width=0.1f, float vmin=0.f, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox_array={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generate a heightmap based on a set of ridgelines with quadratic Bezier interpolation. | |
| Array | stamping (glm::ivec2 shape, const std::vector< float > &xr, const std::vector< float > &yr, const std::vector< float > &zr, Array kernel, int kernel_ir, bool kernel_scale_radius, bool kernel_scale_amplitude, StampingBlendMethod blend_method, uint seed, float k_smoothing=0.1f, bool kernel_flip=true, bool kernel_rotate=false, glm::vec4 bbox_array={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generate a heightmap by stamping a kernel at predefined locations. | |
| Array | blend_exclusion (const Array &array1, const Array &array2) |
| Return the 'exclusion' blending of two arrays. | |
| Array | blend_gradients (const Array &array1, const Array &array2, int ir=4) |
| Return the blending of two arrays based on their gradients. | |
| Array | blend_negate (const Array &array1, const Array &array2) |
| Return the 'negate' blending of two arrays. | |
| Array | blend_overlay (const Array &array1, const Array &array2) |
| Return the 'overlay' blending of two arrays. | |
| Array | blend_soft (const Array &array1, const Array &array2) |
| Return the 'soft' blending of two arrays. | |
| Array | mixer (const Array &t, const std::vector< const Array * > &arrays, float gain_factor=1.f) |
Return the mixing of a set of arrays based on a parameter t. | |
| Array | transfer (const Array &source, const Array &target, int ir, float amplitude, bool target_prefiltering=false) |
| Transfers spatial details from a source array onto a target array. | |
| void | extrapolate_borders (Array &array, int nbuffer=1, float sigma=0.f) |
Performs linear extrapolation of values at the borders of an array (e.g., i = 0, j = 0, etc.) based on the inner values of the array. | |
| void | falloff (Array &array, float strength=1.f, DistanceFunction dist_fct=DistanceFunction::EUCLIDIAN, const Array *p_noise=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Applies a falloff effect to the input array based on distance. | |
| void | fill_borders (Array &array) |
Fills the border values of an array (e.g., i = 0, j = 0, etc.) based on the values of the first neighboring cells. | |
| void | fill_borders (Array &array, int nbuffer) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| Array | generate_buffered_array (const Array &array, glm::ivec4 buffers, bool zero_padding=false) |
| Creates and returns a new array with additional buffer zones at the boundaries, where the buffer values are filled either by symmetry or by zero-padding. | |
| void | make_periodic (Array &array, int nbuffer, const PeriodicityType &periodicity_type=PeriodicityType::PERIODICITY_XY) |
| Adjusts the input array to be periodic in both directions by transitioning smoothly at the boundaries. | |
| Array | make_periodic_stitching (const Array &array, float overlap) |
| Creates a periodic array in both directions using a stitching operation that minimizes errors at the boundaries. | |
| Array | make_periodic_tiling (const Array &array, float overlap, glm::ivec2 tiling) |
| Creates a tiled, periodic array by applying a transition with overlap in both directions. | |
| void | set_borders (Array &array, glm::vec4 border_values, glm::ivec4 buffer_sizes) |
| Enforces specific values at the boundaries of the array. | |
| void | set_borders (Array &array, float border_values, int buffer_sizes) |
| Enforces a uniform value at all boundaries of the array. | |
| void | sym_borders (Array &array, glm::ivec4 buffer_sizes) |
| Fills the values at the domain borders using symmetry over a specified buffer depth. | |
| void | zeroed_borders (Array &array) |
Fills the border values (e.g., i = 0, j = 0, etc.) of the array with zeros. | |
| void | zeroed_edges (Array &array, float sigma=1.f, DistanceFunction dist_fct=DistanceFunction::EUCLIDIAN, const Array *p_noise=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Applies a smooth transition to zero at the array borders. | |
| void | apply_hillshade (Tensor &img, const Array &array, float vmin=0.f, float vmax=1.f, float exponent=1.f) |
| Apply hillshading to a Tensor image. | |
| void | apply_hillshade (std::vector< uint8_t > &img, const Array &array, float vmin=0.f, float vmax=1.f, float exponent=1.f, bool is_img_rgba=false) |
| Apply hillshading to an 8-bit image. | |
| void | color_adjust (VirtualTexture &tex, ColorAdjust param, const ComputeMode &cm) |
| Tensor | colorize (const Array &array, float vmin, float vmax, int cmap, bool hillshading, bool reverse=false, const Array *p_noise=nullptr) |
| Apply colorization to an array. | |
| void | colorize (VirtualTexture &out, VirtualArray &level, const ComputeMode &cm, float vmin, float vmax, int cmap, VirtualArray *p_alpha=nullptr, bool reverse=false, VirtualArray *p_noise=nullptr) |
| Colorize a scalar field into a texture using a predefined colormap. | |
| void | colorize (VirtualTexture &out, VirtualArray &level, const ComputeMode &cm, float vmin, float vmax, const std::vector< float > &positions, const std::vector< glm::vec3 > &colormap_colors, VirtualArray *p_alpha=nullptr, bool reverse=false, VirtualArray *p_noise=nullptr) |
| Colorize a scalar field into a texture using a custom colormap. | |
| Tensor | colorize_grayscale (const Array &array) |
| Convert an array to a grayscale image. | |
| Tensor | colorize_histogram (const Array &array) |
| Convert an array to a histogram-based grayscale image. | |
| Tensor | colorize_slope_height_heatmap (const Array &array, int cmap) |
| Colorizes a slope height heatmap based on the gradient norms of a given array. | |
| Tensor | colorize_vec2 (const Array &array1, const Array &array2) |
| Combine two arrays into a colored image. | |
| void | luminance (VirtualArray &out, VirtualTexture &tex, const ComputeMode &cm) |
| Compute luminance from a texture. | |
| void | mix (VirtualTexture &out, VirtualTexture &tex1, VirtualTexture &tex2, const ComputeMode &cm, bool use_sqrt_avg=true) |
| Mix two textures into an output texture. | |
| void | mix (VirtualTexture &out, std::vector< VirtualTexture * > &texs, const ComputeMode &cm, bool use_sqrt_avg=true) |
| void | mix_normal_map (VirtualTexture &out, VirtualTexture &nmap_base, VirtualTexture &nmap_detail, const ComputeMode &cm, float detail_scaling, NormalMapBlendingMethod blending_method) |
| Blend two normal maps into a single output normal map. | |
| std::vector< glm::vec3 > | get_colormap_data (int cmap) |
| Array | convolve1d_i (const Array &array, const std::vector< float > &kernel) |
| Return the convolution product of the array with a 1D kernel along the 'i' direction. | |
| Array | convolve1d_j (const Array &array, const std::vector< float > &kernel) |
| Return the convolution product of the array with a 1D kernel along the 'j' direction. | |
| Array | convolve2d (const Array &array, const Array &kernel) |
| Return the convolution product of the array with a given 2D kernel. | |
| Array | convolve2d_truncated (const Array &array, const Array &kernel) |
| Return the convolution product of the array with a given 2D kernel, with a truncated output size. | |
| Array | convolve2d_svd (const Array &z, const Array &kernel, int rank=3) |
| Return the approximate convolution product of the array with a Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) of a kernel. | |
| Array | convolve2d_svd_rotated_kernel (const Array &z, const Array &kernel, int rank=3, int n_rotations=6, uint seed=1) |
| Return the approximate convolution product of the array with a Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) of a kernel combined with kernel rotations. | |
| Array | accumulation_curvature (const Array &z, int ir) |
| Computes the accumulation curvature of a heightmap. Acumulation curvature is a measure of the extent of local accumulation of flows at a given point. | |
| Array | curvature_gaussian (const Array &z) |
| Calculates the Gaussian curvature of a heightmap, providing insights into the surface's intrinsic curvature at each point. Gaussian curvature is a fundamental measure of surface curvature, indicating how the surface bends in multiple directions at each point. This metric is often used in geomorphology to understand landform shapes. Usage: Use this function to analyze the overall shape of terrain features, identifying whether regions are saddle-like, dome-like, or basin-like. Useful in studies related to tectonics, erosion patterns, and landform development. | |
| Array | curvature_horizontal_cross_sectional (const Array &z, int ir) |
| TODO. | |
| Array | curvature_horizontal_plan (const Array &z, int ir) |
| TODO. | |
| Array | curvature_horizontal_tangential (const Array &z, int ir) |
| TODO. | |
| Array | curvature_mean (const Array &z) |
| Computes the mean curvature of a heightmap, indicating the average curvature at each point on the surface. Mean curvature is another critical metric in geomorphology, representing the average bending of the surface. This measure is useful in understanding terrain smoothness and can help identify areas of potential erosion or deposition. Usage: Apply this function to detect areas prone to erosion or sediment deposition. Useful in landscape evolution models and in analyzing the stability of slopes. | |
| Array | curvature_ring (const Array &z, int ir) |
| Ring curvature is a second-order derivative of the elevation surface. It describes how the surface bends along a ring-like shape, often computed from the principal curvatures. Positive Values: Indicate convex surfaces where flow disperses (ridges, hilltops). Negative Values: Indicate concave surfaces where flow converges (valleys, depressions). | |
| Array | curvature_rotor (const Array &z, int ir) |
| Rotor curvature, also called flow line curvature, describes how the curvature of a terrain surface influences the acceleration or deceleration of flow (e.g., water, debris, or air) along the direction of maximum slope. Positive values: Flow is decelerating (convex-up terrain, such as ridges or crests). Negative values: Flow is accelerating (concave-down terrain, such as valleys or channels). Zero values: Flow moves in a linear, constant-slope manner. | |
| Array | curvature_vertical_longitudinal (const Array &z, int ir) |
| TODO. | |
| Array | curvature_vertical_profile (const Array &z, int ir) |
| TODO. | |
| Array | shape_index (const Array &z, int ir) |
| Computes the Shape Index (SI) of the terrain, quantifying landform complexity based on curvature. The Shape Index is a metric used to describe the shape of landforms, particularly in digital elevation models (DEMs). It differentiates between convex (e.g., hilltops), concave (e.g., valleys), and flat surfaces. Usage: Use this function to classify terrain into different morphological types, which can be important in land use planning and environmental studies. Useful in landscape ecology and in understanding geomorphological processes. | |
| Array | level_set_curvature (const Array &array, int prefilter_ir) |
| Computes a signed level-set curvature. | |
| Array | unsphericity (const Array &z, int ir) |
| Calculates the unsphericity of a surface, indicating how much the terrain deviates from a perfect spherical shape. Unsphericity is a measure used to understand the degree of asymmetry in terrain surfaces. It quantifies how much a surface deviates from being perfectly spherical or symmetrical, which can be critical in various geomorphological analyses. Usage: Use this function to identify areas of terrain that significantly deviate from a spherical shape, which may indicate unique geological formations or erosion patterns. Helpful in identifying and analyzing landforms that are not perfectly round or symmetrical, such as irregular hills or basins. | |
| void | compute_curvature_gradients (const Array &z, Array &p, Array &q, Array &r, Array &s, Array &t) |
| Array | compute_curvature_h (const Array &r, const Array &t) |
| Array | compute_curvature_k (const Array &p, const Array &q, const Array &r, const Array &s, const Array &t) |
| bool | assert_almost_equal (const Array &a, const Array &b, float tolerance, const std::string &fname="", AssertResults *p_results=nullptr) |
| std::function< float(float)> | get_erosion_profile_function (const ErosionProfile &erosion_profile, float delta, float &profile_avg) |
| void | coastal_erosion_diffusion (Array &z, Array &water_depth, float additional_depth, int iterations=10, Array *p_water_mask=nullptr) |
| Simulates terrain diffusion due to coastal erosion. | |
| void | coastal_erosion_profile (Array &z, Array &water_depth, float shore_ground_extent, float shore_water_extent, float slope_shore=0.5f, float slope_shore_water=0.5f, float scarp_extent_ratio=0.5f, bool apply_post_filter=true, Array *p_shore_mask=nullptr) |
| Applies a coastal erosion profile to a terrain elevation field. | |
| void | coastal_erosion_profile (Array &z, const Array *p_mask, Array &water_depth, float shore_ground_extent, float shore_water_extent, float slope_shore=0.5f, float slope_shore_water=0.5f, float scarp_extent_ratio=0.5f, bool apply_post_filter=true, Array *p_shore_mask=nullptr) |
| void | depression_filling (Array &z, int iterations=1000, float epsilon=1e-4f) |
| Fill the depressions of the heightmap using the Planchon-Darboux algorithm. | |
| void | depression_filling_priority_flood (Array &z) |
| void | erosion_maps (Array &z_before, Array &z_after, Array &erosion_map, Array &deposition_map, float tolerance=0.f) |
| void | hydraulic_algebric (Array &z, Array *p_mask, float talus_ref, int ir, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_erosion_map=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, float c_erosion=0.05f, float c_deposition=0.05f, int iterations=1) |
| Apply an algerbic formula based on the local gradient to perform erosion/deposition. | |
| void | hydraulic_algebric (Array &z, float talus_ref, int ir, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_erosion_map=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, float c_erosion=0.05f, float c_deposition=0.05f, int iterations=1) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | hydraulic_benes (Array &z, Array *p_mask, int iterations=50, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_moisture_map=nullptr, Array *p_erosion_map=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, float c_capacity=40.f, float c_erosion=0.2f, float c_deposition=0.8f, float water_level=0.005f, float evap_rate=0.01f, float rain_rate=0.5f) |
| Apply cell-based hydraulic erosion/deposition based on Benes et al. procedure. | |
| void | hydraulic_benes (Array &z, int iterations=50, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_moisture_map=nullptr, Array *p_erosion_map=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, float c_capacity=40.f, float c_erosion=0.2f, float c_deposition=0.8f, float water_level=0.005f, float evap_rate=0.01f, float rain_rate=0.5f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | hydraulic_blur (Array &z, float radius, float vmax, float k_smoothing=0.1f) |
| Apply cell-based hydraulic erosion using a nonlinear diffusion model. | |
| void | hydraulic_diffusion (Array &z, float c_diffusion, float talus, int iterations) |
| Apply cell-based hydraulic erosion using a nonlinear diffusion model. | |
| void | hydraulic_musgrave (Array &z, Array &moisture_map, int iterations=100, float c_capacity=1.f, float c_erosion=0.1f, float c_deposition=0.1f, float water_level=0.01f, float evap_rate=0.01f) |
| Apply cell-based hydraulic erosion/deposition of Musgrave et al. (1989). | |
| void | hydraulic_musgrave (Array &z, int iterations=100, float c_capacity=1.f, float c_erosion=0.1f, float c_deposition=0.1f, float water_level=0.01f, float evap_rate=0.01f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | hydraulic_particle (Array &z, Array *p_mask, int nparticles, int seed, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_moisture_map=nullptr, Array *p_erosion_map=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, float c_capacity=10.f, float c_erosion=0.05f, float c_deposition=0.05f, float c_inertia=0.3f, float drag_rate=0.001f, float evap_rate=0.001f, bool post_filtering=false) |
| Apply hydraulic erosion using a particle based procedure. | |
| void | hydraulic_particle (Array &z, int nparticles, int seed, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_moisture_map=nullptr, Array *p_erosion_map=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, float c_capacity=10.f, float c_erosion=0.05f, float c_deposition=0.05f, float c_inertia=0.3f, float drag_rate=0.001f, float evap_rate=0.001f, bool post_filtering=false) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | hydraulic_particle_multiscale (Array &z, float particle_density, int seed, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_moisture_map=nullptr, Array *p_erosion_map=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, float c_capacity=10.f, float c_erosion=0.05f, float c_deposition=0.01f, float c_inertia=0.3f, float drag_rate=0.01f, float evap_rate=0.001f, int pyramid_finest_level=0) |
| Apply hydraulic erosion using a particle based procedure, using a pyramid decomposition to allow a multiscale approach. | |
| void | hydraulic_procedural (Array &z, uint seed, float ridge_wavelength, float ridge_scaling=0.1f, ErosionProfile erosion_profile=ErosionProfile::TRIANGLE_SMOOTH, float delta=0.02f, float noise_ratio=0.2f, int prefilter_ir=-1, float density_factor=1.f, float kernel_width_ratio=2.f, float phase_smoothing=2.f, float phase_noise_amp=M_PI, bool reverse_phase=false, bool rotate90=false, bool use_default_mask=true, float talus_mask=0.f, Array *p_mask=nullptr, Array *p_ridge_mask=nullptr, float vmin=0.f, float vmax=-1.f) |
| Generates a procedurally eroded terrain using hydraulic erosion and ridge generation techniques. | |
| void | hydraulic_spl (Array &z) |
| void | hydraulic_stream (Array &z, float c_erosion, float talus_ref, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_moisture_map=nullptr, Array *p_erosion_map=nullptr, int ir=1, float clipping_ratio=10.f) |
| Apply hydraulic erosion based on a flow accumulation map. | |
| void | hydraulic_stream (Array &z, Array *p_mask, float c_erosion, float talus_ref, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_moisture_map=nullptr, Array *p_erosion_map=nullptr, int ir=1, float clipping_ratio=10.f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | hydraulic_stream_log (Array &z, float c_erosion, float talus_ref, int deposition_ir=32, float deposition_scale_ratio=1.f, float gradient_power=0.8f, float gradient_scaling_ratio=1.f, int gradient_prefilter_ir=16, float saturation_ratio=1.f, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_moisture_map=nullptr, Array *p_erosion_map=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, Array *p_flow_map=nullptr) |
| Apply hydraulic erosion based on a flow accumulation map, alternative formulation. | |
| void | hydraulic_stream_log (Array &z, float c_erosion, float talus_ref, Array *p_mask, int deposition_ir=32, float deposition_scale_ratio=1.f, float gradient_power=0.8f, float gradient_scaling_ratio=1.f, int gradient_prefilter_ir=16, float saturation_ratio=1.f, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_moisture_map=nullptr, Array *p_erosion_map=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, Array *p_flow_map=nullptr) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | hydraulic_stream_upscale_amplification (Array &z, float c_erosion, float talus_ref, int upscaling_levels=1, float persistence=1.f, int ir=1, float clipping_ratio=10.f) |
| Applies hydraulic erosion with upscaling amplification. | |
| void | hydraulic_stream_upscale_amplification (Array &z, Array *p_mask, float c_erosion, float talus_ref, int upscaling_levels=1, float persistence=1.f, int ir=1, float clipping_ratio=10.f) |
| Applies hydraulic erosion with upscaling amplification, with a post-processing intensity mask. | |
| void | hydraulic_vpipes (Array &z, Array *p_mask, int iterations, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_moisture_map=nullptr, Array *p_erosion_map=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, float water_height=0.1f, float c_capacity=0.1f, float c_erosion=0.05f, float c_deposition=0.05f, float rain_rate=0.f, float evap_rate=0.01f) |
| Apply hydraulic erosion using the 'virtual pipes' algorithm. | |
| void | hydraulic_vpipes (Array &z, int iterations, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_moisture_map=nullptr, Array *p_erosion_map=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, float water_height=0.1f, float c_capacity=0.1f, float c_erosion=0.05f, float c_deposition=0.05f, float rain_rate=0.f, float evap_rate=0.01f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | sediment_deposition (Array &z, Array *p_mask, const Array &talus, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, float max_deposition=0.01, int iterations=5, int thermal_subiterations=10) |
| Perform sediment deposition combined with thermal erosion. | |
| void | sediment_deposition (Array &z, const Array &talus, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, float max_deposition=0.01, int iterations=5, int thermal_subiterations=10) |
| void | sediment_deposition_particle (Array &z, Array *p_mask, int nparticles, int ir, int seed=1, Array *p_spawning_map=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, float particle_initial_sediment=0.1f, float deposition_velocity_limit=0.01f, float drag_rate=0.001f) |
| void | sediment_deposition_particle (Array &z, int nparticles, int ir, int seed=1, Array *p_spawning_map=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, float particle_initial_sediment=0.1f, float deposition_velocity_limit=0.01f, float drag_rate=0.001f) |
| void | sediment_layer (Array &z, const Array &talus_layer, const Array &talus_upper_limit, int iterations, bool apply_post_filter=true, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| void | stratify (Array &z, Array *p_mask, std::vector< float > hs, std::vector< float > gamma, Array *p_noise=nullptr) |
| Stratify the heightmap by creating a series of layers with elevations corrected by a gamma factor. | |
| void | stratify (Array &z, std::vector< float > hs, std::vector< float > gamma, Array *p_noise=nullptr) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | stratify (Array &z, std::vector< float > hs, float gamma=0.5f, Array *p_noise=nullptr) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | stratify (Array &z, Array &partition, int nstrata, float strata_noise, float gamma, float gamma_noise, int npartitions, uint seed, float mixing_gain_factor=1.f, Array *p_noise=nullptr, float vmin=1.f, float vmax=0.f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | stratify_multiscale (Array &z, float zmin, float zmax, std::vector< int > n_strata, std::vector< float > strata_noise, std::vector< float > gamma_list, std::vector< float > gamma_noise, uint seed, Array *p_mask=nullptr, Array *p_noise=nullptr) |
| Stratify the heightmap by creating a multiscale series of layers with elevations corrected by a gamma factor. | |
| void | stratify_oblique (Array &z, Array *p_mask, std::vector< float > hs, std::vector< float > gamma, float talus, float angle, Array *p_noise=nullptr) |
| Stratify the heightmap by creating a series of oblique layers with elevations corrected by a gamma factor. | |
| void | stratify_oblique (Array &z, std::vector< float > hs, std::vector< float > gamma, float talus, float angle, Array *p_noise=nullptr) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | thermal (Array &z, Array *p_mask, const Array &talus, int iterations=10, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| Apply thermal weathering erosion. | |
| void | thermal (Array &z, const Array &talus, int iterations=10, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| void | thermal (Array &z, float talus, int iterations=10, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | thermal_auto_bedrock (Array &z, const Array &talus, int iterations=10, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| Apply thermal weathering erosion with automatic determination of the bedrock. | |
| void | thermal_auto_bedrock (Array &z, float talus, int iterations=10, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | thermal_auto_bedrock (Array &z, Array *p_mask, float talus, int iterations=10, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | thermal_flatten (Array &z, const Array &talus, const Array &bedrock, int iterations=10, int post_filter_ir=1) |
| Apply modified thermal weathering of Olsen. | |
| void | thermal_flatten (Array &z, float talus, int iterations=10, int post_filter_ir=1) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | thermal_olsen (Array &z, const Array &talus, int iterations=10, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| Apply thermal weathering erosion. | |
| void | thermal_rib (Array &z, int iterations, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr) |
| Apply thermal erosion using a 'rib' algorithm (taken from Geomorph). | |
| void | thermal_schott (Array &z, const Array &talus, int iterations=10, float intensity=0.001f) |
| Applies the thermal erosion process to an array of elevation values. | |
| void | thermal_schott (Array &z, const Array &talus, Array *p_mask, int iterations=10, float intensity=0.001f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | thermal_schott (Array &z, const float talus, int iterations=10, float intensity=0.001f) |
| Applies the thermal erosion process with a uniform slope threshold. | |
| void | thermal_schott (Array &z, const float talus, Array *p_mask, int iterations=10, float intensity=0.001f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| Array | watershed_ridge (const Array &z, float amplitude=0.5f, int ir=1, float edt_exponent=0.5f, FlowDirectionMethod fd_method=FlowDirectionMethod::FDM_D8) |
| Carves watershed ridges using basin-wise distance transforms. | |
| Array | watershed_ridge (const Array &z, Array *p_mask, float amplitude=0.5f, int ir=1, float edt_exponent=0.5f, FlowDirectionMethod fd_method=FlowDirectionMethod::FDM_D8) |
| bool | export_asset (const std::string &fname, const Array &array, MeshType mesh_type=MeshType::TRI, AssetExportFormat export_format=AssetExportFormat::GLB2, float elevation_scaling=0.2f, const std::string &texture_fname="", const std::string &normal_map_fname="", float max_error=5e-4f) |
| Exports a heightmap to various 3D file formats. | |
| std::string | export_as_ascii (const Array &array, const glm::ivec2 &export_shape={64, 64}, const std::string chars_map=" .:-=+*#%@") |
| Export a 2D array as an ASCII-art string representation. | |
| void | export_as_cubemap (const std::string &fname, const Array &z, int cubemap_resolution=128, float overlap=0.25f, int ir=16, Cmap cmap=Cmap::GRAY, bool splitted=false, Array *p_cubemap=nullptr) |
| Exports a 2D array as a cubemap texture with continuity enforcement and overlapping regions. | |
| void | export_banner_png (const std::string &fname, const std::vector< Array > &arrays, int cmap, bool hillshading=false, bool normalize_arrays=false) |
| Exports a set of arrays as a banner PNG image file. | |
| void | export_normal_map_png (const std::string &fname, const Array &array, int depth=CV_8U) |
| Exports the heightmap normal map as an 8-bit PNG file. | |
| void | export_splatmap_png (const std::string &fname, const Array *p_r, const Array *p_g=nullptr, const Array *p_b=nullptr, const Array *p_a=nullptr, int depth=CV_8U) |
| Exports four arrays as an RGBA PNG splatmap. | |
| void | export_points_to_ply (const std::string &fname, const std::vector< float > &x, const std::vector< float > &y, const std::vector< float > &z, const std::map< std::string, std::vector< float > > &custom_fields={}) |
| Exports 3D points with optional custom fields to an ASCII PLY file. | |
| void | export_tiled (const std::string &fname_radical, const std::string &fname_extension, const Array &array, const glm::ivec2 &tiling, int leading_zeros=0, int depth=CV_8U, bool overlapping_edges=false, bool reverse_tile_y_indexing=false) |
| Exports a 2D array as a set of grayscale PNG image tiles. | |
| Array | read_to_array (const std::string &fname, bool flip_j=false) |
| Reads an image file and converts it to a 2D array. | |
| void | write_raw_16bit (const std::string &fname, const Array &array) |
| Exports an array to a 16-bit 'raw' file format, commonly used for Unity terrain imports. | |
| Array | connected_components (const Array &array, float surface_threshold=0.f, float background_value=0.f, std::vector< float > *p_surfaces=nullptr, std::vector< std::array< float, 2 > > *p_centroids=nullptr) |
| Identifies and labels connected components within a binary or labeled array, with optional filtering by size. | |
| Array | geomorphons (const Array &array, int irmin, int irmax, float epsilon) |
| Classifies terrain into geomorphological features based on the geomorphons method. | |
| Array | kmeans_clustering2 (const Array &array1, const Array &array2, int nclusters, std::vector< Array > *p_scoring=nullptr, Array *p_aggregate_scoring=nullptr, glm::vec2 weights={1.f, 1.f}, uint seed=1) |
| Performs k-means clustering on two input arrays, grouping similar data points into clusters. | |
| Array | kmeans_clustering3 (const Array &array1, const Array &array2, const Array &array3, int nclusters, std::vector< Array > *p_scoring=nullptr, Array *p_aggregate_scoring=nullptr, glm::vec3 weights={1.f, 1.f, 1.f}, uint seed=1) |
| Performs k-means clustering on three input arrays, providing more detailed cluster analysis by considering an additional dimension. | |
| Array | local_median_deviation (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Computes the local median deviation of a 2D array. | |
| Array | mean_local (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Return the local mean based on a mean filter with a square kernel. | |
| Array | relative_elevation (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Calculates the relative elevation within a specified radius, helping to identify local highs and lows. | |
| Array | ruggedness (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Computes the ruggedness of each element in the input array. | |
| Array | rugosity (const Array &z, int ir, bool convex=true) |
| Estimates the rugosity of a surface by analyzing the skewness of the elevation data, which reflects surface roughness. | |
| Array | std_local (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Computes the local standard deviation of a 2D array. | |
| Array | valley_width (const Array &z, int ir=0, bool ridge_select=false) |
| Measures the valley width by calculating the distance from each point in a concave region to the frontier of that region. | |
| Array | z_score (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Array | bulkify (const Array &z, const PrimitiveType &primitive_type, float amp=1.f, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Array | diffusion_retargeting (const Array &array_before, const Array &array_after, int ir) |
| Applies diffusion retargeting by detecting local maxima and adjusting based on the difference between two arrays. | |
| Array | diffusion_retargeting (const Array &array_before, const Array &array_after, const Array &mask, int iterations) |
| void | directional_blur (Array &array, int ir, float angle, float intensity, float stretch=1.f, float spread=1.f) |
| Applies a directional blur to a 2D array based on a spatially varying angle field. | |
| void | directional_blur (Array &array, int ir, const Array &angle, float intensity, float stretch=1.f, float spread=1.f) |
| Applies a directional blur to the provided 2D array with a constant angle. | |
| void | equalize (Array &array) |
| Apply histogram equalization to the array values. | |
| void | equalize (Array &array, const Array *p_mask) |
| Apply histogram equalization to the array values with a mask. | |
| void | expand (Array &array, int ir, const Array *p_mask, int iterations=1) |
| Apply expansion, or "inflation", to emphasize the bulk of the terrain. | |
| void | expand (Array &array, int ir, int iterations=1) |
| Apply expansion to emphasize the bulk of the terrain using a filter radius. | |
| void | expand (Array &array, const Array &kernel, int iterations=1) |
| Apply expansion using a custom kernel. | |
| void | expand (Array &array, const Array &kernel, const Array *p_mask, int iterations=1) |
| Apply expansion using a custom kernel with an optional mask. | |
| void | expand_directional (Array &array, int ir, float angle, float aspect_ratio, float anisotropy=1.f, const Array *p_mask=nullptr) |
| Apply expansion, or "inflation", to emphasize the bulk of the terrain, using a directional kernel. | |
| void | expand_talus (Array &z, const Array &mask, float talus, uint seed, int ir=1, float noise_ratio=0.2f) |
| Array | faceted (const Array &array, int neighborhood=0, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr) |
| Generate a faceted heightmap that retains the main features of the input heightmap. | |
| void | fill_talus (Array &z, float talus, uint seed, int ir=1, float noise_ratio=0.2f, const Array *p_seed_mask=nullptr) |
| Modifies a terrain array by filling it with talus slopes. | |
| void | fill_talus (Array &z, const Array &talus, uint seed, int ir=1, float noise_ratio=0.2f, const Array *p_seed_mask=nullptr) |
| void | fill_talus_fast (Array &z, glm::ivec2 shape_coarse, float talus, uint seed, int ir=1, float noise_ratio=0.2f) |
| Fill terrain values with a given downslope talus, optimized using a coarse mesh for faster computation. | |
| void | fold (Array &array, float vmin, float vmax, int iterations=3, float k=0.05f) |
| Apply a "folding" filter (successive absolute values) to the array elements. | |
| void | fold (Array &array, int iterations=3, float k=0.05f) |
| Apply a "folding" filter with default reference values and parameters. | |
| void | gain (Array &array, float factor, const Array *p_mask) |
| Apply a gain correction to the array elements. | |
| void | gain (Array &array, float factor) |
| Apply a gain correction to the array elements without a mask. | |
| void | gamma_correction (Array &array, float gamma, const Array *p_mask) |
| Apply gamma correction to the input array. | |
| void | gamma_correction (Array &array, float gamma) |
| Apply gamma correction to the input array without a mask. | |
| void | gamma_correction_local (Array &array, float gamma, int ir, float k=0.1f) |
| Apply a "local" gamma correction to the input array. | |
| void | gamma_correction_local (Array &array, float gamma, int ir, const Array *p_mask, float k=0.1f) |
| Apply a "local" gamma correction with a mask to the input array. | |
| void | kuwahara (Array &array, int ir, float mix_ratio=1.f) |
| Applies the Kuwahara filter to an array with optional per-pixel masking. | |
| void | kuwahara (Array &array, int ir, const Array *p_mask, float mix_ratio=1.f) |
| Applies the Kuwahara filter to an array with optional per-pixel masking. | |
| void | laplace (Array &array, float sigma=0.125f, int iterations=3) |
| Applies an iterative 8-neighbor Laplacian smoothing filter on an array. | |
| void | laplace (Array &array, const Array *p_mask, float sigma=0.125f, int iterations=3) |
| Apply a low-pass Laplace filter with a mask. | |
| void | laplace1d (std::vector< float > &v, float sigma=0.5f, int iterations=1) |
| Apply a low-pass Laplace filter to a vector. | |
| void | laplace_edge_preserving (Array &array, float talus, float sigma=0.2f, int iterations=3) |
| Apply a low-pass anisotropic Laplace filter to the input array. | |
| void | laplace_edge_preserving (Array &array, float talus, const Array *p_mask, float sigma=0.2f, int iterations=3) |
| Apply a low-pass anisotropic Laplace filter with a mask. | |
| void | low_pass_high_order (Array &array, int order=9, float sigma=1.f) |
| Apply a low-pass high-order filter to the input array. | |
| void | make_binary (Array &array, float threshold=0.f) |
| Convert array values to binary using a threshold. | |
| Array | maximum_local (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Return the local maxima based on a maximum filter with a square kernel. | |
| Array | maximum_local_disk (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Return the local maxima based on a maximum filter using a disk kernel. | |
| void | match_histogram (Array &array, const Array &array_reference) |
| Transform the input array elevation to match the histogram of a reference array. | |
| Array | mean_shift (const Array &array, int ir, float talus, int iterations=1, bool talus_weighted=true) |
| Applies the mean shift algorithm to the input array. | |
| Array | mean_shift (const Array &array, int ir, float talus, const Array *p_mask, int iterations=1, bool talus_weighted=true) |
| void | median_3x3 (Array &array, const Array *p_mask) |
| Apply a 3x3 median filter to the input array. | |
| void | median_3x3 (Array &array) |
| Apply a 3x3 median filter to the input array without a mask. | |
| Array | median_pseudo (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Computes a fast pseudo-median approximation of a local neighborhood in an array. | |
| Array | minimum_local (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Return the local minima based on a maximum filter with a square kernel. | |
| Array | minimum_local_disk (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Return the local minima based on a maximum filter using a disk kernel. | |
| void | normal_displacement (Array &array, float amount=0.1f, int ir=0, bool reverse=false) |
| Apply a displacement to the terrain along the normal direction. | |
| void | normal_displacement (Array &array, const Array *p_mask, float amount=0.1f, int ir=0, bool reverse=false) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | plateau (Array &array, const Array *p_mask, int ir, float factor) |
| Apply a plateau-shape filter to the input array. | |
| void | plateau (Array &array, int ir, float factor) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | recast_billow (Array &array, float vref, float k) |
| Transform heightmap to give a "billow" like appearance. | |
| void | recast_canyon (Array &array, const Array &vcut, float gamma=4.f) |
| Transform heightmap to give a "canyon" like appearance. | |
| void | recast_canyon (Array &array, const Array &vcut, const Array *p_mask, float gamma=4.f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | recast_canyon (Array &array, float vcut, const Array *p_mask, float gamma=4.f, const Array *p_noise=nullptr) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | recast_canyon (Array &array, float vcut, float gamma=4.f, const Array *p_noise=nullptr) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | recast_cliff (Array &array, float talus, int ir, float amplitude, float gain=2.f) |
| Transform heightmap to add cliffs where gradients are steep enough. | |
| void | recast_cliff (Array &array, float talus, int ir, float amplitude, const Array *p_mask, float gain=2.f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | recast_cliff_directional (Array &array, float talus, int ir, float amplitude, float angle, float gain=2.f) |
| Transform heightmap to add directional cliffs where gradients are steep enough. | |
| void | recast_cliff_directional (Array &array, float talus, int ir, float amplitude, float angle, const Array *p_mask, float gain=2.f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | recast_cracks (Array &array, float cut_min=0.05f, float cut_max=0.5f, float k_smoothing=0.01f, float vmin=0.f, float vmax=-1.f) |
| void | recast_escarpment (Array &array, int ir=16, float ratio=0.1f, float scale=1.f, bool reverse=false, bool transpose_effect=false, float global_scaling=0.f) |
| Applies an escarpment effect to the given 2D array, modifying its values based on cumulative displacement with optional directional and transpositional transformations. | |
| void | recast_escarpment (Array &array, const Array *p_mask, int ir=16, float ratio=0.1f, float scale=1.f, bool reverse=false, bool transpose_effect=false, float global_scaling=0.f) |
| Applies an escarpment effect to the given 2D array, with an optional mask to blend the effect. | |
| void | recast_peak (Array &array, int ir, float gamma=2.f, float k=0.1f) |
| Transform heightmap to give a "peak" like appearance. | |
| void | recast_peak (Array &array, int ir, const Array *p_mask, float gamma=2.f, float k=0.1f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | recast_rocky_slopes (Array &array, float talus, int ir, float amplitude, uint seed, float kw, float gamma=0.5f, const Array *p_noise=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Transform heightmap by adding "rock-like" features at higher slopes. | |
| void | recast_rocky_slopes (Array &array, float talus, int ir, float amplitude, uint seed, float kw, const Array *p_mask, float gamma=0.5f, const Array *p_noise=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | recast_sag (Array &array, float vref, float k) |
| Transform heightmap to give a "cliff" like appearance. | |
| void | recast_sag (Array &array, float vref, float k, const Array *p_mask) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | recurve (Array &array, const std::vector< float > &t, const std::vector< float > &v) |
| Apply a curve adjustment filter to the array. | |
| void | recurve (Array &array, const std::vector< float > &t, const std::vector< float > &v, const Array *p_mask) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | recurve_bexp (Array &array, float tau=0.5f) |
| Apply a curve adjustment filter using a "bumpy exponential-shape" curve. | |
| void | recurve_bexp (Array &array, const Array *p_mask, float tau=0.5f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | recurve_exp (Array &array, float tau=0.5f) |
| Apply a curve adjustment filter using a "sharp exponential-shape" curve. | |
| void | recurve_exp (Array &array, const Array *p_mask, float tau=0.5f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | recurve_kura (Array &array, float a, float b) |
| Apply a curve adjustment filter using Kumaraswamy's cumulative distribution function (CDF). | |
| void | recurve_kura (Array &array, float a, float b, const Array *p_mask) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | recurve_s (Array &array) |
| Apply a curve adjustment filter using a smooth "S-shape" curve. | |
| void | recurve_s (Array &array, const Array *p_mask) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | recurve_smoothstep_rational (Array &array, float n) |
| Apply a curve adjustment filter using an nth-order smoothstep curve. | |
| void | recurve_smoothstep_rational (Array &array, float n, const Array *p_mask) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | reverse_above_theshold (Array &array, const Array &threshold, float scaling=1.f, float transition_extent=0.f) |
| Applies a smooth reversal of values above a given threshold. | |
| void | reverse_above_theshold (Array &array, float threshold, float scaling=1.f, float transition_extent=0.f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | reverse_above_theshold (Array &array, const Array &threshold, const Array *p_mask, float scaling=1.f, float transition_extent=0.f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | reverse_above_theshold (Array &array, float threshold, const Array *p_mask, float scaling=1.f, float transition_extent=0.f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | saturate (Array &array, float vmin, float vmax, float from_min, float from_max, float k=0.f) |
| Saturate the array values based on the input interval [vmin, vmax] (the output amplitude is not modified). | |
| void | saturate (Array &array, float vmin, float vmax, float k=0.f) |
| void | sharpen (Array &array, float ratio=1.f) |
| Apply a sharpening filter based on the Laplace operator. | |
| void | sharpen (Array &array, const Array *p_mask, float ratio=1.f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | sharpen_cone (Array &array, int ir, float intensity=0.5f) |
| Apply a sharpening filter based on a smooth cone filter. | |
| void | sharpen_cone (Array &array, const Array *p_mask, int ir, float scale=0.5f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | shrink (Array &array, int ir, int iterations=1) |
| Apply shrinking, or "deflating", to emphasize the ridges in the heightmap. | |
| void | shrink (Array &array, int ir, const Array *p_mask, int iterations=1) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | shrink (Array &array, const Array &kernel, int iterations=1) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | shrink (Array &array, const Array &kernel, const Array *p_mask, int iterations=1) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | shrink_directional (Array &array, int ir, float angle, float aspect_ratio, float anisotropy=1.f, const Array *p_mask=nullptr) |
| Apply directional shrinking, or "deflating", to emphasize the ridges in the terrain. | |
| void | smooth_cone (Array &array, int ir) |
| Apply a convolution filter with a cone kernel to smooth the array. | |
| void | smooth_cone (Array &array, int ir, const Array *p_mask) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | smooth_cpulse (Array &array, int ir) |
| Apply filtering to the array using convolution with a cubic pulse kernel. | |
| void | smooth_cpulse (Array &array, int ir, const Array *p_mask) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | smooth_cpulse_edge_removing (Array &array, float talus, float talus_width, int ir) |
| Smooths an array while attenuating edges using a gradient-based pulse. | |
| void | smooth_flat (Array &array, int ir) |
| Applies a smoothing average filter to the given 2D array in both dimensions. | |
| void | smooth_gaussian (Array &array, int ir) |
| Apply Gaussian filtering to the array. | |
| void | smooth_gaussian (Array &array, int ir, const Array *p_mask) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | smooth_fill (Array &array, int ir, float k=0.1f, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| Apply cubic pulse smoothing to fill lower flat regions while preserving some sharpness. | |
| void | smooth_fill (Array &array, int ir, const Array *p_mask, float k=0.1f, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | smooth_fill_holes (Array &array, int ir) |
| Apply smoothing to fill holes (elliptic concave surfaces). | |
| void | smooth_fill_holes (Array &array, int ir, const Array *p_mask) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | smooth_fill_smear_peaks (Array &array, int ir) |
| Apply smoothing to smear peaks (elliptic convex surfaces). | |
| void | smooth_fill_smear_peaks (Array &array, int ir, const Array *p_mask) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | smoothstep_local (Array &array, int ir) |
| Applies a localized smoothstep operation to the provided array. | |
| void | smoothstep_local (Array &array, int ir, const Array *p_mask) |
| Applies a localized smoothstep operation to the provided array with an optional mask. | |
| void | steepen (Array &array, float scale, int ir=8) |
| Steepen (or flatten) the array map. | |
| void | steepen (Array &array, float scale, const Array *p_mask, int ir=8) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | steepen_convective (Array &array, float angle, int iterations=1, int ir=0, float dt=0.1f) |
| Steepen array values by applying a nonlinear convection operator in a given direction. | |
| void | steepen_convective (Array &array, float angle, const Array *p_mask, int iterations=1, int ir=0, float dt=0.1f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | terrace (Array &array, uint seed, int nlevels, float gain=0.9f, float noise_ratio=0.f, const Array *p_noise=nullptr, float vmin=0.f, float vmax=-1.f) |
| Applies a terrace effect to the values in an array. | |
| void | terrace (Array &array, uint seed, int nlevels, const Array *p_mask, float gain=0.9f, float noise_ratio=0.f, const Array *p_noise=nullptr, float vmin=0.f, float vmax=-1.f) |
| Applies a terrace effect to an array with optional masking. | |
| Array | tessellate (Array &array, uint seed, float node_density=0.001f, const Array *p_weight=nullptr) |
| Apply tessellation to the array with random node placement. | |
| void | wrinkle (Array &array, float wrinkle_amplitude, const Array *p_mask, float wrinkle_angle=0.f, float displacement_amplitude=1.f, int ir=0, float kw=2.f, uint seed=1, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Apply wrinkle effect to the array, creating wrinkled or bumpy features. | |
| void | wrinkle (Array &array, float wrinkle_amplitude, float wrinkle_angle=0.f, float displacement_amplitude=1.f, int ir=0, float kw=2.f, uint seed=1, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| std::function< float(float, float)> | make_xy_function_from_array (const Array &array, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Create a continuous 2D function from a sampled array. | |
| std::unique_ptr< hmap::NoiseFunction > | create_noise_function_from_type (NoiseType noise_type, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed) |
| Create a noise function based on the specified noise type. | |
| Cloud | merge_cloud (const Cloud &cloud1, const Cloud &cloud2) |
| Merges two point clouds into one. | |
| Cloud | merge_clouds (const std::vector< Cloud > &clouds) |
| Cloud | random_cloud (size_t count, uint seed, const PointSamplingMethod &method=PointSamplingMethod::RND_LHS, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a random cloud of points within a bounding box. | |
| Cloud | random_cloud_density (size_t count, const Array &density, uint seed, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a random cloud of points based on a spatial density map. | |
| Cloud | random_cloud_distance (float min_dist, uint seed, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a random cloud of points separated by at least a given minimum distance. | |
| Cloud | random_cloud_distance (float min_dist, float max_dist, const Array &density, uint seed, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a random cloud of points separated by a distance range, influenced by a density map. | |
| Cloud | random_cloud_distance_power_law (float dist_min, float dist_max, float alpha, uint seed, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a random cloud of points with distances drawn from a power-law distribution. | |
| Cloud | random_cloud_distance_weibull (float dist_min, float lambda, float k, uint seed, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a random cloud of points with distances drawn from a Weibull distribution. | |
| Cloud | random_cloud_jittered (size_t count, const glm::vec2 &jitter_amount, const glm::vec2 &stagger_ratio, uint seed, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a jittered grid cloud of points. | |
| int | convert_length_to_pixel (float x, int nx, bool lim_inf=true, bool lim_sup=false, float scale=1.f) |
| Converts a length value to a pixel index in a discretized space. | |
| void | grid_xy_vector (std::vector< float > &x, std::vector< float > &y, glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, bool endpoint=false) |
| Return x and y coordinates of a regular grid, as two 1D vectors. | |
| void | dig_path (Array &z, Path &path, int width=1, int decay=2, int flattening_radius=16, bool force_downhill=false, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, float depth=0.f) |
| Dig a path on a heightmap. | |
| void | dig_river (Array &z, const std::vector< Path > &path_list, float riverbank_talus, int river_width=0, int merging_width=0, float depth=0.f, float riverbed_talus=0.f, float noise_ratio=0.9f, uint seed=0, Array *p_mask=nullptr) |
| Modifies the elevation array to carve a river along a specified path. | |
| void | dig_river (Array &z, const Path &path, float riverbank_talus, int river_width=0, int merging_width=0, float depth=0.f, float riverbed_talus=0.f, float noise_ratio=0.9f, uint seed=0, Array *p_mask=nullptr) |
| Path | find_cut_path_dijkstra (const Array &z, DomainBoundary start, DomainBoundary end, float dijk_elevation_ratio=0.9f, float dijk_distance_exponent=2.f, float dijk_upward_penalization=100.f) |
| Find a Dijkstra-based cut path between two domain boundaries. | |
| Path | find_cut_path_midpoint (const Array &z, DomainBoundary start, DomainBoundary end, uint seed, int midp_iterations=4, float midp_sigma=0.2f) |
| float | angle (const Point &p1, const Point &p2) |
| Computes the angle between two points relative to the x-axis. | |
| float | angle (const Point &p0, const Point &p1, const Point &p2) |
| Computes the angle formed by three points with the reference point as the origin. | |
| float | cross_product (const Point &p0, const Point &p1, const Point &p2) |
| Computes the 2D cross product of vectors formed by three points. | |
| float | curvature (const Point &p1, const Point &p2, const Point &p3) |
| Calculates the curvature formed by three points in 2D space. | |
| float | distance (const Point &p1, const Point &p2) |
| Calculates the distance between two points. | |
| Point | interp_bezier (const Point &p_start, const Point &p_ctrl_start, const Point &p_ctrl_end, const Point &p_end, float t) |
| Performs a cubic Bezier interpolation. | |
| Point | interp_bspline (const Point &p0, const Point &p1, const Point &p2, const Point &p3, float t) |
| Performs a cubic B-spline interpolation. | |
| Point | interp_catmullrom (const Point &p0, const Point &p1, const Point &p2, const Point &p3, float t) |
| Performs a Catmull-Rom spline interpolation. | |
| Point | interp_decasteljau (const std::vector< Point > &points, float t) |
| Performs a De Casteljau algorithm-based interpolation for Bezier curves. | |
| glm::vec4 | intersect_bounding_boxes (const glm::vec4 &bbox1, const glm::vec4 &bbox2) |
| Determines the intersection of two bounding boxes. | |
| bool | is_point_within_bounding_box (Point p, glm::vec4 bbox) |
| Checks if a point is within a specified bounding box. | |
| bool | is_point_within_bounding_box (float x, float y, glm::vec4 bbox) |
| Checks if a point is within a specified bounding box. | |
| Point | lerp (const Point &p1, const Point &p2, float t) |
| Linearly interpolates between two points. | |
| Point | midpoint (const Point &p1, const Point &p2, int orientation, float distance_ratio, float t=0.5f) |
| Computes the midpoint displacement in 1D with a perpendicular displacement. | |
| void | sort_points (std::vector< Point > &points) |
| Sorts a vector of points in ascending order based on their coordinates. | |
| float | triangle_area (const Point &p1, const Point &p2, const Point &p3) |
| Calculates the area of a triangle formed by three points in 2D space. | |
| glm::vec4 | unit_square_bbox () |
| Constructs a 4D bounding box for a unit square. | |
| std::array< std::pair< float, float >, 2 > | bbox_to_ranges2d (const glm::vec4 &bbox) |
| Converts a 2D bounding box into coordinate ranges. | |
| void | expand_points_domain (std::vector< float > &x, std::vector< float > &y, std::vector< float > &value, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Expand grid by translating and copying the values of the current bounding box to the 8 first neighboring bounding boxes. | |
| void | expand_points_at_domain_boundaries (std::vector< float > &x, std::vector< float > &y, std::vector< float > &value, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, float boundary_value=0.f) |
| Expand the grid by adding points on the boundaries of the bounding box. | |
| void | expand_points_domain_corners (std::vector< float > &x, std::vector< float > &y, std::vector< float > &value, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, float corner_value=0.f) |
| Expand the grid by adding four points at the corner of the bounding box. | |
| std::function< float(const ps::Point< float, 2 > &)> | make_pointwise_function_from_array (const Array &array, const glm::vec4 &bbox) |
| Create a continuous 2D function from a sampled array. | |
| std::array< std::vector< float >, 2 > | random_points (size_t count, uint seed, const PointSamplingMethod &method=PointSamplingMethod::RND_RANDOM, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates random 2D points within a bounding box using a sampling method. | |
| std::array< std::vector< float >, 2 > | random_points_density (size_t count, const Array &density, uint seed, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates random 2D points within a bounding box based on a density map. | |
| std::array< std::vector< float >, 2 > | random_points_distance (float min_dist, uint seed, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates random 2D points with a minimum separation distance. | |
| std::array< std::vector< float >, 2 > | random_points_distance (float min_dist, float max_dist, const Array &density, uint seed, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates random 2D points with distance constraints and a density map. | |
| std::array< std::vector< float >, 2 > | random_points_distance_power_law (float dist_min, float dist_max, float alpha, uint seed, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates random 2D points with distances drawn from a power-law distribution. | |
| std::array< std::vector< float >, 2 > | random_points_distance_weibull (float dist_min, float lambda, float k, uint seed, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates random 2D points with distances drawn from a Weibull distribution. | |
| std::array< std::vector< float >, 2 > | random_points_jittered (size_t count, const glm::vec2 &jitter_amount, const glm::vec2 &stagger_ratio, uint seed, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates jittered grid-based 2D points. | |
| void | remove_points_outside_bbox (std::vector< float > &x, std::vector< float > &y, std::vector< float > &value, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Remove grid points that are outside a given bounding box. | |
| void | rescale_points_to_unit_square (std::vector< float > &x, std::vector< float > &y, glm::vec4 bbox) |
| Rescale coordinate (x, y) so that they fit in a unit-square box based on a given initial bounding box. | |
| Array | divergence_from_gradients (const Array &dx, const Array &dy) |
| Compute the divergence of a 2D gradient field. | |
| std::vector< float > | gradient1d (const std::vector< float > &v) |
| Compute the gradient of a 1D vector. | |
| Array | gradient_angle (const Array &array, bool downward=false) |
| Compute the polar angle of the gradient of a 2D array. | |
| Array | gradient_angle_circular_smoothing (const Array &array, int ir, bool downward=false) |
| Computes a smoothed gradient angle (aspect) field with circular unwrapping. | |
| Array | gradient_norm (const Array &array, Array *p_dx=nullptr, Array *p_dy=nullptr) |
| Compute the gradient norm of a 2D array. | |
| Array | gradient_norm_prewitt (const Array &array, Array *p_dx=nullptr, Array *p_dy=nullptr) |
| Compute the gradient norm of a 2D array using the Prewitt filter. | |
| Array | gradient_norm_scharr (const Array &array, Array *p_dx=nullptr, Array *p_dy=nullptr) |
| Compute the gradient norm of a 2D array using the Scharr filter. | |
| Array | gradient_norm_sobel (const Array &array, Array *p_dx=nullptr, Array *p_dy=nullptr) |
| Compute the gradient norm of a 2D array using the Sobel filter. | |
| Array | gradient_talus (const Array &array) |
| Compute the gradient talus slope of a 2D array. | |
| void | gradient_talus (const Array &array, Array &talus) |
| Compute the gradient talus slope and store it in the provided array. | |
| Array | gradient_x (const Array &array) |
| Compute the gradient in the x-direction of a 2D array. | |
| void | gradient_x (const Array &array, Array &dx) |
| Compute the gradient in the x-direction of a 2D array and store it. | |
| Array | gradient_y (const Array &array) |
| Compute the gradient in the y-direction of a 2D array. | |
| void | gradient_y (const Array &array, Array &dy) |
| Compute the gradient in the y-direction of a 2D array and store it. | |
| Array | laplacian (const Array &array) |
| Compute the Laplacian of a 2D array. | |
| Tensor | normal_map (const Array &array) |
| Generates a normal map from a given 2D array. | |
| Array | normal_map_to_heightmap (const Tensor &nmap) |
| Converts a normal map to a heightmap using direct summation of gradients. | |
| Array | normal_map_to_heightmap_poisson (const Tensor &nmap, int iterations=500, float omega=1.5f) |
| Reconstruct a height/displacement map from a normal map by solving a Poisson equation with Gauss–Seidel iteration. | |
| Array | phase_field (const Array &array, float kw, int width, uint seed, float noise_amp=0.f, int prefilter_ir=-1, float density_factor=1.f, bool rotate90=false, Array *p_gnoise_x=nullptr, Array *p_gnoise_y=nullptr) |
| Computes a phase field using spatially varying Gabor noise based on the input heightmap. | |
| void | solve_poisson_gauss_seidel (const Array &rhs, Array &h, int iterations=500, float omega=1.0f) |
| Solve the Poisson equation ∇²h = rhs using Gauss–Seidel iteration. | |
| Array | unwrap_phase (const Array &alpha) |
| Unwraps a 2D phase array to correct discontinuities in phase data. | |
| Array | basin_id (const Array &z, FlowDirectionMethod fd_method=FlowDirectionMethod::FDM_D8, bool remove_lakes=true) |
| Label drainage basins using a priority-flood algorithm. | |
| Array | d8_compute_ndip (const Array &d8) |
| Computes the number of drainage paths for each cell based on the D8 flow direction model. | |
| void | find_flow_apex (const Array &z, std::vector< int > &is, std::vector< int > &js) |
| Identifies flow apex (source) cells using D8 flow routing. | |
| void | find_flow_sinks (const Array &z, std::vector< int > &is, std::vector< int > &js) |
| Identifies the indices of flow sinks within the heightmap. | |
| std::vector< glm::ivec2 > | find_flow_sinks (const Array &z) |
| Array | flooding_uniform_level (const Array &z, float zref) |
| Compute water depth for a uniform flooding level. | |
| Array | flooding_from_boundaries (const Array &z, float zref, bool from_east=true, bool from_west=true, bool from_north=true, bool from_south=true) |
| Compute flooding starting from the lowest boundary points. | |
| Array | flooding_from_point (const Array &z, int i, int j, float depth_min=std::numeric_limits< float >::max()) |
| Flood terrain starting from a single seed point. | |
| Array | flooding_from_point (const Array &z, const std::vector< int > &i, const std::vector< int > &j, float depth_min=std::numeric_limits< float >::max()) |
| Flood terrain starting from multiple seed points. | |
| Array | flooding_lake_system (const Array &z, float surface_threshold=0) |
| Estimate lake water depths on a terrain by filling depressions. | |
| Array | flow_accumulation_d8 (const Array &z) |
| Computes the flow accumulation for each cell using the D8 flow direction model. | |
| Array | flow_accumulation_dinf (const Array &z, float talus_ref) |
| Computes the flow accumulation for each cell using the Multiple Flow Direction (MFD) model. | |
| Array | flow_direction_d8 (const Array &z) |
| Computes the flow direction from each cell to its downslope neighbor using the D8 model. | |
| std::vector< Array > | flow_direction_dinf (const Array &z, float talus_ref) |
| Computes the flow direction and weights for each direction using the Multiple Flow Direction (MFD) model. | |
| std::vector< float > | flow_direction_dinf_flat (const Array &z, float talus_ref) |
| Array | flow_direction_dinf_angle (const Array &z, float talus_ref) |
| Computes the flow direction using the Multiple Flow Direction (MFD) model. | |
| Array | flow_fixing (const Array &z, float riverbed_talus=0.f, int iterations=5, int prefilter_ir=8, bool carve_riverbed=true, bool smooth_river_bottom=true, float talus_riverbank=0.01f, uint seed=0, float riverbank_noise_ratio=0.f, float merging_distance=8.f, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr) |
| Path | flow_stream (const Array &z, const glm::ivec2 ij_start, const float elevation_ratio=0.5f, const float distance_exponent=2.f, const float upward_penalization=100.f) |
| Computes the optimal flow path from a starting point to the boundary of a given elevation array. | |
| Array | generate_riverbed (const Path &path, glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, bool bezier_smoothing=false, float depth_start=0.01f, float depth_end=1.f, float slope_start=64.f, float slope_end=32.f, float shape_exponent_start=1.f, float shape_exponent_end=10.f, float k_smoothing=0.5f, int post_filter_ir=0, Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, Array *p_noise_r=nullptr) |
| Generates a 2D array representing a riverbed based on a specified path. | |
| Array | merge_water_depths (const Array &depth1, const Array &depth2, float k_smooth=0.f) |
| Merge two water depth fields. | |
| Array | water_depth_from_mask (const Array &z, const Array &mask, float mask_threshold=0.f, int iterations_max=10000, float tolerance=1e-2f, float omega=1.8f) |
| Compute water depth over a masked terrain using harmonic interpolation. | |
| void | water_depth_dry_out (Array &water_depth, float dry_out_ratio=0.5f, const Array *p_mask=nullptr, float depth_max=std::numeric_limits< float >::max()) |
| Apply a drying factor to a water depth field. | |
| Array | water_depth_increase (const Array &water_depth, const Array &z, float additional_depth) |
| Simulates the increase in water depth over a terrain. | |
| Array | water_mask (const Array &water_depth) |
| Generates a binary mask representing water presence. | |
| Array | water_mask (const Array &water_depth, const Array &z, float additional_depth) |
| Computes a gradient-based water mask using an extended water depth model. | |
| std::filesystem::path | add_filename_suffix (const std::filesystem::path &file_path, const std::string &suffix) |
| std::filesystem::path | make_unique_temp_dir (const std::string &prefix) |
| Create a unique temporary directory. | |
| std::string | zfill (const std::string &str, int n_zero) |
| size_t | upperbound_right (const std::vector< float > &v, float value) |
| std::vector< size_t > | argsort (const std::vector< float > &v) |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | reindex_vector (std::vector< T > &v, std::vector< size_t > &idx) |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | shuffle_vector (std::vector< T > &values, std::uint32_t seed) |
| template<typename T > | |
| std::vector< T > | shuffled_vector (const std::vector< T > &values, std::uint32_t seed) |
| void | vector_unique_values (std::vector< float > &v) |
| std::string | make_histogram (const std::vector< float > &values, int bin_count, int hist_height) |
| float | bilinear_interp (float f00, float f10, float f01, float f11, float u, float v) |
| Compute the bilinear interpolated value from four input values. | |
| float | cubic_interpolate (float p[4], float x) |
| Array | harmonic_interpolation (const Array &array, const Array &mask_fixed_values, int iterations_max=500, float tolerance=1e-5f, float omega=1.8f) |
| Perform harmonic interpolation on a 2D array using the Successive Over-Relaxation (SOR) method. | |
| Array | interpolate2d (glm::ivec2 shape, const std::vector< float > &x, const std::vector< float > &y, const std::vector< float > &values, InterpolationMethod2D interpolation_method, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generic 2D interpolation function. | |
| Array | interpolate2d_nearest (glm::ivec2 shape, const std::vector< float > &x, const std::vector< float > &y, const std::vector< float > &values, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| 2D interpolation using the nearest neighbor method. | |
| Array | interpolate2d_delaunay (glm::ivec2 shape, const std::vector< float > &x, const std::vector< float > &y, const std::vector< float > &values, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| 2D interpolation using the Delaunay triangulation method. | |
| void | interpolate_array_bicubic (const Array &source, Array &target, bool endpoint=false, bool pixel_centered=true) |
| void | interpolate_array_bicubic (const Array &source, Array &target, const glm::vec4 &bbox_source, const glm::vec4 &bbox_target, bool endpoint=false, bool pixel_centered=true) |
| void | interpolate_array_bilinear (const Array &source, Array &target, bool endpoint=false, bool pixel_centered=true) |
| void | interpolate_array_bilinear (const Array &source, Array &target, const glm::vec4 &bbox_source, const glm::vec4 &bbox_target, bool endpoint=false, bool pixel_centered=true) |
| void | interpolate_array_nearest (const Array &source, Array &target, bool endpoint=false) |
| void | interpolate_array_nearest (const Array &source, Array &target, const glm::vec4 &bbox_source, const glm::vec4 &bbox_target, bool endpoint=false) |
| void | flatten_heightmap (VirtualArray &h_source1, const VirtualArray &h_source2, const CoordFrame &t_source1, const CoordFrame &t_source2, const ComputeMode &cm) |
| void | flatten_heightmap (const std::vector< const VirtualArray * > &h_sources, VirtualArray &h_target, const std::vector< const CoordFrame * > &t_sources, const CoordFrame &t_target, const ComputeMode &cm) |
| void | interpolate_heightmap (const VirtualArray &h_source, VirtualArray &h_target, const CoordFrame &t_source, const CoordFrame &t_target, const ComputeMode &cm) |
| Array | get_kernel (glm::ivec2 shape, KernelType kernel_type) |
| Generate a kernel of the specified type. | |
| Array | biweight (glm::ivec2 shape) |
| Generates a biweight kernel array. | |
| Array | blackman (glm::ivec2 shape) |
| Generates a Blackman window array with the specified shape. | |
| Array | cone (glm::ivec2 shape) |
| Generates a cone-shaped kernel array. | |
| Array | cone_talus (float height, float talus) |
| Generates a cone-shaped kernel with specified height and talus. | |
| Array | cone_smooth (glm::ivec2 shape) |
| Generates a cone-shaped kernel with a smooth landing. | |
| Array | cubic_pulse (glm::ivec2 shape) |
| Generates a cubic pulse kernel array. | |
| std::vector< float > | cubic_pulse_1d (int nk) |
| Generates a 1D cubic pulse kernel. | |
| Array | cubic_pulse_directional (glm::ivec2 shape, float angle, float aspect_ratio, float anisotropy) |
| Generates a "directional" cubic pulse kernel. | |
| Array | cubic_pulse_truncated (glm::ivec2 shape, float slant_ratio, float angle) |
| Generates a truncated cubic pulse kernel. | |
| Array | cupola (glm::ivec2 shape, float rc=0.5f) |
| Generate a 2D radial cupola kernel. | |
| Array | disk (glm::ivec2 shape) |
| Generates a disk-shaped kernel footprint. | |
| Array | disk_smooth (glm::ivec2 shape, float r_cutoff=0.9f) |
| Generates a smooth, disk-shaped kernel footprint with soft edges. | |
| Array | gabor (glm::ivec2 shape, float kw, float angle, bool quad_phase_shift=false) |
| Generates a Gabor kernel of the specified shape. | |
| Array | gabor_dune (glm::ivec2 shape, float kw, float angle, float xtop, float xbottom) |
| Generates a modified dune-like Gabor kernel. | |
| Array | hann (glm::ivec2 shape) |
| Generates a Hann window array with the specified shape. | |
| Array | lorentzian (glm::ivec2 shape, float footprint_threshold=0.1f) |
| Generate a Lorentzian kernel. | |
| Array | lorentzian_compact (glm::ivec2 shape) |
| Generate a modified Lorentzian kernel with compact support. | |
| Array | sinc_radial (glm::ivec2 shape, float kw) |
| Generates a radial sinc function array with the specified shape and wave number. | |
| Array | sinc_separable (glm::ivec2 shape, float kw) |
| Generates a separable sinc function array with the specified shape and wave number. | |
| Array | smooth_cosine (glm::ivec2 shape) |
| Generate a smooth cosine kernel. | |
| Array | square (glm::ivec2 shape) |
| Generate a square-shaped kernel. | |
| Array | tricube (glm::ivec2 shape) |
| Generate a tricube kernel. | |
| Array | abs (const Array &array) |
| Return the absolute value of the array elements. | |
| Array | abs_smooth (const Array &array, float mu, const Array &vshift) |
| Return the smooth absolute value of the array elements. | |
| Array | abs_smooth (const Array &array, float mu, float vshift) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| Array | abs_smooth (const Array &array, float mu) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| float | abs_smooth (float a, float mu) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| Array | almost_unit_identity (const Array &array) |
| Return the almost unit identity function. | |
| float | almost_unit_identity (float x) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| float | almost_unit_identity_c2 (float x) |
| Return the almost unit identity function (with a second-order derivative equals 0 at x = 1 also to avoid discontinuities in some cases) | |
| float | almost_unit_identity_c2 (const Array &array) |
| float | approx_hypot (float a, float b) |
| Return the approximate hypothenuse of two numbers. | |
| float | approx_rsqrt (float a) |
| Return the approximate inverse square root of a number. | |
| Array | atan (const Array &array) |
| Return the arctan of the array elements. | |
| Array | atan2 (const Array &y, const Array &x) |
| Computes the element-wise arctangent of two arrays, considering the signs of both inputs. | |
| int | ceil_div (int a, int b) |
| Integer ceiling division. | |
| Array | cos (const Array &array) |
| Return the cosine of the array elements. | |
| Array | exp (const Array &array) |
| Return the exponantial of the array elements. | |
| float | gain (float x, float factor) |
| Array | gaussian_decay (const Array &array, float sigma) |
| Return the Gaussian of the array elements. | |
| std::function< float(float, float)> | get_distance_function (DistanceFunction dist_fct) |
| Return the requested distance function. | |
| std::function< float(float)> | get_phasor_profile_function (PhasorProfile phasor_profile, float delta, float *p_profile_avg=nullptr) |
| Generates a function representing a phasor profile based on the specified type and parameters. | |
| std::function< float(float)> | get_radial_profile_function (RadialProfile radial_profile, float delta) |
| Returns a normalized radial profile function. | |
| int | highest_power_of_2 (int n) |
| Computes the highest power of 2 less than or equal to the given number. | |
| Array | is_equal (const Array &array, float value) |
| Returns a binary mask of elements equal to value. | |
| Array | is_non_zero (const Array &array) |
| Returns a binary mask of non-zero elements. | |
| Array | is_zero (const Array &array) |
| Returns a binary mask of zero elements. | |
| Array | lerp (const Array &array1, const Array &array2, const Array &t) |
| Return the linear interpolation between two arrays by a parameter t. | |
| Array | lerp (const Array &array1, const Array &array2, float t) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| float | lerp (float a, float b, float t) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| Array | log10 (const Array &array) |
| Return the log10 of the array elements. | |
| Array | pow (const Array &array, float exp) |
| Return the array elements raised to the power 'exp'. | |
| void | radial_displacement_to_xy (const Array &dr, Array &dx, Array &dy, float smoothing=1.f, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
Interpret the input array dr as a radial displacement and convert it to a pair of displacements dx and dy in cartesian coordinates. | |
| void | rotate_displacement (const Array &delta, float angle, Array &dx, Array &dy) |
| Rotates a scalar displacement field into directional X and Y components. | |
| float | sigmoid (float x, float width=1.f, float vmin=0.f, float vmax=1.f, float x0=0.f) |
| Computes the sigmoid function for a scalar value. | |
| Array | sigmoid (const Array &array, float width=1.f, float vmin=0.f, float vmax=1.f, float x0=0.f) |
| Computes the sigmoid function element-wise for an array. | |
| Array | sin (const Array &array) |
| Return the sine of the array elements. | |
| Array | smoothstep3 (const Array &array, float vmin=0.f, float vmax=1.f) |
| Return the 3rd order smoothstep function of the array elements. | |
| float | smoothstep3 (float x) |
| Return the 3rd order smoothstep function. | |
| float | smoothstep3_lower (float x) |
| Return the 3rd order smoothstep function, with zero derivative only at 0. | |
| Array | smoothstep3_lower (const Array &x) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| float | smoothstep3_upper (float x) |
| Return the 3rd order smoothstep function, with zero derivative only at 1. | |
| Array | smoothstep3_upper (const Array &x) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| Array | smoothstep5 (const Array &array, float vmin=0.f, float vmax=1.f) |
| Return the 5rd order smoothstep function of the array elements. | |
| Array | smoothstep5 (const Array &array, const Array &vmin, const Array &vmax) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| float | smoothstep5 (float x) |
| Return the 5rd order smoothstep function. | |
| float | smoothstep5_lower (float x) |
| Return the 5rd order smoothstep function, with zero derivative only at 0. | |
| Array | smoothstep5_lower (const Array &x) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| float | smoothstep5_upper (float x) |
| Return the 5rd order smoothstep function, with zero derivative only at 1. | |
| Array | smoothstep5_upper (const Array &x) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| float | smoothstep7 (float x) |
| Return the 7th order smoothstep function. | |
| Array | smoothstep7 (const Array &x) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| Array | sqrt (const Array &array) |
| Return the square root of the array elements. | |
| Array | sqrt_safe (const Array &array) |
| Array | border (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Apply a border algorithm to the input array using a square structure. | |
| Array | closing (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Apply a closing algorithm to the input array using a square structure. | |
| Array | dilation (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Apply a dilation algorithm to the input array using a square structure. | |
| Array | dilation_expand_border_only (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Expand non-zero regions of an array by morphological dilation, while preserving the original non-zero values. | |
| Array | distance_transform (const Array &array, bool return_squared_distance=false) |
| Return the Euclidean distance transform. | |
| Array | distance_transform_approx (const Array &array, bool return_squared_distance=false) |
| Calculates an approximate distance transform of the input array. | |
| Array | distance_transform_manhattan (const Array &array, bool return_squared_distance=false) |
| Calculates the Manhattan distance transform of an array. | |
| Array | distance_transform_with_closest (const Array &array, Mat< glm::ivec2 > &closest, bool return_squared_distance=false) |
| Return the Euclidean distance transform. | |
| Array | erosion (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Apply an erosion algorithm to the input array using a square structure. | |
| void | flood_fill (Array &array, int i, int j, float fill_value=1.f, float background_value=0.f) |
| Apply a flood fill algorithm to the input array. | |
| Array | morphological_black_hat (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Apply a morphological black hat algorithm to the input array using a square structure. | |
| Array | morphological_gradient (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Apply a morphological gradient algorithm to the input array using a square structure. | |
| Array | morphological_top_hat (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Apply a morphological top hat algorithm to the input array using a square structure. | |
| Array | opening (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Apply an opening algorithm to the input array using a square structure. | |
| Array | relative_distance_from_skeleton (const Array &array, int ir_search, bool zero_at_borders=true, int ir_erosion=1) |
| Computes the relative distance of each non-zero cell in a binary array from the skeleton and border. | |
| Array | signed_curvature_from_distance (const Array &array, int prefilter_ir=0) |
| Computes the signed curvature of the distance transform. | |
| Array | signed_distance_transform (const Array &array, int prefilter_ir=0) |
| Computes a signed distance transform using curvature sign. | |
| Array | skeleton (const Array &array, bool zero_at_borders=true) |
| Computes the skeleton of a binary image using the Zhang-Suen skeletonization algorithm. | |
| void | downscale_transform (Array &array, float kc, std::function< void(Array &x)> unary_op, bool apply_prefiltering=false) |
| Applies a downscaling transformation to a 2D array using Fourier-based filtering. | |
| void | downscale_transform_multi (Array &array, std::vector< float > kc_list, std::function< void(Array &x, const int current_index)> unary_op, bool apply_prefiltering=false) |
| void | upscale_amplification (Array &array, int upscaling_levels, float persistence, std::function< void(Array &x, float current_scaling)> unary_op) |
| Applies an upscaling amplification process to an array, followed by a unary operation. | |
| void | add_kernel (Array &array, const Array &kernel, int i, int j) |
| Add a kernel to a specified position in an array. | |
| void | add_kernel_maximum_smooth (Array &array, const Array &kernel, float k_smooth, int i, int j) |
| Adds a smoothed maximum value from a kernel to a specified position in a 2D array. | |
| Array | detrend_reg (const Array &array) |
| Apply linear regression for detrending of a 2D array. | |
| Array | hstack (const Array &array1, const Array &array2) |
| Horizontally stack two arrays side by side. | |
| Array | inpainting_diffusion (const Array &array, const Array &mask, int iterations) |
| Perform diffusion-based inpainting to fill a specified region of an array. | |
| std::vector< float > | linspace (float start, float stop, int num, bool endpoint=true) |
| Generate a vector of evenly spaced numbers over a specified interval. | |
| std::vector< float > | linspace_jitted (float start, float stop, int num, float ratio, int seed, bool endpoint=true) |
| Generate a vector of jittered (noised) numbers over a specified interval. | |
| void | fill_array_using_xy_function (Array &array, glm::vec4 bbox, const Array *p_ctrl_param, const Array *p_noise_x, const Array *p_noise_y, const Array *p_stretching, std::function< float(float, float, float)> fct_xy) |
| Fill an array using a scalar function based on (x, y) coordinates. | |
| void | fill_array_using_xy_function (Array &array, glm::vec4 bbox, const Array *p_ctrl_param, const Array *p_noise_x, const Array *p_noise_y, const Array *p_stretching, std::function< float(float, float, float)> fct_xy, int subsampling) |
| Fill an array using a scalar function based on (x, y) coordinates with subsampling. | |
| void | find_vertical_cut_path (const Array &error, std::vector< int > &path_i) |
| Find the vertical cut path with the minimum cost using Dijkstra's algorithm. | |
| Array | generate_mask (glm::ivec2 shape, std::vector< int > cut_path_i, int ir) |
| Generate a smooth mask based on a cut path. | |
| Array | get_random_patch (const Array &array, glm::ivec2 patch_shape, std::mt19937 &gen, bool patch_flip=false, bool patch_rotate=false, bool patch_transpose=false, std::vector< Array * > *p_secondary_arrays=nullptr, std::vector< Array > *p_secondary_patches=nullptr) |
| Extracts a random sub-array (patch) from the input array, with optional transformations. | |
| std::vector< float > | random_vector (float min, float max, int num, int seed) |
| Generate a vector filled with random values within a specified range. | |
| void | rescale_vector (std::vector< float > &vec, float vmin, float vmax) |
| Rescales the values of a vector to a specified range. | |
| std::vector< float > | rescaled_vector (const std::vector< float > &vec, float vmin, float vmax) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | swap (Array &a, Array &b) |
| Swaps the contents of two Array objects. | |
| Array | vstack (const Array &array1, const Array &array2) |
| Vertically stack two arrays. | |
| Array | get_primitive_base (const PrimitiveType &primitive_type, const glm::ivec2 &shape, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a primitive shape as a 2D array. | |
| Array | biquad_pulse (glm::ivec2 shape, float gain=1.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return a 'biquadratic pulse'. | |
| Array | bump (glm::ivec2 shape, float gain=1.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return a bump. | |
| Array | bump_lorentzian (glm::ivec2 shape, float shape_factor=0.5f, float radius=0.5f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a 2D Lorentzian bump pattern. | |
| Array | caldera (glm::ivec2 shape, float radius, float sigma_inner, float sigma_outer, float z_bottom, const Array *p_noise, float noise_amp_r, float noise_ratio_z, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return a caldera-shaped heightmap. | |
| Array | caldera (glm::ivec2 shape, float radius, float sigma_inner, float sigma_outer, float z_bottom, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| Array | checkerboard (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return a checkerboard heightmap. | |
| Array | cone (glm::ivec2 shape, float slope, float apex_elevation=1.f, bool smooth_profile=false, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a synthetic conical mountain heightmap. | |
| Array | cone_complex (glm::ivec2 shape, float alpha, float radius=0.5f, bool smooth_profile=true, float valley_amp=0.2f, int valley_nb=5, float valley_decay_ratio=0.5f, float valley_angle0=15.f, const ErosionProfile &erosion_profile=ErosionProfile::TRIANGLE_GRENIER, float erosion_delta=0.01f, float radial_waviness_amp=0.05f, float radial_waviness_kw=2.f, float bias_angle=30.f, float bias_amp=0.75f, float bias_exponent=1.f, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a complex conical heightfield with valleys, directional bias, and radial waviness. | |
| Array | cone_sigmoid (glm::ivec2 shape, float alpha, float radius=0.5f, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a smooth conical heightmap using a sigmoid-based profile. | |
| Array | constant (glm::ivec2 shape, float value=0.f) |
| Return a constant value array. | |
| Array | crater (glm::ivec2 shape, float radius, float depth, float lip_decay, float lip_height_ratio=0.5f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return a crater-shaped heightmap. | |
| Array | cubic_pulse (glm::ivec2 shape, const Array *p_noise_x, const Array *p_noise_y, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a cubic pulse array. | |
| Array | dendry (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, Array &control_function, float eps=0.05, int resolution=1, float displacement=0.075, int primitives_resolution_steps=3, float slope_power=2.f, float noise_amplitude_proportion=0.01, bool add_control_function=true, float control_function_overlap=0.5f, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, int subsampling=1) |
| Dendry is a locally computable procedural function that generates branching patterns at various scales (see [Gaillard2019]). | |
| Array | dendry (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, NoiseFunction &noise_function, float noise_function_offset=0.f, float noise_function_scaling=1.f, float eps=0.05, int resolution=1, float displacement=0.075, int primitives_resolution_steps=3, float slope_power=2.f, float noise_amplitude_proportion=0.01, bool add_control_function=true, float control_function_overlap=0.5f, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Array | diffusion_limited_aggregation (glm::ivec2 shape, float scale, uint seed, float seeding_radius=0.4f, float seeding_outer_radius_ratio=0.2f, float slope=8.f, float noise_ratio=0.2f) |
| Generates a diffusion-limited aggregation (DLA) pattern. | |
| Array | disk (glm::ivec2 shape, float radius, float slope=1.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a disk-shaped heightmap with optional modifications. | |
| Array | gabor_noise (glm::ivec2 shape, float kw, float angle, int width, float density, uint seed) |
| Return a sparse Gabor noise. | |
| Array | gaussian_pulse (glm::ivec2 shape, float sigma, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return a gaussian_decay pulse kernel. | |
| Array | island_land_mask (glm::ivec2 shape, float radius, uint seed, float displacement=0.2f, NoiseType noise_type=NoiseType::SIMPLEX2S, float kw=4.f, int octaves=8, float weight=0.f, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, const glm::vec2 ¢er={0.5f, 0.5f}, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a 2D island mask by perturbing a radial boundary with noise. | |
| Array | multisteps (glm::ivec2 shape, float angle, float r=1.2f, int nsteps=8, float elevation_exponent=0.7f, float shape_gain=4.f, float scale=0.5f, float outer_slope=0.1f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const glm::vec2 ¢er={0.5f, 0.5f}, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generate a multi-step height profile along a rotated axis. | |
| Array | noise (NoiseType noise_type, glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return an array filled with coherence noise. | |
| Array | noise_fbm (NoiseType noise_type, glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return an array filled with coherence fbm noise. | |
| Array | noise_iq (NoiseType noise_type, glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, float gradient_scale=0.05f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return an array filled with coherence fbm noise. | |
| Array | noise_jordan (NoiseType noise_type, glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, float warp0=0.4f, float damp0=1.f, float warp_scale=0.4f, float damp_scale=1.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return an array filled with coherence fbm noise. | |
| Array | noise_parberry (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, float mu=1.02f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return an array filled with coherent fbm Parberry variant of Perlin noise. | |
| Array | noise_pingpong (NoiseType noise_type, glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return an array filled with coherence fbm pingpong noise. | |
| Array | noise_ridged (NoiseType noise_type, glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, float k_smoothing=0.1f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return an array filled with coherence fbm ridged noise. | |
| Array | noise_swiss (NoiseType noise_type, glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, float warp_scale=0.1f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return an array filled with coherence fbm swiss noise. | |
| Array | paraboloid (glm::ivec2 shape, float angle, float a, float b, float v0=0.f, bool reverse_x=false, bool reverse_y=false, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return a paraboloid. | |
| Array | peak (glm::ivec2 shape, float radius, const Array *p_noise, float noise_r_amp, float noise_z_ratio, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return a peak-shaped heightmap. | |
| Array | phasor (PhasorProfile phasor_profile, glm::ivec2 shape, float kw, const Array &angle, uint seed, float profile_delta=0.1f, float density_factor=1.f, float kernel_width_ratio=2.f, float phase_smoothing=2.f) |
| Generates a phasor noise field based on a Gabor noise model and phase profile. | |
| Array | phasor_fbm (PhasorProfile phasor_profile, glm::ivec2 shape, float kw, const Array &angle, uint seed, float profile_delta=0.1f, float density_factor=1.f, float kernel_width_ratio=2.f, float phase_smoothing=2.f, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f) |
| Generates a fractal Brownian motion (fBm) noise field using layered phasor profiles. | |
| Array | rectangle (glm::ivec2 shape, float rx, float ry, float angle, float slope=1.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a rectangle-shaped heightmap with optional modifications. | |
| Array | rift (glm::ivec2 shape, float angle, float slope, float width, bool sharp_bottom=false, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return a rift function (Heaviside with an optional talus slope at the transition). | |
| Array | slope (glm::ivec2 shape, float angle, float slope, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return an array corresponding to a slope with a given overall. | |
| Array | smooth_cosine (glm::ivec2 shape, const Array *p_noise_x, const Array *p_noise_y, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a smooth cosine array. | |
| Array | step (glm::ivec2 shape, float angle, float slope, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return a step function (Heaviside with an optional talus slope at the transition). | |
| void | swirl (Array &dx, Array &dy, float amplitude=1.f, float exponent=1.f, const Array *p_noise=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
Generate displacements dx and dy to apply a swirl effect to another primitve. | |
| Array | wave_dune (glm::ivec2 shape, float kw, float angle, float xtop, float xbottom, float phase_shift=0.f, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return a dune shape wave. | |
| Array | wave_sine (glm::ivec2 shape, float kw, float angle, float phase_shift=0.f, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return a sine wave. | |
| Array | wave_square (glm::ivec2 shape, float kw, float angle, float phase_shift=0.f, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return a square wave. | |
| Array | wave_triangular (glm::ivec2 shape, float kw, float angle, float slant_ratio, float phase_shift=0.f, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return a triangular wave. | |
| Array | white (glm::ivec2 shape, float a, float b, uint seed) |
| Return an array filled with white noise. | |
| Array | white_density_map (const Array &density_map, uint seed) |
Return an array filled 1 with a probability based on a density map. | |
| Array | white_sparse (glm::ivec2 shape, float a, float b, float density, uint seed) |
| Return an array sparsely filled with white noise. | |
| Array | white_sparse_binary (glm::ivec2 shape, float density, uint seed) |
| Return an array sparsely filled with random 0 and 1. | |
| Array | worley_double (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, float ratio=0.5f, float k=0.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return an array filled with the maximum of two Worley (cellular) noises. | |
| void | chop (Array &array, float vmin) |
Set to zero any value lower than vmin. | |
| void | chop_max_smooth (Array &array, float vmax) |
Set to zero any value lower than vmax and apply a linear decrease slope between vmax / 2 and vmax. | |
| void | clamp (Array &array, float vmin=0.f, float vmax=1.f) |
| Clamp array elements to a target range. | |
| void | clamp (Array &array, float vmax, ClampMode mode) |
| Clamps the values of an array according to the specified mode. | |
| void | clamp_min (Array &array, float vmin) |
| Clamp array values lower than a given bound. | |
| void | clamp_min (Array &array, const Array &vmin) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | clamp_min_smooth (Array &array, float vmin, float k=0.2f) |
| Clamp array values lower than a given bound with a smooth transition. | |
| void | clamp_min_smooth (Array &array, const Array &vmin, float k=0.2f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| float | clamp_min_smooth (float x, float vmin, float k=0.2f) |
| Clamp a single value lower than a given bound with a smooth transition. | |
| void | clamp_max (Array &array, float vmax) |
| Clamp array values larger than a given bound. | |
| void | clamp_max (Array &array, const Array &vmax) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | clamp_max_smooth (Array &array, float vmax, float k=0.2f) |
| Clamp array values larger than a given bound with a smooth transition. | |
| void | clamp_max_smooth (Array &array, const Array &vmax, float k=0.2f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | clamp_oblique_plane (Array &array, float vmax, float angle, float slope, bool use_max_operator=true, float k=0.f, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Clamps an array against an oblique plane. | |
| void | clamp_smooth (Array &array, float vmin, float vmax, float k=0.2f) |
| Clamp array values within a given interval with a smooth transition. | |
| Array | maximum (const Array &array1, const Array &array2) |
| Return the element-wise maximum of two arrays. | |
| Array | maximum (const Array &array1, const float value) |
| Return the element-wise maximum of an array and a scalar value. | |
| Array | maximum_smooth (const Array &array1, const Array &array2, float k=0.2) |
| Return the polynomial cubic smooth element-wise maximum of two arrays. | |
| float | maximum_smooth (const float a, const float b, float k=0.2) |
| Return the polynomial cubic smooth maximum of two scalar values. | |
| Array | minimum (const Array &array1, const Array &array2) |
| Return the element-wise minimum of two arrays. | |
| Array | minimum (const Array &array1, const float value) |
| Return the element-wise minimum of an array and a scalar value. | |
| Array | minimum_smooth (const Array &array1, const Array &array2, float k=0.2) |
| Return the polynomial cubic smooth element-wise minimum of two arrays. | |
| float | minimum_smooth (const float a, const float b, float k) |
| Return the polynomial cubic smooth minimum of two scalar values. | |
| void | remap (Array &array, float vmin, float vmax, float from_min, float from_max) |
| Remap array elements from a starting range to a target range. | |
| void | remap (Array &array, float vmin=0, float vmax=1) |
| Remap array elements from a starting range to a target range (default range). | |
| void | rescale (Array &array, float scaling, float vref=0.f) |
| Remap array elements from a starting range to a target range. | |
| Graph | generate_network_alpha_model (const std::vector< float > &xc, const std::vector< float > &yc, const std::vector< float > &size, glm::vec4 bbox, const Array &z, uint seed, float alpha=0.7f, int n_dummy_nodes=2500, float dz_weight=1.f, const Array *p_weight=nullptr) |
| Generate a large scale road network between "nodes" (or cities) using the alpha model. | |
| Array | sdf_2d_polyline (const Path &path, glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr) |
| Computes the signed distance field (SDF) of a 2D polyline. | |
| Array | sdf_2d_polyline_bezier (const Path &path, glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr) |
| See hmap::sdf_2d_polyline, with a Bezier approximation of the path. | |
| Array | perturb_mask_contour (const Array &mask, const Array &noise, float max_displacement, int ir=1) |
| Perturb the contour of a binary mask using a displacement field, while trying to preserve a single connected component without holes. | |
| Array | scan_mask (const Array &array, float contrast=0.5f, float brightness=0.5f) |
| Mask adjustement using a 'scanning' method. | |
| Array | select_angle (const Array &array, float angle, float sigma, int ir=0) |
| Return angle selection for a given angle and a tolerance half-width on this value. | |
| Array | select_blob_log (const Array &array, int ir) |
| Return blob detection using the Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) approach. | |
| Array | select_cavities (const Array &array, int ir, bool concave=true) |
| Return holes or bumps detection based on the mean curvature of the heightmap. | |
| Array | select_elevation_slope (const Array &array, float gradient_scale) |
| Array | select_elevation_slope (const Array &array, float gradient_scale, float vmax) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| Array | select_eq (const Array &array, float value) |
Return an array with elements equal to 1 where input elements are equal to value. | |
| Array | select_gradient_angle (const Array &array, float angle) |
| Return an array weighted by the gap between the gradient angle and a given angle. | |
| Array | select_gradient_binary (const Array &array, float talus_center) |
| Return an array filled with 1 where the gradient is larger than a given value and 0 elsewhere. | |
| Array | select_gradient_exp (const Array &array, float talus_center, float talus_sigma) |
| Return an array weighted (exponantial decay) by the gradient norm of the input array. | |
| Array | select_gradient_inv (const Array &array, float talus_center, float talus_sigma) |
| Return an array weighted (square inverse) by the gradient norm of the input array. | |
| Array | select_gt (const Array &array, float value) |
Return an array with elements equal to 1 where input elements are larger than value. | |
| Array | select_interval (const Array &array, float value1, float value2) |
| Return an array with elements equal to 1 where input elements are within the bounds provided. | |
| Array | select_inward_outward_slope (const Array &array, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return an array with positive values if the slope is pointing to the center (slope is inward), and negative values otherwise (slope is outward). | |
| Array | select_lt (const Array &array, float value) |
Return an array with elements equal to 1 where input elements are smaller than value. | |
| Array | select_midrange (const Array &array, float gain, float vmin, float vmax) |
| Selects the midrange values of the input array within a specified range. | |
| Array | select_midrange (const Array &array, float gain) |
| Selects and scales the midrange values of the input array. | |
| void | select_multiband3 (const Array &array, Array &band_low, Array &band_mid, Array &band_high, float ratio1, float ratio2, float overlap, float vmin, float vmax) |
| Splits the input array into three bands (low, mid, and high) based on given ratios and overlap. | |
| void | select_multiband3 (const Array &array, Array &band_low, Array &band_mid, Array &band_high, float ratio1, float ratio2, float overlap) |
| Splits the input array into three bands (low, mid, and high) based on given ratios and overlap. | |
| Array | select_pulse (const Array &array, float value, float sigma) |
| Return an array filled with non-zero values where the input is in the interval [value - sigma, value + sigma]. Output array values have a cubic pulse distribution within this interval. | |
| Array | select_rivers (const Array &array, float talus_ref, float clipping_ratio) |
| Return an array filled with a criterion based on the occurence of a river bed. | |
| Array | select_transitions (const Array &array1, const Array &array2, const Array &array_blend) |
| Return an array filled with 1 at the blending transition between two arrays, and 0 elsewhere. | |
| Array | select_valley (const Array &z, int ir, bool ridge_select=false) |
| Array | hillshade (const Array &z, float azimuth, float zenith, float talus_ref=1.f) |
| Compute the shaded relief map (hillshading) from a heightmap. | |
| Array | shadow_grid (const Array &z, float shadow_talus) |
| Compute the shadow intensity using a grid-based technique. | |
| Array | shadow_heightmap (const Array &z, float azimuth=180.f, float zenith=45.f, float distance=0.2f) |
| Compute crude shadows from a heightmap. | |
| Array | topographic_shading (const Array &z, float azimuth, float zenith, float talus_ref=1.f) |
| Compute the topographic shadow intensity in the range [-1, 1]. | |
| void | find_path_dijkstra (const Array &z, glm::ivec2 ij_start, glm::ivec2 ij_end, std::vector< int > &i_path, std::vector< int > &j_path, float elevation_ratio=0.1f, float distance_exponent=2.f, float upward_penalization=1.f, const Array *p_mask_nogo=nullptr) |
| Finds the path with the lowest elevation and elevation difference between two points in a 2D array using Dijkstra's algorithm. | |
| void | find_path_dijkstra (const Array &z, glm::ivec2 ij_start, std::vector< glm::ivec2 > ij_end_list, std::vector< std::vector< int > > &i_path_list, std::vector< std::vector< int > > &j_path_list, float elevation_ratio=0.1f, float distance_exponent=2.f, float upward_penalization=1.f, const Array *p_mask_nogo=nullptr) |
| Array | non_parametric_sampling (const Array &array, glm::ivec2 patch_shape, uint seed, float error_threshold=0.1f) |
| Synthesize a new heightmap based on an input array using a non-parametric sampling method. | |
| Array | quilting (const std::vector< const Array * > &p_arrays, glm::ivec2 patch_base_shape, glm::ivec2 tiling, float overlap, uint seed, std::vector< Array * > secondary_arrays={}, bool patch_flip=true, bool patch_rotate=true, bool patch_transpose=true, float filter_width_ratio=0.25f) |
| Synthesize a new heightmap by stitching together small patches from input heightmaps. | |
| Array | quilting_blend (const std::vector< const Array * > &p_arrays, glm::ivec2 patch_base_shape, float overlap, uint seed, bool patch_flip=true, bool patch_rotate=true, bool patch_transpose=true, float filter_width_ratio=0.25f) |
| Synthesize a new heightmap by stitching together small patches from a list of input heightmaps. | |
| Array | quilting_expand (const Array &array, float expansion_ratio, glm::ivec2 patch_base_shape, float overlap, uint seed, std::vector< Array * > secondary_arrays={}, bool keep_input_shape=false, bool patch_flip=true, bool patch_rotate=true, bool patch_transpose=true, float filter_width_ratio=0.25f) |
| Synthesize a new heightmap by expanding the input heightmap and stitching patches. | |
| Array | quilting_shuffle (const Array &array, glm::ivec2 patch_base_shape, float overlap, uint seed, std::vector< Array * > secondary_arrays={}, bool patch_flip=true, bool patch_rotate=true, bool patch_transpose=true, float filter_width_ratio=0.25f) |
| Synthesize a new heightmap by reshuffling patches of the input heightmap. | |
| void | flip_lr (Array &array) |
| Flip the array horizontally (left/right). | |
| void | flip_ud (Array &array) |
| Flip the array vertically (up/down). | |
| void | rot180 (Array &array) |
| Rotate the array by 180 degrees. | |
| void | rot270 (Array &array) |
| Rotate the array by 270 degrees. | |
| void | rot90 (Array &array) |
| Rotate the array by 90 degrees. | |
| void | rotate (Array &array, float angle, bool zoom_in=true, bool zero_padding=false) |
| Rotate the array by a specified angle. | |
| Array | transpose (const Array &array) |
| Return the transposed array. | |
| Array | translate (const Array &array, float dx, float dy, bool periodic=false, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Translates a 2D array by a specified amount along the x and y axes. | |
| void | warp (Array &array, const Array *p_dx, const Array *p_dy) |
| Apply a warping effect to the array. | |
| void | warp_directional (Array &array, float angle, float amount=0.02f, int ir=4, bool reverse=false) |
| Apply a warping effect following the downward local gradient direction (deflate/inflate effect). | |
| void | warp_directional (Array &array, float angle, const Array *p_mask, float amount=0.02f, int ir=4, bool reverse=false) |
| Apply a warping effect following the downward local gradient direction (deflate/inflate effect) with a mask. | |
| void | warp_downslope (Array &array, float amount=0.02f, int ir=4, bool reverse=false) |
| Apply a warping effect following the downward local gradient direction (deflate/inflate effect). | |
| void | warp_downslope (Array &array, const Array *p_mask, float amount=0.02f, int ir=4, bool reverse=false) |
| Apply a warping effect following the downward local gradient direction (deflate/inflate effect) with a mask. | |
| Array | zoom (const Array &array, float zoom_factor, bool periodic=false, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Applies a zoom effect to a 2D array with an adjustable center. | |
| std::string | to_string (StorageMode m) |
| std::unique_ptr< TileStorage > | make_storage (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::ivec2 tile_shape, StorageMode storage_mode) |
| std::string | to_string (ForEachMode m) |
| void | copy_data (VirtualArray &src, VirtualArray &dst, const ComputeMode &cm) |
| VirtualTexture | convert_texture_channels (const VirtualTexture &src, int dst_channels, float fill_value, const ComputeMode &cm) |
| template<typename Func > | |
| void | for_each_tile (VirtualTexture &tex, Func &&func, const ComputeMode &cm) |
| template<typename Func > | |
| void | for_each_pixel (VirtualTexture &tex, Func &&func, const ComputeMode &cm) |
| Array | operator* (const float value, const Array &array) |
| Array | operator/ (const float value, const Array &array) |
| Array | operator+ (const float value, const Array &array) |
| const Array | operator- (const float value, const Array &array) |
| template<typename T > | |
| void | convert_mat_to_array (const cv::Mat &mat, Array &array, bool flip_j) |
| void | square_fill_md (Array &array, Mat< int > &is_done, int i1, int i2, int j1, int j2, float noise_scale, std::mt19937 gen, std::uniform_real_distribution< float > dis) |
| void | square_md (Array &array, Mat< int > &is_done, int step, float noise_scale, std::mt19937 gen, std::uniform_real_distribution< float > dis) |
| uint32_t | helper_hash_u32 (uint32_t x) |
| float | helper_hash_01 (uint32_t x) |
| std::vector< glm::vec3 > | helper_tov3 (const std::vector< std::vector< float > > &colors) |
| float | helper_thermal_exchange (float self, float other, float dist, float talus) |
| void | helper_smooth_corners (Array &cubemap, int noverlap, int ir, glm::ivec4 idx_front, glm::ivec4 idx_back) |
| void | helper_get_rtheta_stretch (int i, int j, int ic, int jc, int nradius, float &radius, float &theta, int config) |
| float | helper_get_distance_polar (float r1, float theta1, float r2, float theta2) |
| void | helper_smooth_triple_corner (Array &zfull, int ic, int jc, int noverlap, int ir, int config) |
| Tensor | compute_splatmap (const Array *p_r, const Array *p_g, const Array *p_b, const Array *p_a) |
| glm::ivec4 | helper_compute_tile_bounds (int tile_x, int tile_y, const glm::ivec2 &tile_count, const glm::ivec2 &array_shape, bool overlapping_edges, bool reverse_tile_y_indexing) |
| void | recurve_bexp (Array &array, float tau, const Array *p_mask) |
| void | recurve_exp (Array &array, float tau, const Array *p_mask) |
| void | rescale_grid_from_unit_square_to_bbox (std::vector< float > &x, std::vector< float > &y, glm::vec4 bbox) |
| size_t | helper_estimate_count (const glm::vec4 &bbox, float distance) |
| bool | cmp_inf (Point &a, Point &b) |
| void | compute_gradient (const Array &array, Array &dx, Array &dy, float x_coeff[3], float y_coeff[3], float normalize_factor) |
| Array | compute_gradient_norm (const Array &array, float x_coeff[3], float y_coeff[3], float normalize_factor, Array *p_dx=nullptr, Array *p_dy=nullptr) |
| void | helper_find_up_downslope (const Array &z, const glm::ivec2 &ij, glm::ivec2 &ij_dw, glm::ivec2 &ij_up) |
| bool | is_monotonic (const std::vector< float > &data) |
| int | find_last_index_smaller_than (const std::vector< float > &vec, float threshold) |
| Array | hypot (const Array &array1, const Array &array2) |
| void | helper_thinning (Array &in, int iter) |
| bool | cmp_path (std::pair< float, std::vector< int > > &a, std::pair< float, std::vector< int > > &b) |
| void | helper_flip_rot_transpose (Array &array, bool do_flip_ud, bool do_flip_lr, bool do_rot90, bool do_transpose) |
| void | reindex_vector (std::vector< int > &v, std::vector< size_t > &idx) |
| void | reindex_vector (std::vector< float > &v, std::vector< size_t > &idx) |
| int | count_neighbors_to_fill (int i, int j, Mat< int > &is_cell_done) |
| bool | cmp_queue (std::pair< int, std::pair< int, int > > &a, std::pair< int, std::pair< int, int > > &b) |
Enumeration Type Documentation
◆ StampingBlendMethod
| enum hmap::StampingBlendMethod : int |
◆ PeriodicityType
| enum hmap::PeriodicityType : int |
◆ DomainBoundary
| enum hmap::DomainBoundary : int |
◆ NormalMapBlendingMethod
| enum hmap::NormalMapBlendingMethod : int |
◆ Cmap
| enum hmap::Cmap : int |
Enumeration for different colormap types.
Enumeration of colormap types for image processing.
This enumeration is defined in the highmap/colormap.hpp file and is used for selecting the colormap to be applied during colorization.
This enumeration defines various colormap options that can be used for visualizing data in image processing. Each colormap provides a different color mapping scheme, which can be applied to grayscale images or data to enhance visual interpretation.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| BONE | |
| GRAY | |
| HOT | |
| INFERNO | |
| JET | |
| MAGMA | |
| NIPY_SPECTRAL | |
| SEISMIC | |
| TERRAIN | |
| TURBO | |
| VIRIDIS | |
| WHITE_UNIFORM | |
◆ ErosionProfile
| enum hmap::ErosionProfile : int |
◆ MeshType
| enum hmap::MeshType : int |
◆ AssetExportFormat
| enum hmap::AssetExportFormat : int |
Enumeration for asset export formats supported by Assimp.
This enum lists the various file formats supported for asset export, as recognized by the Assimp library. Each format is associated with a specific file extension and usage.
◆ neighborhood
| enum hmap::neighborhood : int |
Enum representing different types of neighborhood lattices.
This enumeration defines the different types of neighborhoods that can be used in a lattice-based system. These neighborhoods determine how cells or nodes are connected to their immediate surroundings.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| MOORE | Moore neighborhood: includes all eight surrounding cells. |
| VON_NEUMANN | Von Neumann neighborhood: includes only the four. |
| CROSS | Cross-shaped neighborhood: includes only the diagonal. |
◆ NoiseType
| enum hmap::NoiseType : int |
Enumeration of various noise types used for procedural generation.
This enumeration defines different types of noise algorithms that can be used for procedural generation tasks such as terrain generation, texture synthesis, and other applications where pseudo-random patterns are required.
◆ PointSamplingMethod
| enum hmap::PointSamplingMethod : int |
◆ FlowDirectionMethod
| enum hmap::FlowDirectionMethod : int |
◆ InterpolationMethod1D
| enum hmap::InterpolationMethod1D : int |
Enumeration of the available 1D interpolation methods.
This enumeration defines the different types of interpolation methods that can be used with the Interpolator1D class.
◆ InterpolationMethod2D
| enum hmap::InterpolationMethod2D : int |
◆ InterpolationMethodCurve
| enum hmap::InterpolationMethodCurve : int |
Enumeration for specifying the interpolation method for curves.
Defines the available methods for curve interpolation:
BEZIER: Requires the number of points to be a multiple of 4 minus 1, like (4 * n - 1).BSPLINE: B-spline interpolation method.CATMULLROM: Catmull-Rom spline interpolation method.DECASTELJAU: Uses De Casteljau's algorithm to compute Bézier curves at a given parameter. This is an alternative to the standard Bézier curve method.POINTS_LERP: Linear interpolation between points.
◆ KernelType
| enum hmap::KernelType : int |
Enumeration for different kernel functions used in various algorithms.
This enumeration defines the types of kernel functions that can be used for smoothing, interpolation, and other operations requiring a kernel. Each kernel type represents a specific mathematical function used to weight data points based on their distance from a central point.
These kernels are used in algorithms that require weighting functions, such as kernel density estimation, interpolation, and data smoothing.
◆ DistanceFunction
| enum hmap::DistanceFunction : int |
◆ PhasorProfile
| enum hmap::PhasorProfile : int |
◆ RadialProfile
| enum hmap::RadialProfile : int |
◆ DistanceTransformType
| enum hmap::DistanceTransformType : int |
◆ pyramid_transform_support
| enum hmap::pyramid_transform_support : int |
◆ VoronoiReturnType
| enum hmap::VoronoiReturnType : int |
Selects the value returned by the Voronoi evaluation.
F1 is the distance to the nearest site, F2 to the second nearest.
◆ PrimitiveType
| enum hmap::PrimitiveType : int |
◆ ClampMode
| enum hmap::ClampMode : int |
◆ StorageMode
| enum hmap::StorageMode : int |
◆ ForEachMode
| enum hmap::ForEachMode : int |
Function Documentation
◆ adjust()
|
inline |
◆ cv_mat_to_array()
| Array hmap::cv_mat_to_array | ( | const cv::Mat & | mat, |
| bool | remap_values = true, |
||
| bool | flip_j = false |
||
| ) |
Converts an OpenCV cv::Mat to a 2D Array with optional value scaling to [0, 1].
This function converts an OpenCV cv::Mat object into a 2D Array. The conversion process creates a new Array object and copies the data from the cv::Mat into this Array. If the remap_values parameter is set to true (the default), the values in the resulting Array will be scaled to the interval [0, 1]. If set to false, the values will be copied directly without scaling. Modifications to the Array will not affect the original cv::Mat and vice versa.
- Parameters
-
mat Reference to the OpenCV cv::Matobject that will be converted.remap_values A boolean flag indicating whether to scale the values to [0, 1]. If true, the values will be scaled; iffalse, they will be copied directly. Default istrue.
- Returns
- A 2D
Arrayobject containing a copy of the data from the inputcv::Mat, with optional scaling to the interval [0, 1].
Example
◆ for_each_cell() [1/2]
|
inline |
Apply a function to every cell (mutable).
◆ for_each_cell() [2/2]
|
inline |
Apply a function to every cell (read-only).
◆ reduce_cells() [1/2]
|
inline |
Reduce all cells to a single value.
◆ reduce_cells() [2/2]
|
inline |
Reduce all cells to a single value.
◆ alter_elevation()
| void hmap::alter_elevation | ( | Array & | array, |
| const Cloud & | cloud, | ||
| int | ir, | ||
| float | footprint_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | shift = {0.f, 0.f}, |
||
| glm::vec2 | scale = {1.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Point-wise alteration: locally enforce a new elevation value while maintaining the 'shape' of the heightmap.
This function modifies the elevation values in the input array based on a cloud of points that specify the coordinates and variations for the alterations. The function ensures that the shape of the heightmap is preserved while applying these local changes.
The alteration is performed using a kernel with a minimal radius (ir) and the intensity of the alterations is scaled based on the footprint_ratio. The shift parameter allows for introducing noise or offset in the alteration process, and the scale parameter is used to adjust the domain of the alteration.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap to be altered. The elevation values in this array will be adjusted according to the cloud data. cloud Cloud object that defines the coordinates and elevation variations for the alterations. This object provides the necessary data for applying the local changes. ir Alteration kernel minimal radius. This parameter defines the minimum size of the kernel used for local alterations. footprint_ratio Defines how the radius of the alteration scales with the variation intensity. A higher ratio results in a larger footprint of the alterations. shift Noise shift specified as a vector {xs, ys} for each direction, relative to a unit domain. This allows for adding random offsets to the alteration process. scale Domain scaling in the range [0, 1]. This parameter adjusts the domain size over which the alteration is applied.
Example
Result
◆ base_elevation()
| Array hmap::base_elevation | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| const std::vector< std::vector< float > > & | values, | ||
| float | width_factor = 1.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generate a heightmap from a coarse grid of control points with defined elevation values.
This function creates a heightmap by interpolating elevation values provided at specific control points on a coarse grid. The result is a finer resolution heightmap where the elevation values are smoothly distributed over the entire grid.
The interpolation is performed using a Gaussian function, with the width_factor parameter controlling the half-width of the base Gaussian function used for smoothing. Optionally, noise can be added using the provided p_noise_x and p_noise_y arrays, and the heightmap can be adjusted by a local wavenumber multiplier specified by p_stretching. The bbox parameter defines the domain bounding box for the heightmap.
- Parameters
-
shape Dimensions of the output array (heightmap). values Elevation values at the control points specified on a coarse grid. This 2D vector holds the elevation data at each control point. width_factor Factor applied to the half-width of the Gaussian function used for smoothing the elevations. A value of 1.0 represents the default smoothing width. p_noise_x Optional pointer to an input noise array affecting the x-direction. If provided, it is used to add noise to the elevation values. p_noise_y Optional pointer to an input noise array affecting the y-direction. If provided, it is used to add noise to the elevation values. p_stretching Optional pointer to an input array that acts as a local wavenumber multiplier. If provided, it adjusts the elevation values according to the local wavenumber. bbox Domain bounding box specified as a vector {xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax}. This defines the extent of the heightmap in the coordinate space.
- Returns
- Array A new array representing the generated heightmap with interpolated elevation values.
Example
Result
◆ flatbed_carve() [1/2]
| Array hmap::flatbed_carve | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| const Path & | path, | ||
| float | bottom_extent = 32.f, |
||
| float | vmin = 0.1f, |
||
| float | depth = 0.05f, |
||
| float | falloff_distance = 128.f, |
||
| float | outer_slope = 0.1f, |
||
| bool | preserve_bedshape = true, |
||
| RadialProfile | radial_profile = RadialProfile::RP_GAIN, |
||
| float | radial_profile_parameter = 2.f, |
||
| Array * | p_falloff_mask = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_r = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Carves a flatbed shape along a path.
Generates a height array by carving a flat-bottomed bed around a path, with a radial profile for the bed shape and an optional outer falloff.
- Parameters
-
shape Output array resolution. path Path defining the bed centerline. bottom_extent Radius of the flatbed region. vmin Base height value. depth Bed depth. falloff_distance Falloff width outside the bed. outer_slope Linear slope beyond the bed. preserve_bedshape Preserve relative bed shape under radial noise. radial_profile Radial profile type. radial_profile_parameter Shape parameter for the profile. p_falloff_mask Optional output falloff mask. p_noise_r Optional radial noise. bbox World-space bounding box.
- Returns
- Generated flatbed height array.
Example
Result
◆ flatbed_carve() [2/2]
| void hmap::flatbed_carve | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Path & | path, | ||
| float | bottom_extent = 32.f, |
||
| float | vmin = 0.1f, |
||
| float | depth = 0.05f, |
||
| float | falloff_distance = 128.f, |
||
| float | outer_slope = 0.1f, |
||
| bool | preserve_bedshape = true, |
||
| RadialProfile | radial_profile = RadialProfile::RP_GAIN, |
||
| float | radial_profile_parameter = 2.f, |
||
| Array * | p_falloff_mask = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_r = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Blends a flatbed carve into an existing heightmap.
Carves and blends a flatbed shape along a path into the provided array, using a smooth falloff mask.
- Parameters
-
z Heightmap to modify in place. path Path defining the bed centerline. bottom_extent Radius of the flatbed region. vmin Base height value. depth Bed depth. falloff_distance Falloff width outside the bed. outer_slope Linear slope beyond the bed. preserve_bedshape Preserve relative bed shape under radial noise. radial_profile Radial profile type. radial_profile_parameter Shape parameter for the profile. p_falloff_mask Optional output falloff mask. p_noise_r Optional radial noise. bbox World-space bounding box.
Example
Result

◆ reverse_midpoint()
| Array hmap::reverse_midpoint | ( | const Array & | array, |
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | noise_scale = 1.f, |
||
| float | threshold = 0.f |
||
| ) |
Apply the reverse midpoint displacement algorithm to the input array.
This function implements the reverse midpoint displacement algorithm as described in Belhadj et al. (2005). The algorithm generates a terrain-like structure by applying displacement to the values in the input array based on random noise. The function can be tuned using the seed parameter for random number generation, noise_scale for controlling the amplitude of the noise, and threshold for setting a background value.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the reverse midpoint displacement algorithm will be applied. The array's values are modified to produce the output terrain. seed Random seed number used to initialize the random number generator for reproducibility. noise_scale Amplitude of the noise applied during the displacement process. A higher value results in more pronounced terrain features. threshold Threshold 'background' value used to influence the displacement algorithm. Values below this threshold may be treated differently depending on the algorithm's design.
- Returns
- Array The output array after applying the reverse midpoint displacement algorithm. This array contains the modified values representing the generated terrain.
Example
Result
◆ ridgelines()
| Array hmap::ridgelines | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| const std::vector< float > & | xr, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | yr, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | zr, | ||
| float | slope, | ||
| float | k_smoothing = 1.f, |
||
| float | width = 0.1f, |
||
| float | vmin = 0.f, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox_array = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generate a heightmap based on a set of ridgelines and a specified slope.
This function creates a heightmap using a set of ridgelines defined by their x, y, and z coordinates, and applies a specified slope to the ridgelines. The function can optionally apply smoothing, adjust the ridge edge width, and clamp values below a minimum threshold. Additional noise and stretching parameters can be applied to modify the resulting heightmap.
- Parameters
-
shape The dimensions of the output array (heightmap). xr A vector of x-coordinates defining ridge segments. yr A vector of y-coordinates defining ridge segments. zr A vector of z-coordinates defining ridge segments. slope The slope applied to the ridgelines. Can be negative to invert the slope. k_smoothing Smoothing parameter to control the smoothness of the ridgelines. width Width of the ridge edges. Determines how broad the ridges appear. vmin Minimum value for the heightmap. Values below this threshold will be clamped to vmin.bbox Bounding box for the entire domain, defining the area covered by the heightmap. p_noise_x Pointer to an optional array for x-direction noise to apply to the heightmap. p_noise_y Pointer to an optional array for y-direction noise to apply to the heightmap. p_stretching Pointer to an optional array for local wavenumber multipliers to stretch the ridges. bbox_array Bounding box for the array domain, defining the spatial extent of the heightmap.
- Returns
- Array The generated heightmap with ridgelines and applied slope.
Example
Result

◆ ridgelines_bezier()
| Array hmap::ridgelines_bezier | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| const std::vector< float > & | xr, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | yr, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | zr, | ||
| float | slope, | ||
| float | k_smoothing = 1.f, |
||
| float | width = 0.1f, |
||
| float | vmin = 0.f, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox_array = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generate a heightmap based on a set of ridgelines with quadratic Bezier interpolation.
This function creates a heightmap using ridgelines defined by their x, y, and z coordinates. The ridgelines are interpolated using quadratic Bezier curves to smooth the transitions. The function applies a specified slope to the ridgelines and can optionally apply smoothing, adjust ridge edge width, and clamp values below a minimum threshold. Additional noise and stretching parameters can be used to modify the resulting heightmap.
- Parameters
-
shape The dimensions of the output array (heightmap). xr A vector of x-coordinates defining ridge segments, organized in groups of three (control points of the Bezier curves). yr A vector of y-coordinates defining ridge segments, organized in groups of three (control points of the Bezier curves). zr A vector of z-coordinates defining ridge segments, organized in groups of three (control points of the Bezier curves). slope The slope applied to the ridgelines. Can be negative to invert the slope. k_smoothing Smoothing parameter to control the smoothness of the ridgelines. width Width of the ridge edges. Determines how broad the ridges appear. vmin Minimum value for the heightmap. Values below this threshold will be clamped to vmin.bbox Bounding box for the entire domain, defining the area covered by the heightmap. p_noise_x Pointer to an optional array for x-direction noise to apply to the heightmap. p_noise_y Pointer to an optional array for y-direction noise to apply to the heightmap. p_stretching Pointer to an optional array for local wavenumber multipliers to stretch the ridges. bbox_array Bounding box for the array domain, defining the spatial extent of the heightmap.
- Returns
- Array The generated heightmap with ridgelines interpolated using quadratic Bezier curves and applied slope.
Example
Result
◆ stamping()
| Array hmap::stamping | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| const std::vector< float > & | xr, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | yr, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | zr, | ||
| Array | kernel, | ||
| int | kernel_ir, | ||
| bool | kernel_scale_radius, | ||
| bool | kernel_scale_amplitude, | ||
| StampingBlendMethod | blend_method, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | k_smoothing = 0.1f, |
||
| bool | kernel_flip = true, |
||
| bool | kernel_rotate = false, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox_array = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generate a heightmap by stamping a kernel at predefined locations.
This function creates a heightmap by stamping a specified kernel at given x, y, and z coordinates. The kernel can be scaled and manipulated based on the z-coordinates of the stamping points, and can be optionally flipped or rotated. The heightmap is generated by blending the results using the specified blending method. Randomization options are available for kernel manipulation.
- Parameters
-
shape The dimensions of the output array (heightmap). xr A vector of x-coordinates where the kernel is stamped. yr A vector of y-coordinates where the kernel is stamped. zr A vector of z-coordinates where the kernel is stamped. This affects the kernel radius and amplitude scaling. kernel The kernel to be stamped onto the heightmap. kernel_ir The radius of the kernel in pixels. kernel_scale_radius Boolean flag to scale the kernel radius based on the z-coordinates. kernel_scale_amplitude Boolean flag to scale the kernel amplitude based on the z-coordinates. blend_method The method used for blending multiple kernel stamps. Options may include additive, maximum, minimum, etc. seed Random seed number for kernel randomization. k_smoothing Smoothing parameter for the heightmap (e.g., for smooth minimum or maximum blending). kernel_flip Boolean flag to randomly flip the kernel before stamping. Flipping includes transposing. kernel_rotate Boolean flag to randomly rotate the kernel before stamping. Rotation can be resource-intensive. bbox_array Bounding box for the array domain, defining the spatial extent of the heightmap.
- Returns
- Array The generated heightmap with kernel stamps applied at the specified locations.
Example
Result


- See also
other_related_functions
◆ blend_exclusion()
Return the 'exclusion' blending of two arrays.
The exclusion blend mode creates a blend that is similar to the difference blend mode but with lower contrast. It produces an effect that is often used in image editing for special effects. For more details, see https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blend_modes.
- Warning
- Array values are expected to be in the range [0, 1].
- Parameters
-
array1 First input array. array2 Second input array.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array after applying the exclusion blend mode.
Example
Result
- See also
blend_exclusion,blend_negate,blend_overlay,blend_soft
◆ blend_gradients()
Return the blending of two arrays based on their gradients.
This function blends two arrays by considering their gradients, which can be useful for producing smooth transitions between the arrays based on their directional changes.
- Parameters
-
array1 First input array. array2 Second input array. ir Filtering radius in pixels.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array after blending based on gradients.
◆ blend_negate()
Return the 'negate' blending of two arrays.
The negate blend mode inverts the colors of one of the arrays relative to the other. It creates a high-contrast effect that can be useful for emphasizing differences between two arrays.
- Parameters
-
array1 First input array. array2 Second input array.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array after applying the negate blend mode.
- See also
blend_exclusion,blend_negate,blend_overlay,blend_soft
◆ blend_overlay()
Return the 'overlay' blending of two arrays.
The overlay blend mode combines the colors of two arrays in a way that enhances contrast and emphasizes details.
- Warning
- Array values are expected to be in the range [0, 1].
- Parameters
-
array1 First input array. array2 Second input array.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array after applying the overlay blend mode.
- See also
blend_exclusion,blend_negate,blend_overlay,blend_soft
◆ blend_soft()
Return the 'soft' blending of two arrays.
The soft blend mode applies a soft light effect to the blending of two arrays, based on the soft light mode described in Pegtop soft light mode. It creates a subtle blend with reduced contrast.
- Warning
- Array values are expected to be in the range [0, 1].
- Parameters
-
array1 First input array. array2 Second input array.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array after applying the soft light blend mode.
- See also
blend_exclusion,blend_negate,blend_overlay,blend_soft
◆ mixer()
| Array hmap::mixer | ( | const Array & | t, |
| const std::vector< const Array * > & | arrays, | ||
| float | gain_factor = 1.f |
||
| ) |
Return the mixing of a set of arrays based on a parameter t.
This function mixes a set of arrays based on a mixing coefficient t that determines the contribution of each array. The parameter t should be in the range [0, 1], where t represents the blending ratio.
- Warning
- Values of array
tare expected to be in the range [0, 1].
- Parameters
-
t Mixing coefficient, in the range [0, 1]. arrays References to the input arrays to be mixed.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array after mixing.
Example
Result
◆ transfer()
| Array hmap::transfer | ( | const Array & | source, |
| const Array & | target, | ||
| int | ir, | ||
| float | amplitude, | ||
| bool | target_prefiltering = false |
||
| ) |
Transfers spatial details from a source array onto a target array.
This function applies a high-pass spatial filter to the source array (using a smoothing pulse of radius ir) to extract its high-frequency content. That content is then scaled by amplitude and blended with the target array. Optionally, the target can be prefiltered before blending.
The result is a new array that combines the base structure of target with the high-frequency details from source.
- Parameters
-
source The input array providing high-frequency details. target The input array providing the base structure. ir Radius (in pixels or samples) for the smoothing filter used to separate low/high frequencies. amplitude Scaling factor applied to the high-frequency content extracted from source.target_prefiltering If true, targetis smoothed before blending to better integrate with the transferred details.
- Returns
- A new Array containing the target data enhanced by the source's high-frequency information.
Example
Result
◆ extrapolate_borders()
Performs linear extrapolation of values at the borders of an array (e.g., i = 0, j = 0, etc.) based on the inner values of the array.
This function modifies the borders of the input array by applying a linear extrapolation method, which uses the values inside the array to estimate and fill in the border values. The extrapolation is influenced by a relaxation coefficient (sigma) and a buffer depth (nbuffer), which determines how many layers of the border are extrapolated.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the input array whose borders need extrapolation. nbuffer Optional parameter specifying the buffer depth, i.e., the number of layers at the border to extrapolate. Default is 1. sigma Optional relaxation coefficient that adjusts the influence of inner values on the extrapolated border values. Default is 0.0.
- See also
- fill_borders()
◆ falloff()
| void hmap::falloff | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | strength = 1.f, |
||
| DistanceFunction | dist_fct = DistanceFunction::EUCLIDIAN, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Applies a falloff effect to the input array based on distance.
This function modifies the elements of the input array by applying a falloff effect, which decreases the values based on their distance from a central point or area. The strength of the falloff, the type of distance function used, and optional noise can be specified.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the array that will be modified by the falloff effect. strength The strength of the falloff effect. A higher value results in a stronger falloff. Default is 1.0f. dist_fct The distance function to be used for calculating the falloff. Options include Euclidian and others, with DistanceFunction::EUCLIDIANas the default.p_noise Optional pointer to an array that provides noise to be added to the falloff effect. If nullptr (default), no noise is added. bbox A 4D vector representing the bounding box within which the falloff effect is applied. The default is {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
Example
Result

◆ fill_borders() [1/2]
| void hmap::fill_borders | ( | Array & | array | ) |
Fills the border values of an array (e.g., i = 0, j = 0, etc.) based on the values of the first neighboring cells.
This function modifies the border values of the input array by copying values from their immediate neighbors. The operation ensures that border values are consistent with their adjacent cells, typically used to prepare the array for further processing.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the input array whose borders need to be filled.
- See also
- extrapolate_borders()
◆ fill_borders() [2/2]
| void hmap::fill_borders | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | nbuffer | ||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ generate_buffered_array()
| Array hmap::generate_buffered_array | ( | const Array & | array, |
| glm::ivec4 | buffers, | ||
| bool | zero_padding = false |
||
| ) |
Creates and returns a new array with additional buffer zones at the boundaries, where the buffer values are filled either by symmetry or by zero-padding.
This function takes an input array and generates a new array with extra layers (buffers) added to its boundaries. The size of these buffer zones is specified by the buffers parameter, and the values within these buffers can be filled either by reflecting the values at the boundaries (symmetry) or by padding with zeros.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the input array. buffers A vector specifying the buffer sizes for the east, west, south, and north boundaries. zero_padding Optional boolean flag to use zero-padding instead of symmetry for filling the buffer values. Default is false.
- Returns
- Array A new array with buffers added at the boundaries.
◆ make_periodic()
| void hmap::make_periodic | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | nbuffer, | ||
| const PeriodicityType & | periodicity_type = PeriodicityType::PERIODICITY_XY |
||
| ) |
Adjusts the input array to be periodic in both directions by transitioning smoothly at the boundaries.
This function modifies the input array so that the values at the boundaries transition smoothly, making the array periodic in both the horizontal and vertical directions. The width of the transition zone at the boundaries is controlled by the nbuffer parameter.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the input array to be made periodic. nbuffer The width of the transition zone at the boundaries.
Example
Result
◆ make_periodic_stitching()
Creates a periodic array in both directions using a stitching operation that minimizes errors at the boundaries.
This function generates a new array that is periodic in both directions by applying a stitching operation at the boundaries. The stitching process aims to minimize discrepancies, creating a seamless transition between the edges of the array. The overlap parameter determines the extent of the overlap during the stitching, based on the half-size of the domain. If overlap is set to 1, the transition spans the entire domain.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the input array to be made periodic. overlap A float value representing the overlap based on the domain's half-size. An overlap of 1 means the transition spans the whole domain.
- Returns
- Array A new array that is periodic in both directions with minimized boundary errors.
Example
Result
◆ make_periodic_tiling()
Creates a tiled, periodic array by applying a transition with overlap in both directions.
This function generates a new array that is periodic and tiled according to the specified tiling dimensions. The periodicity is achieved by applying a transition at the boundaries, where the extent of overlap is determined by the overlap parameter. The tiling parameter specifies the number of tiles in the horizontal and vertical directions.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the input array to be tiled and made periodic. overlap A float value representing the overlap based on the domain's half-size. If overlapis 1, the transition spans the entire domain on both sides.tiling A 2D vector specifying the number of tiles in the horizontal and vertical directions.
- Returns
- Array A new tiled array that is periodic in both directions.
Example
Result

◆ set_borders() [1/2]
| void hmap::set_borders | ( | Array & | array, |
| glm::vec4 | border_values, | ||
| glm::ivec4 | buffer_sizes | ||
| ) |
Enforces specific values at the boundaries of the array.
This function sets the values at the borders of the input array to specified values for each side (east, west, south, and north). The size of the buffer zone at each border can also be defined, allowing precise control over how much of the boundary is modified.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the input array whose borders are to be modified. border_values A vector specifying the values to set at the east, west, south, and north borders. buffer_sizes A vector specifying the size of the buffer zones at the east, west, south, and north borders.
Example
Result
◆ set_borders() [2/2]
| void hmap::set_borders | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | border_values, | ||
| int | buffer_sizes | ||
| ) |
Enforces a uniform value at all boundaries of the array.
This overloaded function sets the same value at all borders of the input array. The size of the buffer zone at each border can be defined with a single value that applies uniformly to all sides.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the input array whose borders are to be modified. border_values The value to set at all borders. buffer_sizes The size of the buffer zone to apply uniformly at all borders.
◆ sym_borders()
| void hmap::sym_borders | ( | Array & | array, |
| glm::ivec4 | buffer_sizes | ||
| ) |
Fills the values at the domain borders using symmetry over a specified buffer depth.
This function fills the borders of the input array by reflecting the values inside the array symmetrically. The depth of the buffer at each border (east, west, south, north) is specified by the buffer_sizes parameter.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the input array whose borders are to be filled using symmetry. buffer_sizes A vector specifying the buffer sizes at the east, west, south, and north borders.
◆ zeroed_borders()
| void hmap::zeroed_borders | ( | Array & | array | ) |
Fills the border values (e.g., i = 0, j = 0, etc.) of the array with zeros.
This function sets all the values at the borders of the input array to zero. It can be used to zero out boundary values, preparing the array for specific computations.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the input array whose borders are to be zeroed.
- See also
- fill_borders()
◆ zeroed_edges()
| void hmap::zeroed_edges | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | sigma = 1.f, |
||
| DistanceFunction | dist_fct = DistanceFunction::EUCLIDIAN, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Applies a smooth transition to zero at the array borders.
This function gradually transitions the values at the borders of the array to zero, using a smoothing function defined by the sigma parameter, which controls the half-width of the transition. The transition can be further customized by providing a noise array (p_noise) and a bounding box (bbox) that defines the domain of the operation.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the input array whose borders will be smoothly transitioned to zero. sigma A float value controlling the half-width ratio of the transition. Default is 1.0. dist_fct Distance function used for determining the smoothing (default is Euclidean distance). p_noise Optional pointer to an input noise array, which can be used during the transition process. Default is nullptr.bbox A vector defining the domain's bounding box. Default is {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
Example
Result
◆ apply_hillshade() [1/2]
| void hmap::apply_hillshade | ( | Tensor & | img, |
| const Array & | array, | ||
| float | vmin = 0.f, |
||
| float | vmax = 1.f, |
||
| float | exponent = 1.f |
||
| ) |
Apply hillshading to a Tensor image.
This function applies a hillshading effect to the provided tensor image using the elevation data in the input array. The effect is controlled by the power exponent and can be scaled by specifying the minimum and maximum values.
- Parameters
-
img Input image represented as a Tensor. array Elevation data used to generate the hillshading effect. vmin Minimum value for scaling the hillshading effect (default is 0.f). vmax Maximum value for scaling the hillshading effect (default is 1.f). exponent Power exponent applied to the hillshade values (default is 1.f).
◆ apply_hillshade() [2/2]
| void hmap::apply_hillshade | ( | std::vector< uint8_t > & | img, |
| const Array & | array, | ||
| float | vmin = 0.f, |
||
| float | vmax = 1.f, |
||
| float | exponent = 1.f, |
||
| bool | is_img_rgba = false |
||
| ) |
Apply hillshading to an 8-bit image.
This function applies a hillshading effect to a vector of 8-bit image data. The effect is computed based on the elevation data in the input array. The image can be either RGB or RGBA format depending on the is_img_rgba flag.
- Parameters
-
img Input image represented as a vector of 8-bit data. array Elevation data used to generate the hillshading effect. vmin Minimum value for scaling the hillshading effect (default is 0.f). vmax Maximum value for scaling the hillshading effect (default is 1.f). exponent Power exponent applied to the hillshade values (default is 1.f). is_img_rgba Boolean flag indicating if the input image has an alpha channel (default is false).
◆ color_adjust()
| void hmap::color_adjust | ( | VirtualTexture & | tex, |
| ColorAdjust | param, | ||
| const ComputeMode & | cm | ||
| ) |
◆ colorize() [1/3]
| Tensor hmap::colorize | ( | const Array & | array, |
| float | vmin, | ||
| float | vmax, | ||
| int | cmap, | ||
| bool | hillshading, | ||
| bool | reverse = false, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Apply colorization to an array.
This function applies a colormap to the input array and optionally applies hillshading and noise. The colorization can be reversed, and the function returns a Tensor representing the colorized image.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be colorized. vmin Minimum value for scaling the colormap. vmax Maximum value for scaling the colormap. cmap Colormap to be applied (using the Cmap enum). hillshading Boolean flag to apply hillshading. reverse Boolean flag to reverse the colormap (default is false). p_noise Optional pointer to a noise array (default is nullptr).
◆ colorize() [2/3]
| void hmap::colorize | ( | VirtualTexture & | out, |
| VirtualArray & | level, | ||
| const ComputeMode & | cm, | ||
| float | vmin, | ||
| float | vmax, | ||
| int | cmap, | ||
| VirtualArray * | p_alpha = nullptr, |
||
| bool | reverse = false, |
||
| VirtualArray * | p_noise = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Colorize a scalar field into a texture using a predefined colormap.
- Parameters
-
out Output texture. level Input scalar values. cm Compute mode (CPU/GPU). vmin Lower bound for normalization. vmax Upper bound for normalization. cmap Colormap identifier. p_alpha Optional alpha channel. reverse Reverse colormap mapping. p_noise Optional noise for dithering.
Example
Result

◆ colorize() [3/3]
| void hmap::colorize | ( | VirtualTexture & | out, |
| VirtualArray & | level, | ||
| const ComputeMode & | cm, | ||
| float | vmin, | ||
| float | vmax, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | positions, | ||
| const std::vector< glm::vec3 > & | colormap_colors, | ||
| VirtualArray * | p_alpha = nullptr, |
||
| bool | reverse = false, |
||
| VirtualArray * | p_noise = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Colorize a scalar field into a texture using a custom colormap.
- Parameters
-
out Output texture. level Input scalar values. cm Compute mode (CPU/GPU). vmin Lower bound for normalization. vmax Upper bound for normalization. positions Normalized color positions. colormap_colors RGB(A) colors per position. p_alpha Optional alpha channel. reverse Reverse colormap mapping. p_noise Optional noise for dithering.
Example
Result

◆ colorize_grayscale()
◆ colorize_histogram()
◆ colorize_slope_height_heatmap()
Colorizes a slope height heatmap based on the gradient norms of a given array.
This function computes a colorized heatmap using a two-dimensional histogram that considers the gradient norm of the input array. It normalizes both the input array values and their corresponding gradient norms, calculates a 2D histogram, and then applies a colormap to visualize the heatmap.
- Parameters
-
array The input array for which the slope height heatmap is computed. This should be a 2D array representing height values. cmap An integer representing the colormap to be used for colorization. Colormap options depend on the colorization function used internally.
- Returns
- Tensor representing the colorized heatmap, which visualizes the distribution of height values and their corresponding gradient norms.
- The function normalizes the height values and gradient norms independently using the minimum and maximum values.
- A 2D histogram is constructed, where each bin corresponds to a pair of normalized height and gradient values.
- The colormap is then applied to this histogram to produce a colorized output.
- Note
- If the input array has a constant value (i.e., min == max), no normalization is applied, and the function may not produce meaningful results.
- Warning
- Ensure that the input array is non-empty and has valid dimensions.
Example
Result
◆ colorize_vec2()
Combine two arrays into a colored image.
This function takes two input arrays and combines them into a single 8-bit colored Tensor image. The resulting image uses the data from both arrays to create a composite color representation.
- Parameters
-
array1 First input array. array2 Second input array.
Example
Result

◆ luminance()
| void hmap::luminance | ( | VirtualArray & | out, |
| VirtualTexture & | tex, | ||
| const ComputeMode & | cm | ||
| ) |
Compute luminance from a texture.
Computes a grayscale luminance array from the RGB channels of a virtual texture and stores the result in out.
- Parameters
-
out Output luminance array. tex Input virtual texture (expects at least 3 channels). cm Compute mode (execution and storage behavior).
◆ mix() [1/2]
| void hmap::mix | ( | VirtualTexture & | out, |
| VirtualTexture & | tex1, | ||
| VirtualTexture & | tex2, | ||
| const ComputeMode & | cm, | ||
| bool | use_sqrt_avg = true |
||
| ) |
Mix two textures into an output texture.
- Parameters
-
out Output texture. tex1 First input texture. tex2 Second input texture. cm Compute mode (CPU/GPU). use_sqrt_avg Use square-root averaging.
Example
Result

◆ mix() [2/2]
| void hmap::mix | ( | VirtualTexture & | out, |
| std::vector< VirtualTexture * > & | texs, | ||
| const ComputeMode & | cm, | ||
| bool | use_sqrt_avg = true |
||
| ) |
◆ mix_normal_map()
| void hmap::mix_normal_map | ( | VirtualTexture & | out, |
| VirtualTexture & | nmap_base, | ||
| VirtualTexture & | nmap_detail, | ||
| const ComputeMode & | cm, | ||
| float | detail_scaling, | ||
| NormalMapBlendingMethod | blending_method | ||
| ) |
Blend two normal maps into a single output normal map.
Combines a base normal map with a detail normal map using the specified blending method and scaling factor.
- Parameters
-
out Output normal map texture. nmap_base Base normal map texture. nmap_detail Detail normal map texture. cm Compute mode (execution and storage behavior). detail_scaling Strength of the detail normal map. blending_method Normal map blending method.
◆ get_colormap_data()
| std::vector< glm::vec3 > hmap::get_colormap_data | ( | int | cmap | ) |
◆ convolve1d_i()
Return the convolution product of the array with a 1D kernel along the 'i' direction.
This function applies a 1D convolution to the input array using the provided kernel, considering the convolution in the row direction ('i' direction).
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be convolved. kernel 1D kernel to be used for the convolution.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array after applying the 1D convolution.
Example
Result
- See also
convolve1d_j
◆ convolve1d_j()
Return the convolution product of the array with a 1D kernel along the 'j' direction.
This function applies a 1D convolution to the input array using the provided kernel, considering the convolution in the column direction ('j' direction).
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be convolved. kernel 1D kernel to be used for the convolution.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array after applying the 1D convolution.
Example
Result

- See also
convolve1d_i
◆ convolve2d()
Return the convolution product of the array with a given 2D kernel.
This function performs a 2D convolution on the input array using the specified 2D kernel. The output array has the same shape as the input array, and symmetry boundary conditions are used.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be convolved. kernel 2D kernel to be used for the convolution.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array after applying the 2D convolution.
Example
◆ convolve2d_truncated()
Return the convolution product of the array with a given 2D kernel, with a truncated output size.
This function performs a 2D convolution on the input array using the specified 2D kernel. The resulting output array is smaller than the input array by the dimensions of the kernel.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be convolved. kernel 2D kernel to be used for the convolution.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array after applying the truncated 2D convolution. Shape: {array.shape[0] - kernel.shape[0], array.shape[1] - kernel.shape[1]}.
◆ convolve2d_svd()
Return the approximate convolution product of the array with a Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) of a kernel.
This function approximates the convolution of the input array with a 2D kernel by using its Singular Value Decomposition (SVD). The approximation is based on the first rank singular values and vectors.
- Parameters
-
z Input array to be convolved. kernel 2D kernel to be used for the convolution. rank Approximation rank: number of singular values/vectors used for the approximation.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array after applying the SVD-based convolution approximation.
Example
Result
◆ convolve2d_svd_rotated_kernel()
| Array hmap::convolve2d_svd_rotated_kernel | ( | const Array & | z, |
| const Array & | kernel, | ||
| int | rank = 3, |
||
| int | n_rotations = 6, |
||
| uint | seed = 1 |
||
| ) |
Return the approximate convolution product of the array with a Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) of a kernel combined with kernel rotations.
This function approximates the convolution of the input array with a 2D kernel using its SVD, combined with multiple rotations of the kernel. This can enhance the convolution approximation by considering different orientations of the kernel.
- Parameters
-
z Input array to be convolved. kernel 2D kernel to be used for the convolution. rank Approximation rank: number of singular values/vectors used for the approximation. n_rotations Number of kernel rotations to be considered. seed Random seed number for kernel rotations.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array after applying the SVD-based convolution approximation with rotations.
Example
Result

◆ accumulation_curvature()
Computes the accumulation curvature of a heightmap. Acumulation curvature is a measure of the extent of local accumulation of flows at a given point.
- Parameters
-
z The input array representing the heightmap data (elevation values). ir The radius used for pre-filtering, which controls the scale of the analysis (in pixels).
- Returns
- Array An output array containing the calculated accumulation curvature values for each point in the input heightmap.
Example
Result
◆ curvature_gaussian()
Calculates the Gaussian curvature of a heightmap, providing insights into the surface's intrinsic curvature at each point. Gaussian curvature is a fundamental measure of surface curvature, indicating how the surface bends in multiple directions at each point. This metric is often used in geomorphology to understand landform shapes. Usage: Use this function to analyze the overall shape of terrain features, identifying whether regions are saddle-like, dome-like, or basin-like. Useful in studies related to tectonics, erosion patterns, and landform development.
- Parameters
-
z The input array representing the heightmap data (elevation values).
- Returns
- Array An output array containing the Gaussian curvature values, with positive values indicating dome-like shapes and negative values indicating saddle shapes.
Example
Result

◆ curvature_horizontal_cross_sectional()
TODO.
- Parameters
-
z The input array representing the heightmap data (elevation values).
- Returns
- Array An output array containing the curvature values.
Example
Result

◆ curvature_horizontal_plan()
TODO.
- Parameters
-
z The input array representing the heightmap data (elevation values).
- Returns
- Array An output array containing the curvature values.
Example
Result

◆ curvature_horizontal_tangential()
TODO.
- Parameters
-
z The input array representing the heightmap data (elevation values).
- Returns
- Array An output array containing the curvature values.
Example
Result

◆ curvature_mean()
Computes the mean curvature of a heightmap, indicating the average curvature at each point on the surface. Mean curvature is another critical metric in geomorphology, representing the average bending of the surface. This measure is useful in understanding terrain smoothness and can help identify areas of potential erosion or deposition. Usage: Apply this function to detect areas prone to erosion or sediment deposition. Useful in landscape evolution models and in analyzing the stability of slopes.
- Parameters
-
z The input array representing the heightmap data (elevation values).
- Returns
- Array An output array containing the mean curvature values, where positive values indicate convex regions and negative values indicate concave regions.
Example
Result

◆ curvature_ring()
Ring curvature is a second-order derivative of the elevation surface. It describes how the surface bends along a ring-like shape, often computed from the principal curvatures. Positive Values: Indicate convex surfaces where flow disperses (ridges, hilltops). Negative Values: Indicate concave surfaces where flow converges (valleys, depressions).
- Parameters
-
z The input array representing the heightmap data (elevation values).
- Returns
- Array An output array containing the curvature values.
Example
Result

◆ curvature_rotor()
Rotor curvature, also called flow line curvature, describes how the curvature of a terrain surface influences the acceleration or deceleration of flow (e.g., water, debris, or air) along the direction of maximum slope. Positive values: Flow is decelerating (convex-up terrain, such as ridges or crests). Negative values: Flow is accelerating (concave-down terrain, such as valleys or channels). Zero values: Flow moves in a linear, constant-slope manner.
- Parameters
-
z The input array representing the heightmap data (elevation values).
- Returns
- Array An output array containing the curvature values.
Example
Result

◆ curvature_vertical_longitudinal()
TODO.
- Parameters
-
z The input array representing the heightmap data (elevation values).
- Returns
- Array An output array containing the curvature values.
Example
Result

◆ curvature_vertical_profile()
TODO.
- Parameters
-
z The input array representing the heightmap data (elevation values).
- Returns
- Array An output array containing the curvature values.
Example
Result

◆ shape_index()
Computes the Shape Index (SI) of the terrain, quantifying landform complexity based on curvature. The Shape Index is a metric used to describe the shape of landforms, particularly in digital elevation models (DEMs). It differentiates between convex (e.g., hilltops), concave (e.g., valleys), and flat surfaces. Usage: Use this function to classify terrain into different morphological types, which can be important in land use planning and environmental studies. Useful in landscape ecology and in understanding geomorphological processes.
- Parameters
-
z The input array representing the heightmap data (elevation values). ir The radius used for pre-filtering, which controls the scale of the analysis (in pixels).
- Returns
- Array An output array containing Shape Index values, where values above 0.5 indicate convex shapes, and values below 0.5 indicate concave shapes.
Example
Result

◆ level_set_curvature()
Computes a signed level-set curvature.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. prefilter_ir Optional smoothing radius for curvature evaluation.
- Returns
- Signed curvature.
◆ unsphericity()
Calculates the unsphericity of a surface, indicating how much the terrain deviates from a perfect spherical shape. Unsphericity is a measure used to understand the degree of asymmetry in terrain surfaces. It quantifies how much a surface deviates from being perfectly spherical or symmetrical, which can be critical in various geomorphological analyses. Usage: Use this function to identify areas of terrain that significantly deviate from a spherical shape, which may indicate unique geological formations or erosion patterns. Helpful in identifying and analyzing landforms that are not perfectly round or symmetrical, such as irregular hills or basins.
- Parameters
-
z The input array representing the heightmap data (elevation values). ir The radius used for pre-filtering, controlling the scale of analysis (in pixels).
- Returns
- Array An output array containing unsphericity values, where values greater than 0.5 indicate convex regions (e.g., peaks) and values less than 0.5 indicate concave regions (e.g., valleys).
Example
Result

◆ compute_curvature_gradients()
| void hmap::compute_curvature_gradients | ( | const Array & | z, |
| Array & | p, | ||
| Array & | q, | ||
| Array & | r, | ||
| Array & | s, | ||
| Array & | t | ||
| ) |
◆ compute_curvature_h()
◆ compute_curvature_k()
| Array hmap::compute_curvature_k | ( | const Array & | p, |
| const Array & | q, | ||
| const Array & | r, | ||
| const Array & | s, | ||
| const Array & | t | ||
| ) |
◆ assert_almost_equal()
| bool hmap::assert_almost_equal | ( | const Array & | a, |
| const Array & | b, | ||
| float | tolerance, | ||
| const std::string & | fname = "", |
||
| AssertResults * | p_results = nullptr |
||
| ) |
◆ get_erosion_profile_function()
| std::function< float(float)> hmap::get_erosion_profile_function | ( | const ErosionProfile & | erosion_profile, |
| float | delta, | ||
| float & | profile_avg | ||
| ) |
◆ coastal_erosion_diffusion()
| void hmap::coastal_erosion_diffusion | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array & | water_depth, | ||
| float | additional_depth, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| Array * | p_water_mask = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Simulates terrain diffusion due to coastal erosion.
This function applies an iterative coastal erosion diffusion process on a terrain elevation array (z), taking into account the presence and depth of water. The erosion model smooths the terrain near shorelines while maintaining constant water-surface height.
At each iteration:
- A local water mask is computed using
water_mask(water_depth, z, additional_depth). - The terrain elevations are smoothed (diffused) using a masked Laplacian filter, applied only near the water boundary.
- The water depth is adjusted to preserve the total water surface height (i.e.,
z + water_depthremains constant).
This results in a realistic simulation of coastal erosion processes where the terrain near the waterline is progressively smoothed and redistributed.
- Parameters
-
z Reference to the terrain elevation array (modified in place). water_depth Reference to the array representing water depth values (modified to preserve water surface level). additional_depth Additional virtual water depth used to estimate the influence region of the shoreline during mask computation. iterations Number of erosion–diffusion iterations to apply. p_water_mask Optional output pointer. If non-null, it receives the last computed water mask used during the final iteration.
Example
Result
◆ coastal_erosion_profile() [1/2]
| void hmap::coastal_erosion_profile | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array & | water_depth, | ||
| float | shore_ground_extent, | ||
| float | shore_water_extent, | ||
| float | slope_shore = 0.5f, |
||
| float | slope_shore_water = 0.5f, |
||
| float | scarp_extent_ratio = 0.5f, |
||
| bool | apply_post_filter = true, |
||
| Array * | p_shore_mask = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Applies a coastal erosion profile to a terrain elevation field.
This function modifies the elevation array z by carving a coastal profile at the interface between ground and water. It uses distance transforms both from ground regions and from water regions to determine how far each point is from the shoreline. According to this distance, the function applies:
- A ground-side shore slope with an optional scarp transition.
- A water-side underwater slope ensuring continuity with the ground slope.
- An optional post-filtering step (Laplace smoothing) restricted to the shoreline region.
Water depth is adjusted after filtering to preserve the original water surface height.
Optionally, a shoreline mask can be returned describing the region influenced by the coastal transformation.
- Parameters
-
z Array of terrain elevations. Modified in-place. water_depth Array of water depths. Modified to preserve water surface height after terrain changes. shore_ground_extent Horizontal extent (in grid units) over which the ground-side shore profile is applied. shore_water_extent Horizontal extent (in grid units) over which the underwater profile is applied. slope_shore Ground-side slope magnitude of the coastal profile. Expressed in elevation units per domain width. slope_shore_water Water-side slope magnitude of the underwater profile. Expressed similarly to slope_shore.scarp_extent_ratio Ratio defining the relative extent of the scarp region. A value in [0,1]: - 0 → no scarp, only slope
- 1 → all scarp
apply_post_filter If true, applies Laplacian smoothing to zrestricted to shoreline areas.p_shore_mask Optional output pointer. If non-null, receives the shoreline mask (values in [0,1]) indicating where the coastal transformation was applied.
Example
Result
◆ coastal_erosion_profile() [2/2]
| void hmap::coastal_erosion_profile | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| Array & | water_depth, | ||
| float | shore_ground_extent, | ||
| float | shore_water_extent, | ||
| float | slope_shore = 0.5f, |
||
| float | slope_shore_water = 0.5f, |
||
| float | scarp_extent_ratio = 0.5f, |
||
| bool | apply_post_filter = true, |
||
| Array * | p_shore_mask = nullptr |
||
| ) |
◆ depression_filling()
Fill the depressions of the heightmap using the Planchon-Darboux algorithm.
Fill heightmap depressions to ensure that every cell can be connected to the boundaries following a downward slope [Planchon2002].
- Parameters
-
z Input array. iterations Number of iterations. epsilon
Example
Result
◆ depression_filling_priority_flood()
| void hmap::depression_filling_priority_flood | ( | Array & | z | ) |
◆ erosion_maps()
| void hmap::erosion_maps | ( | Array & | z_before, |
| Array & | z_after, | ||
| Array & | erosion_map, | ||
| Array & | deposition_map, | ||
| float | tolerance = 0.f |
||
| ) |
- Parameters
-
z_before Input array (before erosion). z_after Input array (after erosion). erosion_map Erosion map. deposition_map Deposition map. tolerance Tolerance for erosion / deposition definition.
Example
Result
◆ hydraulic_algebric() [1/2]
| void hmap::hydraulic_algebric | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | talus_ref, | ||
| int | ir, | ||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_erosion_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| float | c_erosion = 0.05f, |
||
| float | c_deposition = 0.05f, |
||
| int | iterations = 1 |
||
| ) |
Apply an algerbic formula based on the local gradient to perform erosion/deposition.
- Parameters
-
z Input array. p_mask Intensity mask, expected in [0, 1] (applied as a post-processing). talus_ref Reference talus. ir Smoothing prefilter radius. p_bedrock Reference to the bedrock heightmap. p_erosion_map[out] Reference to the erosion map, provided as an output field. p_deposition_map [out] Reference to the deposition map, provided as an output field. c_erosion Erosion coefficient. c_deposition Deposition coefficient. iterations Number of iterations.
Example
Result
◆ hydraulic_algebric() [2/2]
| void hmap::hydraulic_algebric | ( | Array & | z, |
| float | talus_ref, | ||
| int | ir, | ||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_erosion_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| float | c_erosion = 0.05f, |
||
| float | c_deposition = 0.05f, |
||
| int | iterations = 1 |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ hydraulic_benes() [1/2]
| void hmap::hydraulic_benes | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| int | iterations = 50, |
||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_moisture_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_erosion_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| float | c_capacity = 40.f, |
||
| float | c_erosion = 0.2f, |
||
| float | c_deposition = 0.8f, |
||
| float | water_level = 0.005f, |
||
| float | evap_rate = 0.01f, |
||
| float | rain_rate = 0.5f |
||
| ) |
Apply cell-based hydraulic erosion/deposition based on Benes et al. procedure.
See [Benes2002] and [Olsen2004].
- Parameters
-
z Input array. p_mask Intensity mask, expected in [0, 1] (applied as a post-processing). iterations Number of iterations. p_bedrock Reference to the bedrock heightmap. p_moisture_map Reference to the moisture map (quantity of rain), expected to be in [0, 1]. p_erosion_map[out] Reference to the erosion map, provided as an output field. p_deposition_map [out] Reference to the deposition map, provided as an output field. c_capacity Sediment capacity. c_deposition Deposition coefficient. c_erosion Erosion coefficient. water_level Water level. evap_rate Water evaporation rate. rain_rate Rain relaxation rate.
Example
Result
◆ hydraulic_benes() [2/2]
| void hmap::hydraulic_benes | ( | Array & | z, |
| int | iterations = 50, |
||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_moisture_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_erosion_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| float | c_capacity = 40.f, |
||
| float | c_erosion = 0.2f, |
||
| float | c_deposition = 0.8f, |
||
| float | water_level = 0.005f, |
||
| float | evap_rate = 0.01f, |
||
| float | rain_rate = 0.5f |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ hydraulic_blur()
Apply cell-based hydraulic erosion using a nonlinear diffusion model.
- Parameters
-
z Input array. radius Gaussian filter radius (with respect to a unit domain). vmax Maximum elevation for the details. k_smoothing Smoothing factor, if any.
Example
Result
◆ hydraulic_diffusion()
| void hmap::hydraulic_diffusion | ( | Array & | z, |
| float | c_diffusion, | ||
| float | talus, | ||
| int | iterations | ||
| ) |
Apply cell-based hydraulic erosion using a nonlinear diffusion model.
See [Roering2001].
- Parameters
-
z Input array. c_diffusion Diffusion coefficient. talus Reference talus (must be higher than the maximum talus of the map). iterations Number of iterations.
Example
Result
◆ hydraulic_musgrave() [1/2]
| void hmap::hydraulic_musgrave | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array & | moisture_map, | ||
| int | iterations = 100, |
||
| float | c_capacity = 1.f, |
||
| float | c_erosion = 0.1f, |
||
| float | c_deposition = 0.1f, |
||
| float | water_level = 0.01f, |
||
| float | evap_rate = 0.01f |
||
| ) |
Apply cell-based hydraulic erosion/deposition of Musgrave et al. (1989).
A simple grid-based erosion technique was published by Musgrave, Kolb, and Mace in 1989 [Musgrave1989].
- Parameters
-
z Input array. moisture_map Moisture map (quantity of rain), expected to be in [0, 1]. iterations Number of iterations. c_capacity Sediment capacity. c_deposition Deposition coefficient. c_erosion Erosion coefficient. water_level Water level. evap_rate Water evaporation rate.
Example
Result
◆ hydraulic_musgrave() [2/2]
| void hmap::hydraulic_musgrave | ( | Array & | z, |
| int | iterations = 100, |
||
| float | c_capacity = 1.f, |
||
| float | c_erosion = 0.1f, |
||
| float | c_deposition = 0.1f, |
||
| float | water_level = 0.01f, |
||
| float | evap_rate = 0.01f |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ hydraulic_particle() [1/2]
| void hmap::hydraulic_particle | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| int | nparticles, | ||
| int | seed, | ||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_moisture_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_erosion_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| float | c_capacity = 10.f, |
||
| float | c_erosion = 0.05f, |
||
| float | c_deposition = 0.05f, |
||
| float | c_inertia = 0.3f, |
||
| float | drag_rate = 0.001f, |
||
| float | evap_rate = 0.001f, |
||
| bool | post_filtering = false |
||
| ) |
Apply hydraulic erosion using a particle based procedure.
Adapted from [Beyer2015] and [Hjulstroem1935].
- Parameters
-
z Input array. p_mask Intensity mask, expected in [0, 1] (applied as a post-processing). nparticles Number of particles. seed Random seed number. p_bedrock Reference to the bedrock heightmap. p_moisture_map Reference to the moisture map (quantity of rain), expected to be in [0, 1]. p_erosion_map[out] Reference to the erosion map, provided as an output field. p_deposition_map [out] Reference to the deposition map, provided as an output field. c_capacity Sediment capacity. c_deposition Deposition coefficient. c_erosion Erosion coefficient. drag_rate Drag rate. evap_rate Particle evaporation rate.
Example
Result
◆ hydraulic_particle() [2/2]
| void hmap::hydraulic_particle | ( | Array & | z, |
| int | nparticles, | ||
| int | seed, | ||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_moisture_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_erosion_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| float | c_capacity = 10.f, |
||
| float | c_erosion = 0.05f, |
||
| float | c_deposition = 0.05f, |
||
| float | c_inertia = 0.3f, |
||
| float | drag_rate = 0.001f, |
||
| float | evap_rate = 0.001f, |
||
| bool | post_filtering = false |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ hydraulic_particle_multiscale()
| void hmap::hydraulic_particle_multiscale | ( | Array & | z, |
| float | particle_density, | ||
| int | seed, | ||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_moisture_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_erosion_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| float | c_capacity = 10.f, |
||
| float | c_erosion = 0.05f, |
||
| float | c_deposition = 0.01f, |
||
| float | c_inertia = 0.3f, |
||
| float | drag_rate = 0.01f, |
||
| float | evap_rate = 0.001f, |
||
| int | pyramid_finest_level = 0 |
||
| ) |
Apply hydraulic erosion using a particle based procedure, using a pyramid decomposition to allow a multiscale approach.
- Parameters
-
z Input array. particle_density Particles density (with respect to the number of cells of the input array). seed Random seed number. p_bedrock Reference to the bedrock heightmap. p_moisture_map Reference to the moisture map (quantity of rain), expected to be in [0, 1]. p_erosion_map[out] Reference to the erosion map, provided as an output field. p_deposition_map [out] Reference to the deposition map, provided as an output field. c_capacity Sediment capacity. c_deposition Deposition coefficient. c_erosion Erosion coefficient. drag_rate Drag rate. evap_rate Particle evaporation rate. pyramid_finest_level First level at which the erosion is applied (default is 0, meaning it is applied to the current resolution, the 0th pyramid level, and then to the coarser pyramid levels, if set to 1 it starts with the first pyramid level and so on).
Example
Result
◆ hydraulic_procedural()
| void hmap::hydraulic_procedural | ( | Array & | z, |
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | ridge_wavelength, | ||
| float | ridge_scaling = 0.1f, |
||
| ErosionProfile | erosion_profile = ErosionProfile::TRIANGLE_SMOOTH, |
||
| float | delta = 0.02f, |
||
| float | noise_ratio = 0.2f, |
||
| int | prefilter_ir = -1, |
||
| float | density_factor = 1.f, |
||
| float | kernel_width_ratio = 2.f, |
||
| float | phase_smoothing = 2.f, |
||
| float | phase_noise_amp = M_PI, |
||
| bool | reverse_phase = false, |
||
| bool | rotate90 = false, |
||
| bool | use_default_mask = true, |
||
| float | talus_mask = 0.f, |
||
| Array * | p_mask = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_ridge_mask = nullptr, |
||
| float | vmin = 0.f, |
||
| float | vmax = -1.f |
||
| ) |
Generates a procedurally eroded terrain using hydraulic erosion and ridge generation techniques.
This function applies a combination of hydraulic erosion and ridge formation to modify a heightmap, leveraging parameters such as erosion profiles, ridge scaling, and noise characteristics. It also supports custom or default masks to influence the erosion process.
- Parameters
-
[out] z The heightmap to be modified, represented as a 2D array. [in] seed Random seed for procedural generation. [in] ridge_wavelength Wavelength of the ridge structures in the heightmap. [in] ridge_scaling Scaling factor for the ridge height. [in] erosion_profile The profile that defines the erosion curve behavior. [in] delta Parameter controlling the erosion intensity. [in] noise_ratio Ratio of noise added to the ridge crest lines. [in] prefilter_ir Kernel radius for pre-smoothing the heightmap. If negative, a default value is computed. [in] density_factor Factor influencing the density of the ridges. [in] kernel_width_ratio Ratio defining the width of the ridge generation kernel. [in] phase_smoothing Smoothing factor for the phase field used in ridge generation. [in] use_default_mask Whether to use a default mask for erosion if no mask is provided. [in] talus_mask Threshold for default mask slope to identify regions prone to erosion. [in] p_mask Optional pointer to a custom mask array to influence the erosion process. [out] p_ridge_mask Optional pointer to store the ridge mask resulting from the operation. [in] vmin Minimum elevation value. If set to a sentinel value (vmax < vmin), it is calculated from the heightmap. [in] vmax Maximum elevation value. If set to a sentinel value (vmax < vmin), it is calculated from the heightmap.
Example
Result
◆ hydraulic_spl()
| void hmap::hydraulic_spl | ( | Array & | z | ) |
◆ hydraulic_stream() [1/2]
| void hmap::hydraulic_stream | ( | Array & | z, |
| float | c_erosion, | ||
| float | talus_ref, | ||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_moisture_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_erosion_map = nullptr, |
||
| int | ir = 1, |
||
| float | clipping_ratio = 10.f |
||
| ) |
Apply hydraulic erosion based on a flow accumulation map.
- Parameters
-
z Input array. p_mask Intensity mask, expected in [0, 1] (applied as a post-processing). c_erosion Erosion coefficient. talus_ref Reference talus used to localy define the flow-partition exponent (small values of talus_refwill lead to thinner flow streams, seeflow_accumulation_dinf).p_bedrock Lower elevation limit. p_moisture_map Reference to the moisture map (quantity of rain), expected to be in [0, 1]. p_erosion_map[out] Reference to the erosion map, provided as an output field. ir Kernel radius. If ir > 1, a cone kernel is used to carv channel flow erosion.clipping_ratio Flow accumulation clipping ratio.
Example
Result

◆ hydraulic_stream() [2/2]
| void hmap::hydraulic_stream | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | c_erosion, | ||
| float | talus_ref, | ||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_moisture_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_erosion_map = nullptr, |
||
| int | ir = 1, |
||
| float | clipping_ratio = 10.f |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ hydraulic_stream_log() [1/2]
| void hmap::hydraulic_stream_log | ( | Array & | z, |
| float | c_erosion, | ||
| float | talus_ref, | ||
| int | deposition_ir = 32, |
||
| float | deposition_scale_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| float | gradient_power = 0.8f, |
||
| float | gradient_scaling_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| int | gradient_prefilter_ir = 16, |
||
| float | saturation_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_moisture_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_erosion_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_flow_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Apply hydraulic erosion based on a flow accumulation map, alternative formulation.
- Parameters
-
z Input array representing the terrain elevation. c_erosion Erosion coefficient controlling the intensity of erosion. talus_ref Reference talus used to locally define the flow-partition exponent. Small values lead to thinner flow streams (see flow_accumulation_dinf).deposition_ir Kernel radius for sediment deposition. If greater than 1, a smoothing effect is applied. deposition_scale_ratio Scaling factor for sediment deposition. gradient_power Exponent applied to the terrain gradient to control erosion intensity. gradient_scaling_ratio Scaling factor for gradient-based erosion. gradient_prefilter_ir Kernel radius for pre-filtering the terrain gradient. saturation_ratio Ratio controlling the water saturation threshold for erosion processes. p_bedrock Pointer to an optional lower elevation limit. p_moisture_map Pointer to the moisture map (rainfall quantity), expected to be in [0, 1]. p_erosion_map[out] Pointer to the erosion map, provided as an output field. p_flow_map[out] Pointer to the flow accumulation map, provided as an output field. ir Kernel radius. If ir > 1, a cone kernel is used to carve channel flow erosion.
Example
Result


◆ hydraulic_stream_log() [2/2]
| void hmap::hydraulic_stream_log | ( | Array & | z, |
| float | c_erosion, | ||
| float | talus_ref, | ||
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| int | deposition_ir = 32, |
||
| float | deposition_scale_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| float | gradient_power = 0.8f, |
||
| float | gradient_scaling_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| int | gradient_prefilter_ir = 16, |
||
| float | saturation_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_moisture_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_erosion_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_flow_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ hydraulic_stream_upscale_amplification() [1/2]
| void hmap::hydraulic_stream_upscale_amplification | ( | Array & | z, |
| float | c_erosion, | ||
| float | talus_ref, | ||
| int | upscaling_levels = 1, |
||
| float | persistence = 1.f, |
||
| int | ir = 1, |
||
| float | clipping_ratio = 10.f |
||
| ) |
Applies hydraulic erosion with upscaling amplification.
This function progressively upscales the input array z by powers of 2 and applies hydraulic erosion based on flow accumulation at each level of upscaling. After all upscaling levels are processed, the array is resampled back to its original resolution using bilinear interpolation.
- Parameters
-
z Input array representing elevation data. c_erosion Erosion coefficient. talus_ref Reference talus used to locally define the flow-partition exponent. Smaller values lead to thinner flow streams. upscaling_levels Number of upscaling levels to apply. The function will resample the array at each level. persistence A scaling factor applied at each level to adjust the impact of the unary operation. Higher persistence values will amplify the effects at each level. ir Kernel radius. If ir > 1, a cone kernel is used to carve channel flow erosion.clipping_ratio Flow accumulation clipping ratio.
- Note
- The function first applies upscaling using bicubic resampling, performs hydraulic erosion at each level, and finally resamples the array back to its initial resolution using bilinear interpolation.
Example
Result
◆ hydraulic_stream_upscale_amplification() [2/2]
| void hmap::hydraulic_stream_upscale_amplification | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | c_erosion, | ||
| float | talus_ref, | ||
| int | upscaling_levels = 1, |
||
| float | persistence = 1.f, |
||
| int | ir = 1, |
||
| float | clipping_ratio = 10.f |
||
| ) |
Applies hydraulic erosion with upscaling amplification, with a post-processing intensity mask.
Similar to the overloaded version, this function progressively upscales the input array z and applies hydraulic erosion. Additionally, an intensity mask p_mask is applied as a post-processing step.
- Parameters
-
z Input array representing elevation data. p_mask Intensity mask, expected in [0, 1], which is applied as a post-processing step. c_erosion Erosion coefficient. talus_ref Reference talus used to locally define the flow-partition exponent. Smaller values lead to thinner flow streams. upscaling_levels Number of upscaling levels to apply. The function will resample the array at each level. persistence A scaling factor applied at each level to adjust the impact of the unary operation. Higher persistence values will amplify the effects at each level. ir Kernel radius. If ir > 1, a cone kernel is used to carve channel flow erosion.clipping_ratio Flow accumulation clipping ratio.
- Note
- This version of the function applies an additional intensity mask as part of the upscaling amplification process.
Example
Result

This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ hydraulic_vpipes() [1/2]
| void hmap::hydraulic_vpipes | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| int | iterations, | ||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_moisture_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_erosion_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| float | water_height = 0.1f, |
||
| float | c_capacity = 0.1f, |
||
| float | c_erosion = 0.05f, |
||
| float | c_deposition = 0.05f, |
||
| float | rain_rate = 0.f, |
||
| float | evap_rate = 0.01f |
||
| ) |
Apply hydraulic erosion using the 'virtual pipes' algorithm.
See [Chiba1998], [Isheden2022], [Mei2007] and [Stava2008].
- Parameters
-
z Input array. p_mask Intensity mask, expected in [0, 1] (applied as a iterations Number of iterations. p_bedrock Lower elevation limit. p_moisture_map Reference to the moisture map (quantity of rain), expected to be in [0, 1]. p_erosion_map[out] Reference to the erosion map, provided as an output field. p_deposition_map [out] Reference to the deposition map, provided as an output field. water_height Water height. c_capacity Sediment capacity. c_deposition Deposition coefficient. c_erosion Erosion coefficient. rain_rate Rain rate. evap_rate Particle evaporation rate.
Example
Result
◆ hydraulic_vpipes() [2/2]
| void hmap::hydraulic_vpipes | ( | Array & | z, |
| int | iterations, | ||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_moisture_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_erosion_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| float | water_height = 0.1f, |
||
| float | c_capacity = 0.1f, |
||
| float | c_erosion = 0.05f, |
||
| float | c_deposition = 0.05f, |
||
| float | rain_rate = 0.f, |
||
| float | evap_rate = 0.01f |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ sediment_deposition() [1/2]
| void hmap::sediment_deposition | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| float | max_deposition = 0.01, |
||
| int | iterations = 5, |
||
| int | thermal_subiterations = 10 |
||
| ) |
Perform sediment deposition combined with thermal erosion.
- Todo:
- deposition map
- Parameters
-
z Input array. p_mask Intensity mask, expected in [0, 1] (applied as a post-processing). talus Talus limit. p_deposition_map [out] Reference to the deposition map, provided as an output field. max_deposition Maximum height of sediment deposition. iterations Number of iterations. thermal_erosion_subiterations Number of thermal erosion iterations for each pass.
Example
Result
◆ sediment_deposition() [2/2]
| void hmap::sediment_deposition | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| float | max_deposition = 0.01, |
||
| int | iterations = 5, |
||
| int | thermal_subiterations = 10 |
||
| ) |
◆ sediment_deposition_particle() [1/2]
| void hmap::sediment_deposition_particle | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| int | nparticles, | ||
| int | ir, | ||
| int | seed = 1, |
||
| Array * | p_spawning_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| float | particle_initial_sediment = 0.1f, |
||
| float | deposition_velocity_limit = 0.01f, |
||
| float | drag_rate = 0.001f |
||
| ) |
- Parameters
-
z Input array. p_mask Intensity mask, expected in [0, 1] (applied as a post-processing). nparticles Number of particles. ir Particle deposition radius. seed Random seed number. p_spawning_map Reference to the particle spawning density map. p_deposition_map Reference to the deposition map (output). particle_initial_sediment Initial sediment amount carried out by the particles. deposition_velocity_limit Deposition at which the deposition occurs. drag_rate Particle drag rate.
Example
Result
◆ sediment_deposition_particle() [2/2]
| void hmap::sediment_deposition_particle | ( | Array & | z, |
| int | nparticles, | ||
| int | ir, | ||
| int | seed = 1, |
||
| Array * | p_spawning_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| float | particle_initial_sediment = 0.1f, |
||
| float | deposition_velocity_limit = 0.01f, |
||
| float | drag_rate = 0.001f |
||
| ) |
◆ sediment_layer()
| void hmap::sediment_layer | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array & | talus_layer, | ||
| const Array & | talus_upper_limit, | ||
| int | iterations, | ||
| bool | apply_post_filter = true, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
◆ stratify() [1/4]
| void hmap::stratify | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| std::vector< float > | hs, | ||
| std::vector< float > | gamma, | ||
| Array * | p_noise = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Stratify the heightmap by creating a series of layers with elevations corrected by a gamma factor.
- Parameters
-
z Input array. p_mask Intensity mask, expected in [0, 1] (applied as a post-processing). hs Layer elevations. For 'n' layers, 'n + 1' values must be provided. gamma Layer gamma correction factors, 'n' values.
- See also
- gamma_correction.
Example
Result
◆ stratify() [2/4]
| void hmap::stratify | ( | Array & | z, |
| std::vector< float > | hs, | ||
| std::vector< float > | gamma, | ||
| Array * | p_noise = nullptr |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ stratify() [3/4]
| void hmap::stratify | ( | Array & | z, |
| std::vector< float > | hs, | ||
| float | gamma = 0.5f, |
||
| Array * | p_noise = nullptr |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ stratify() [4/4]
| void hmap::stratify | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array & | partition, | ||
| int | nstrata, | ||
| float | strata_noise, | ||
| float | gamma, | ||
| float | gamma_noise, | ||
| int | npartitions, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | mixing_gain_factor = 1.f, |
||
| Array * | p_noise = nullptr, |
||
| float | vmin = 1.f, |
||
| float | vmax = 0.f |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ stratify_multiscale()
| void hmap::stratify_multiscale | ( | Array & | z, |
| float | zmin, | ||
| float | zmax, | ||
| std::vector< int > | n_strata, | ||
| std::vector< float > | strata_noise, | ||
| std::vector< float > | gamma_list, | ||
| std::vector< float > | gamma_noise, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| Array * | p_mask = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_noise = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Stratify the heightmap by creating a multiscale series of layers with elevations corrected by a gamma factor.
- Parameters
-
z Input array. zmin Minimum elevation for the strata zmax Maximum elevation for the strata n_strata Number of strata for each stratification iteration. strata_noise Elevation relative noise. gamma_list Gamma value for each stratification iteration. gamma_noise Gamma relative noise. seed Random seed number. p_mask Intensity mask, expected in [0, 1] (applied as a post-processing). p_noise Local elevation noise.
Example
Result
◆ stratify_oblique() [1/2]
| void hmap::stratify_oblique | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| std::vector< float > | hs, | ||
| std::vector< float > | gamma, | ||
| float | talus, | ||
| float | angle, | ||
| Array * | p_noise = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Stratify the heightmap by creating a series of oblique layers with elevations corrected by a gamma factor.
- Parameters
-
z Input array. p_mask Intensity mask, expected in [0, 1] (applied as a post-processing). hs Layer elevations. For 'n' layers, 'n + 1' values must be provided. gamma Layer gamma correction factors, 'n' values. talus Layer talus value (slope). angle Slope orientation (in degrees). p_noise Local elevation noise.
Example
Result

◆ stratify_oblique() [2/2]
| void hmap::stratify_oblique | ( | Array & | z, |
| std::vector< float > | hs, | ||
| std::vector< float > | gamma, | ||
| float | talus, | ||
| float | angle, | ||
| Array * | p_noise = nullptr |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ thermal() [1/3]
| void hmap::thermal | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Apply thermal weathering erosion.
Based on https://www.shadertoy.com/view/XtKSWh
- Parameters
-
z Input array. p_mask Filter mask, expected in [0, 1]. talus Talus limit. p_bedrock Lower elevation limit. p_deposition_map [out] Reference to the deposition map, provided as an output field. iterations Number of iterations.
Example
Result
◆ thermal() [2/3]
| void hmap::thermal | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
◆ thermal() [3/3]
| void hmap::thermal | ( | Array & | z, |
| float | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ thermal_auto_bedrock() [1/3]
| void hmap::thermal_auto_bedrock | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Apply thermal weathering erosion with automatic determination of the bedrock.
- Todo:
more comprehensive documentation on auto-bedrock algo.
fix hard-coded parameters.
- See also
thermal
- Parameters
-
z Input array. talus Local talus limit. iterations Number of iterations. p_deposition_map [out] Reference to the deposition map, provided as an output field.
Example
Result
◆ thermal_auto_bedrock() [2/3]
| void hmap::thermal_auto_bedrock | ( | Array & | z, |
| float | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ thermal_auto_bedrock() [3/3]
| void hmap::thermal_auto_bedrock | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ thermal_flatten() [1/2]
| void hmap::thermal_flatten | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| const Array & | bedrock, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| int | post_filter_ir = 1 |
||
| ) |
Apply modified thermal weathering of Olsen.
Based on the algorithm of Olsen [Olsen2004], which "causes slopes steeper than the talus threshold to remain unaffected while flatter areas are levelled out".
- Parameters
-
z Input array. talus Local talus limit. iterations Number of iterations.
Example
Result
◆ thermal_flatten() [2/2]
| void hmap::thermal_flatten | ( | Array & | z, |
| float | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| int | post_filter_ir = 1 |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ thermal_olsen()
| void hmap::thermal_olsen | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Apply thermal weathering erosion.
Based on averaging over first neighbors, see [Olsen2004]. Refer to [Musgrave1989] for the original formulation.
Thermal erosion refers to the process in which surface sediment weakens due to temperature and detaches, falling down the slopes of the terrain until a resting place is reached, where smooth plateaus tend to form [Musgrave1989].
- Parameters
-
z Input array. p_mask Filter mask, expected in [0, 1]. talus Talus limit. p_bedrock Lower elevation limit. p_deposition_map [out] Reference to the deposition map, provided as an output field. iterations Number of iterations.
◆ thermal_rib()
Apply thermal erosion using a 'rib' algorithm (taken from Geomorph).
- Parameters
-
z Input heightmap. iterations Number of iterations. p_bedrock Lower elevation limit.
Example
Result
◆ thermal_schott() [1/4]
| void hmap::thermal_schott | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| float | intensity = 0.001f |
||
| ) |
Applies the thermal erosion process to an array of elevation values.
This function simulates thermal erosion by modifying the elevation values in the array z. It compares the slope between each cell and its neighbors with a specified threshold (talus). If the slope exceeds the threshold, material is considered to move from higher to lower cells, resulting in a smoother terrain.
- Parameters
-
z Reference to the array of elevation values that will be modified. talus Array of threshold slope values for each cell, representing stability criteria. iterations Number of erosion iterations to apply. intensity Intensity factor controlling the amount of change per iteration.
Example
Result
◆ thermal_schott() [2/4]
| void hmap::thermal_schott | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| float | intensity = 0.001f |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ thermal_schott() [3/4]
| void hmap::thermal_schott | ( | Array & | z, |
| const float | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| float | intensity = 0.001f |
||
| ) |
Applies the thermal erosion process with a uniform slope threshold.
This overload of thermal_schott applies thermal erosion with a uniform threshold value. It generates an internal talus map using the specified constant talus value and applies the erosion process in the same manner as the other overload.
- Parameters
-
z Reference to the array of elevation values that will be modified. talus Constant threshold slope value used for all cells. iterations Number of erosion iterations to apply. intensity Intensity factor controlling the amount of change per iteration.
Example
Result

◆ thermal_schott() [4/4]
| void hmap::thermal_schott | ( | Array & | z, |
| const float | talus, | ||
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| float | intensity = 0.001f |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ watershed_ridge() [1/2]
| Array hmap::watershed_ridge | ( | const Array & | z, |
| float | amplitude = 0.5f, |
||
| int | ir = 1, |
||
| float | edt_exponent = 0.5f, |
||
| FlowDirectionMethod | fd_method = FlowDirectionMethod::FDM_D8 |
||
| ) |
Carves watershed ridges using basin-wise distance transforms.
Drainage basins are computed using D8 flow routing. For each basin, a distance transform to the basin boundary is evaluated and used to lower elevations near watershed divides, forming ridge lines.
- Parameters
-
z Input elevation field. amplitude Ridge carving strength. ir Smoothing. edt_exponent Exponent applied to the distance field to control ridge sharpness.
- Returns
- Elevation field with watershed ridges emphasized.
Example
Result
◆ watershed_ridge() [2/2]
| Array hmap::watershed_ridge | ( | const Array & | z, |
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | amplitude = 0.5f, |
||
| int | ir = 1, |
||
| float | edt_exponent = 0.5f, |
||
| FlowDirectionMethod | fd_method = FlowDirectionMethod::FDM_D8 |
||
| ) |
◆ export_asset()
| bool hmap::export_asset | ( | const std::string & | fname, |
| const Array & | array, | ||
| MeshType | mesh_type = MeshType::TRI, |
||
| AssetExportFormat | export_format = AssetExportFormat::GLB2, |
||
| float | elevation_scaling = 0.2f, |
||
| const std::string & | texture_fname = "", |
||
| const std::string & | normal_map_fname = "", |
||
| float | max_error = 5e-4f |
||
| ) |
Exports a heightmap to various 3D file formats.
This function exports the input heightmap array as a 3D asset in the specified format. The export can include different mesh types, elevation scaling, and optional texture and normal maps. The function supports optimized Delaunay triangulation for mesh generation, with a configurable maximum error.
- Parameters
-
fname The name of the file to which the 3D asset will be exported. array The input heightmap array to be converted into a 3D asset. mesh_type The type of mesh to generate (see MeshType).export_format The format in which to export the asset (see AssetExportFormat).elevation_scaling A scaling factor applied to the elevation values of the heightmap. Default is 0.2f. texture_fname The name of the texture file to be applied to the asset (optional). normal_map_fname The name of the normal map file to be applied to the asset (optional). max_error The maximum allowable error for optimized Delaunay triangulation. Default is 5e-4f.
- Returns
trueif the export is successful,falseotherwise.
◆ export_as_ascii()
| std::string hmap::export_as_ascii | ( | const Array & | array, |
| const glm::ivec2 & | export_shape = {64, 64}, |
||
| const std::string | chars_map = " .:-=+*#%@" |
||
| ) |
Export a 2D array as an ASCII-art string representation.
This function rescales the input array to a given export resolution, remaps its values to the [0,1] range, and then converts each value to a character from a user-provided character map. The characters are arranged row by row to form a textual representation of the array, similar to rendering a heightmap in ASCII.
- Parameters
-
array The input 2D array to be exported. export_shape The desired shape (width, height) of the ASCII output. chars_map A string containing characters ordered from "low" to "high" intensity. For example: " .:-=+*#%@"
- Returns
- A string containing the ASCII-art representation of the array.
- Note
- The function resamples the array using nearest-neighbor interpolation.
- The y-axis is flipped so that higher indices appear lower in the text output.
◆ export_as_cubemap()
| void hmap::export_as_cubemap | ( | const std::string & | fname, |
| const Array & | z, | ||
| int | cubemap_resolution = 128, |
||
| float | overlap = 0.25f, |
||
| int | ir = 16, |
||
| Cmap | cmap = Cmap::GRAY, |
||
| bool | splitted = false, |
||
| Array * | p_cubemap = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Exports a 2D array as a cubemap texture with continuity enforcement and overlapping regions.
This function generates a cubemap texture from the input array z, resamples the data to fit the cubemap resolution with optional overlapping regions, and ensures seamless transitions between the six faces of the cubemap. The cubemap can either be saved as a single texture or split into individual face textures.
- Parameters
-
fname Output file name or base name for the cubemap files. z Input 2D array representing the data to be converted into a cubemap. cubemap_resolution Resolution (width and height) of each individual face of the cubemap. overlap Fraction (0 to 1) of overlap between adjacent faces to ensure smooth transitions. ir Radius parameter for smoothing at triple corners. cmap Colormap to be applied when exporting the textures. splitted If true, exports each face of the cubemap as a separate image; otherwise, exports the entire cubemap as a single texture. p_cubemap Pointer to an optional output array where the final cubemap data will be stored.
The generated cubemap maintains continuity between faces, adjusting values at overlapping regions and corners using smooth transitions. If the splitted flag is set, six individual PNG images are generated for the cubemap faces with appropriate suffixes appended to the base name. Otherwise, the entire cubemap is exported as a single texture file.
Example
Result

◆ export_banner_png()
| void hmap::export_banner_png | ( | const std::string & | fname, |
| const std::vector< Array > & | arrays, | ||
| int | cmap, | ||
| bool | hillshading = false, |
||
| bool | normalize_arrays = false |
||
| ) |
Exports a set of arrays as a banner PNG image file.
This function takes a vector of arrays and exports them as a single banner PNG image. The arrays are displayed side by side in the image, using the specified colormap cmap. Optionally, hillshading can be applied to enhance the visual representation of the data.
- Parameters
-
fname The name of the file to which the banner image will be exported. arrays A vector of arrays to be included in the banner image. cmap An integer representing the colormap to be applied to the arrays. hillshading A boolean flag to activate hillshading for enhanced visual depth. Default is false.
◆ export_normal_map_png()
| void hmap::export_normal_map_png | ( | const std::string & | fname, |
| const Array & | array, | ||
| int | depth = CV_8U |
||
| ) |
Exports the heightmap normal map as an 8-bit PNG file.
This function generates a normal map from the input heightmap array and exports it as an 8-bit PNG image. The normal map can be used in 3D rendering engines to create realistic lighting and shading effects.
- Parameters
-
fname The name of the file to which the normal map will be exported. array The input heightmap array from which the normal map is derived. depth The depth of the PNG image, e.g., CV_8Ufor 8-bit orCV_16Ufor 16-bit. Default isCV_8U.
Example
◆ export_splatmap_png()
| void hmap::export_splatmap_png | ( | const std::string & | fname, |
| const Array * | p_r, | ||
| const Array * | p_g = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_b = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_a = nullptr, |
||
| int | depth = CV_8U |
||
| ) |
Exports four arrays as an RGBA PNG splatmap.
This function combines four input arrays, representing the red (R), green (G), blue (B), and alpha (A) channels, into a single RGBA PNG image. The resulting splatmap can be used in applications like terrain texturing. The PNG image is saved to the specified file name fname. Channels G, B, and A are optional; if not provided, they will default to zero.
- Parameters
-
fname The name of the file to which the RGBA splatmap will be exported. p_r Pointer to the array representing the red (R) channel. p_g Pointer to the array representing the green (G) channel. Default is nullptr.p_b Pointer to the array representing the blue (B) channel. Default is nullptr.p_a Pointer to the array representing the alpha (A) channel. Default is nullptr.depth The depth of the PNG image, e.g., CV_8Ufor 8-bit orCV_16Ufor 16-bit. Default isCV_8U.
Example
Result

◆ export_points_to_ply()
| void hmap::export_points_to_ply | ( | const std::string & | fname, |
| const std::vector< float > & | x, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | y, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | z, | ||
| const std::map< std::string, std::vector< float > > & | custom_fields = {} |
||
| ) |
Exports 3D points with optional custom fields to an ASCII PLY file.
This function writes vertex data (x, y, z) and optional additional per-point attributes to a PLY file in ASCII format. Each key in custom_fields defines a new property in the PLY header, and its associated vector provides per-point values for that property.
- Parameters
-
fname The output file name. x Vector of x coordinates. y Vector of y coordinates. z Vector of z coordinates. custom_fields A map of custom field names to their per-point float values.
Example
◆ export_tiled()
| void hmap::export_tiled | ( | const std::string & | fname_radical, |
| const std::string & | fname_extension, | ||
| const Array & | array, | ||
| const glm::ivec2 & | tiling, | ||
| int | leading_zeros = 0, |
||
| int | depth = CV_8U, |
||
| bool | overlapping_edges = false, |
||
| bool | reverse_tile_y_indexing = false |
||
| ) |
Exports a 2D array as a set of grayscale PNG image tiles.
This function divides a given 2D array into smaller rectangular tiles and saves each tile as a grayscale PNG image file. Tiles are named using a combination of the provided file name radical, tile indices, and file extension.
- Parameters
-
fname_radical Base name (radical) for output image files. fname_extension File extension to use for exported images (e.g., "png"). array The input 2D array to be tiled and exported. tiling A 2D vector specifying the number of tiles in the x and y directions. leading_zeros Number of digits used to pad the tile indices in the filename. depth Bit depth of the output PNG images (commonly 8 or 16). overlapping_edges If true, each tile includes an extra row/column from neighboring tiles (for overlap). reverse_tile_y_indexing If true, Y tile indices are reversed (tile 0 is at the top).
Each tile is extracted using slicing, adjusted for overlap if specified, and then exported as an individual image file named with its tile indices. For example, an output file might be named radical_01_03.png.
Example
◆ read_to_array()
| Array hmap::read_to_array | ( | const std::string & | fname, |
| bool | flip_j = false |
||
| ) |
Reads an image file and converts it to a 2D array.
This function uses the OpenCV imread function to load an image from the specified file. The supported file formats are those recognized by OpenCV's imread function, such as JPEG, PNG, BMP, and others. If the image is in color, it is automatically converted to grayscale using the built-in OpenCV codec converter. This conversion process may introduce artifacts depending on the image's original format and content.
- Parameters
-
fname The name of the image file to be read.
- Returns
- Array A 2D array containing the pixel values of the grayscale image.
◆ write_raw_16bit()
| void hmap::write_raw_16bit | ( | const std::string & | fname, |
| const Array & | array | ||
| ) |
Exports an array to a 16-bit 'raw' file format, commonly used for Unity terrain imports.
This function saves the input array to a file in a 16-bit 'raw' format, which is suitable for importing heightmaps into Unity or other applications that support this format. The array values are converted and written to the file specified by fname.
- Parameters
-
fname The name of the file to which the array will be exported. array The input array containing the data to be exported.
◆ connected_components()
| Array hmap::connected_components | ( | const Array & | array, |
| float | surface_threshold = 0.f, |
||
| float | background_value = 0.f, |
||
| std::vector< float > * | p_surfaces = nullptr, |
||
| std::vector< std::array< float, 2 > > * | p_centroids = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Identifies and labels connected components within a binary or labeled array, with optional filtering by size.
Connected-component labeling is a technique used to identify clusters of connected pixels (or components) in an array. This function can be used in image processing and spatial analysis to isolate regions of interest, such as detecting distinct objects or areas within a heightmap.
Usage
- Use this function to label distinct features within an array, such as individual water bodies, forest patches, or elevation features.
- Apply the surface threshold to filter out small, insignificant components that might be noise or irrelevant.
- Parameters
-
array The input array where connected components are to be identified. surface_threshold The minimum number of pixels a component must have to be retained. Components smaller than this threshold will be removed. The default value is 0 (no filtering). background_value The value used to represent background pixels, which are not part of any component. Default is 0.
- Returns
- Array An array with labeled connected components, where each component is assigned a unique identifier.
Example
Result

◆ geomorphons()
Classifies terrain into geomorphological features based on the geomorphons method.
The geomorphons method classifies each point in a terrain into one of several landform types (e.g., ridge, valley, plain) based on the surrounding topography. This classification is useful for automated landform mapping and terrain analysis.
Usage
- Use this function to automatically categorize terrain into different geomorphological units.
- Useful in large-scale landform mapping and environmental modeling.
- Parameters
-
array The input array representing the terrain elevation data. irmin The minimum radius (in pixels) for considering the surrounding area during classification. irmax The maximum radius (in pixels) for considering the surrounding area during classification. epsilon The slope tolerance that defines 'flat' regions, affecting the classification.
- Returns
- Array An output array with each pixel classified into a geomorphological feature.
Example
Result
◆ kmeans_clustering2()
| Array hmap::kmeans_clustering2 | ( | const Array & | array1, |
| const Array & | array2, | ||
| int | nclusters, | ||
| std::vector< Array > * | p_scoring = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_aggregate_scoring = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec2 | weights = {1.f, 1.f}, |
||
| uint | seed = 1 |
||
| ) |
Performs k-means clustering on two input arrays, grouping similar data points into clusters.
K-means clustering is a popular unsupervised learning algorithm used to partition data into clusters. This function applies k-means clustering to two arrays, which might represent different terrain attributes or environmental variables.
Usage:
- Use this function to identify regions with similar characteristics based on multiple terrain features.
- Useful in ecological modeling, land cover classification, and resource management.
- Parameters
-
[in] array1 The first input array for clustering, typically representing one attribute of the terrain. [in] array2 The second input array for clustering, representing another attribute. [in] nclusters The number of clusters (k) to be formed. [out] p_scoring (optional) A pointer to a vector of arrays where the clustering scores will be stored. Pass nullptr if scoring is not required. [out] p_aggregate_scoring (optional) A pointer to an array where the aggregate score across all clusters will be stored. Pass nullptr if not required. [in] weights A vector of two floats representing the weight given to array1andarray2. The default weights are {1.f, 1.f}.[in] seed A seed value for random number generation, ensuring reproducibility of the clustering results. The default value is 1.
- Returns
- Array An array representing the clustered data, with each pixel assigned to a cluster.
- An Array containing the clustered data resulting from the k-means algorithm.
Example
Result
◆ kmeans_clustering3()
| Array hmap::kmeans_clustering3 | ( | const Array & | array1, |
| const Array & | array2, | ||
| const Array & | array3, | ||
| int | nclusters, | ||
| std::vector< Array > * | p_scoring = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_aggregate_scoring = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec3 | weights = {1.f, 1.f, 1.f}, |
||
| uint | seed = 1 |
||
| ) |
Performs k-means clustering on three input arrays, providing more detailed cluster analysis by considering an additional dimension.
This version of k-means clustering includes a third array, enabling more complex clustering based on three terrain attributes or environmental variables.
Usage
- Apply this function to analyze the relationships between three different terrain attributes, revealing complex patterns.
- Useful in multi-dimensional environmental modeling and resource management.
- Parameters
-
[in] array1 The first input array for clustering. [in] array2 The second input array for clustering. [in] array3 The third input array for clustering. [in] nclusters The number of clusters (k) to be formed. [out] p_scoring (optional) A pointer to a vector of arrays where the clustering scores will be stored. Pass nullptr if scoring is not required. [out] p_aggregate_scoring (optional) A pointer to an array where the aggregate score across all clusters will be stored. Pass nullptr if not required. [in] weights A vector of three floats representing the weight given to array1,array2, andarray3. The default weights are {1.f, 1.f, 1.f}.[in] seed A seed value for random number generation, ensuring reproducibility of the clustering results. The default value is 1.
- Returns
- Array An array representing the clustered data, with each pixel assigned to a cluster.
Example
Result






◆ local_median_deviation()
Computes the local median deviation of a 2D array.
This function calculates the absolute difference between the local mean and a pseudo-local median of each element in the input array. The local neighborhood is defined by a square window with radius ir.
- Parameters
-
array The input 2D array of values (e.g., a heightmap). ir The radius of the square neighborhood window used for computing local statistics. The window size is (2*ir + 1) x (2*ir + 1).
- Returns
- A new array of the same size as
array, where each element represents the absolute deviation between the local mean and pseudo-local median in its neighborhood.
- Note
- The function uses a pseudo-median approximation. For exact median computation, replace the
median_pseudo()call with a proper median filter implementation.
Example
Result
- See also
- mean_local(), median_pseudo()
◆ mean_local()
Return the local mean based on a mean filter with a square kernel.
This function calculates the local mean of the input array using a mean filter with a square kernel. The local mean is determined by averaging values within a square neighborhood defined by the footprint radius ir. The result is an array where each value represents the mean of the surrounding values within the kernel size.
- Parameters
-
array Input array from which the local mean is to be calculated. ir Square kernel footprint radius. The size of the kernel used to compute the local mean.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array containing the local means.
Example
Result
- See also
maximum_local,minimum_local
◆ relative_elevation()
Calculates the relative elevation within a specified radius, helping to identify local highs and lows.
Relative elevation analysis determines how high or low a point is relative to its surroundings, which can be critical in hydrological modeling and geomorphology.
Usage:
- Use this function to detect local depressions or peaks in the terrain, which could indicate potential water collection points or hilltops.
- Useful in flood risk assessment and landscape classification.
- Parameters
-
array The input array representing the terrain elevation data. ir The radius (in pixels) within which to calculate the relative elevation for each point.
- Returns
- Array An output array containing the relative elevation values, normalized between 0 and 1.
Example
Result
◆ ruggedness()
Computes the ruggedness of each element in the input array.
The ruggedness is calculated as the square root of the sum of squared differences between each element and its neighbors within a specified radius.
- Parameters
-
array The input array for which ruggedness is to be computed. ir The radius within which neighbors are considered for ruggedness calculation.
- Returns
- An array containing the ruggedness values for each element in the input array.
Example
Result
◆ rugosity()
Estimates the rugosity of a surface by analyzing the skewness of the elevation data, which reflects surface roughness.
Rugosity is a measure of terrain roughness, often used in ecological studies and habitat mapping. Higher rugosity values indicate more rugged terrain, which can affect species distribution and water flow.
- Parameters
-
z The input array representing the heightmap data (elevation values). ir The radius of the square kernel used for calculations, determining the scale of the analysis. convex Return the convex rugosity if true, and the concave ones if not.
- Returns
- Array An output array containing the rugosity estimates, where higher values indicate rougher terrain.
Example
Result
◆ std_local()
Computes the local standard deviation of a 2D array.
This function calculates the standard deviation within a square neighborhood around each element in the input array.
- Parameters
-
array The input 2D array of values (e.g., a heightmap or intensity map). ir The radius of the square neighborhood window used for computing local statistics. The window size is (2*ir + 1) x (2*ir + 1).
- Returns
- A new array of the same size as
array, where each element contains the standard deviation of values within its local neighborhood.
Example
Result
- See also
- mean_local()
◆ valley_width()
Measures the valley width by calculating the distance from each point in a concave region to the frontier of that region.
Valley width is a geomorphological metric that represents the distance across valleys or concave regions in a terrain. This measurement is particularly useful in hydrological modeling and landscape analysis, where valley dimensions are important.
Usage
- Use this function to assess the width of valleys within a terrain, which can be important for understanding water flow, sediment transport, and landform development.
- Applicable in studies focusing on river valleys, canyon analysis, and erosion patterns.
- Parameters
-
z The input array representing the heightmap data (elevation values). ir The radius used for pre-filtering, controlling the scale of analysis (in pixels). The default value is 0, meaning no pre-filtering is applied. ridge_select If enabled, selects ridges instead of valleys.
- Returns
- Array An output array containing valley width values, representing the distance to the edge of the concave region for each point.
Example
Result
◆ z_score()
◆ bulkify()
| Array hmap::bulkify | ( | const Array & | z, |
| const PrimitiveType & | primitive_type, | ||
| float | amp = 1.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
◆ diffusion_retargeting() [1/2]
Applies diffusion retargeting by detecting local maxima and adjusting based on the difference between two arrays.
This function identifies points of interest in the array_before (local maxima in a 3x3 neighborhood), computes the difference between the corresponding points in array_before and array_after, and stores these differences in a delta array. It then applies smoothing to the delta values, remaps them within the original min-max range, and returns the corrected array by adding the adjusted delta to array_after.
- Parameters
-
array_before The original 2D array used to detect local maxima for retargeting. array_after The 2D array representing the state after the diffusion process. ir The smoothing radius used in the smoothing step ( smooth_cpulse).
- Returns
- A new 2D array where the delta between the two input arrays has been smoothed and applied as a correction to
array_after.
Example
Result
◆ diffusion_retargeting() [2/2]
| Array hmap::diffusion_retargeting | ( | const Array & | array_before, |
| const Array & | array_after, | ||
| const Array & | mask, | ||
| int | iterations | ||
| ) |
◆ directional_blur() [1/2]
| void hmap::directional_blur | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| float | angle, | ||
| float | intensity, | ||
| float | stretch = 1.f, |
||
| float | spread = 1.f |
||
| ) |
Applies a directional blur to a 2D array based on a spatially varying angle field.
This function performs an anisotropic blur on the input array, using the angle array to determine the direction of blur at each pixel. The blur is computed by sampling values along a line in the specified direction (per-pixel), using linear interpolation through an ArrayFunction. The amount of blur is controlled by parameters for intensity, stretching, and spread.
For each pixel, the function samples values along the blur direction determined by angle(i, j) (in degrees), applies a smooth weight profile (smoothstep3) over a range of 2 * ir - 1 steps, and accumulates the weighted values. The output is then normalized by the total weight sum.
- Parameters
-
array The input/output 2D array to be blurred (modified in-place). ir Blur radius: the number of samples on each side of the center (total samples = 2 * ir - 1). angle A 2D array of the same shape as arraygiving blur direction (in degrees) at each pixel. 0° points to the right (positive X), 90° points upward (positive Y).intensity The overall weight of the blur effect (scales the weight profile). stretch A scaling factor applied to the sampling step along the blur direction. Higher values stretch the blur further along the direction vector. spread Maximum normalized distance at which blur weights are applied (used in smoothstep weight profile).
- Note
- Uses linear interpolation through an
ArrayFunction, and wraps coordinates using clamping (not periodic).
- See also
- smoothstep3(), ArrayFunction
Example
Result
◆ directional_blur() [2/2]
| void hmap::directional_blur | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| const Array & | angle, | ||
| float | intensity, | ||
| float | stretch = 1.f, |
||
| float | spread = 1.f |
||
| ) |
Applies a directional blur to the provided 2D array with a constant angle.
This function is a convenience wrapper that applies a directional blur using a constant angle for all pixels. Internally, it creates a uniform angle array and calls the primary directional_blur function.
- Parameters
-
array The 2D array to be blurred. ir The radius of the blur operation (number of steps). angle The constant directional angle (in degrees) for the blur. intensity The maximum intensity of the blur at the starting point of the radius.
- Note
- The
anglevalue should be in degrees, where 0° points to the right (positive x-direction).
Example
Result

◆ equalize() [1/2]
| void hmap::equalize | ( | Array & | array | ) |
Apply histogram equalization to the array values.
This function performs histogram equalization on the input array to enhance the contrast of the image or data by adjusting the intensity distribution.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be equalized.
◆ equalize() [2/2]
Apply histogram equalization to the array values with a mask.
This function performs histogram equalization on the input array while considering the specified mask. Only the elements of the array corresponding to non-zero values in the mask are equalized.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be equalized. p_mask Optional mask array. Only the elements where the mask is non-zero are equalized.
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ expand() [1/4]
Apply expansion, or "inflation", to emphasize the bulk of the terrain.
This function expands the features of the terrain represented by the input array. The expansion operation, often referred to as "inflation", increases the prominence of elevated regions, effectively making them more pronounced.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the terrain or data to be expanded. ir Filter radius, which determines the extent of the expansion. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask controls which parts of the array are affected by the expansion.
Example
Result
- See also
- ex_shrink
◆ expand() [2/4]
| void hmap::expand | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| int | iterations = 1 |
||
| ) |
Apply expansion to emphasize the bulk of the terrain using a filter radius.
This overload applies expansion without the use of a mask, utilizing only the filter radius.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the terrain or data to be expanded. ir Filter radius, which determines the extent of the expansion.
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ expand() [3/4]
Apply expansion using a custom kernel.
This overload allows the use of a custom kernel for expansion, offering more control over the operation compared to the filter radius method.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the terrain or data to be expanded. kernel Custom kernel array used to perform the expansion.
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ expand() [4/4]
Apply expansion using a custom kernel with an optional mask.
This overload allows the use of a custom kernel for expansion, along with an optional mask to control which parts of the array are affected.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the terrain or data to be expanded. kernel Custom kernel array used to perform the expansion. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask controls which parts of the array are affected by the expansion.
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ expand_directional()
| void hmap::expand_directional | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| float | angle, | ||
| float | aspect_ratio, | ||
| float | anisotropy = 1.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_mask = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Apply expansion, or "inflation", to emphasize the bulk of the terrain, using a directional kernel.
This function expands features of the terrain represented by the input array, with emphasis applied directionally based on the specified angle. The directional kernel allows for anisotropic expansion, making the expansion more pronounced in a specified direction.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the terrain or data to be expanded. ir Filter radius, determining the extent of the expansion. angle Angle (in degrees) that sets the direction of the expansion. aspect_ratio Pulse aspect ratio, determining the shape of the expansion. anisotropy Pulse width ratio between upstream and downstream sides, default is 1.0 (isotropic expansion). p_mask Optional filter mask with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask controls which parts of the array are affected by the expansion.
Example
Result
◆ expand_talus()
| void hmap::expand_talus | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array & | mask, | ||
| float | talus, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| int | ir = 1, |
||
| float | noise_ratio = 0.2f |
||
| ) |
◆ faceted()
| Array hmap::faceted | ( | const Array & | array, |
| int | neighborhood = 0, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Generate a faceted heightmap that retains the main features of the input heightmap.
This function processes the input heightmap to produce a new heightmap with a 'faceted' appearance, where the terrain features are preserved but with a more angular and planar aspect. This effect can be controlled by specifying a neighborhood type and optional noise arrays for domain warping.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the original heightmap. neighborhood Neighborhood type that defines how the faceting effect is applied (see neighborhood). p_noise_x Optional reference to the input noise array used for domain warping in the x-direction (NOT in pixels, with respect to a unit domain). p_noise_y Optional reference to the input noise array used for domain warping in the y-direction (NOT in pixels, with respect to a unit domain).
- Returns
- Array Output array containing the faceted heightmap.
Example
Result
◆ fill_talus() [1/2]
| void hmap::fill_talus | ( | Array & | z, |
| float | talus, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| int | ir = 1, |
||
| float | noise_ratio = 0.2f, |
||
| const Array * | p_seed_mask = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Modifies a terrain array by filling it with talus slopes.
This function applies a talus formation algorithm to an existing terrain array, adjusting the heights to create natural-looking slopes. The process involves random perturbations influenced by noise to simulate erosion or sediment transport.
- Parameters
-
z A reference to the 2D array representing the terrain heights. The function modifies this array in place to introduce talus slopes. talus The critical slope angle that determines where material will move from higher elevations to lower ones. Slopes steeper than this value will be flattened by material transport. seed The seed for the random number generator, ensuring reproducibility of the noise effects in the talus formation process. The same seed will produce the same terrain modifications. noise_ratio A parameter that controls the amount of randomness or noise introduced in the talus formation process. The default value is 0.2.
Example
Result
- See also
thermal_scree,thermal_scree_fast
◆ fill_talus() [2/2]
| void hmap::fill_talus | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| int | ir = 1, |
||
| float | noise_ratio = 0.2f, |
||
| const Array * | p_seed_mask = nullptr |
||
| ) |
◆ fill_talus_fast()
| void hmap::fill_talus_fast | ( | Array & | z, |
| glm::ivec2 | shape_coarse, | ||
| float | talus, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| int | ir = 1, |
||
| float | noise_ratio = 0.2f |
||
| ) |
Fill terrain values with a given downslope talus, optimized using a coarse mesh for faster computation.
This function performs a talus formation process on a terrain array similar to fill_talus, but with an optimization that involves working on a coarser mesh. The coarse mesh reduces the computation time while still producing realistic downslope talus effects. The method starts by filling the values from the cells with the highest elevations and introduces random perturbations to avoid grid orientation artifacts.
- Parameters
-
z Input array representing the terrain heights. The function modifies this array in place to introduce talus slopes, starting from the highest values. shape_coarse Array representing the coarser shape used for the solver, which determines the resolution of the coarse mesh. talus The critical slope angle that determines where material will move from higher elevations to lower ones. Slopes steeper than this value will be flattened by material transport. seed The seed for the random number generator, ensuring reproducibility of the noise effects in the talus formation process. The same seed will produce the same terrain modifications. noise_ratio A parameter that controls the amount of randomness or noise introduced in the talus formation process. The noise helps to avoid grid orientation artifacts. The default value is 0.2.
Example
Result

- See also
thermal_scree,thermal_scree_fast
◆ fold() [1/2]
Apply a "folding" filter (successive absolute values) to the array elements.
This function applies a folding filter to the input array, where the values are successively folded (using absolute values) within a specified range, defined by vmin and vmax. The process can be repeated for a number of iterations, with an optional smoothing parameter k to control the intensity of the folding effect.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the folding filter is applied. vmin Minimum reference value used as a lower bound for the folding operation. vmax Maximum reference value used as an upper bound for the folding operation. iterations Number of iterations for applying the folding filter. The default is 3. k Smoothing parameter for the absolute value operation, expected to be greater than 0. It controls the degree of smoothing applied during folding. The default value is 0.05.
Example
Result
◆ fold() [2/2]
Apply a "folding" filter with default reference values and parameters.
This overload applies the folding filter to the input array with the default number of iterations and smoothing parameter k. The folding is done without explicit minimum and maximum reference values.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the folding filter is applied. iterations Number of iterations for applying the folding filter. The default is 3. k Smoothing parameter for the absolute value operation, expected to be greater than 0. It controls the degree of smoothing applied during folding. The default value is 0.05.
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ gain() [1/3]
Apply a gain correction to the array elements.
This function applies a gain correction to the input array using a power law. The correction enhances or reduces the intensity of the values based on the specified gain factor.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the gain correction is applied. factor Gain factor, expected to be greater than 0. It determines the strength of the gain correction. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask controls which parts of the array are affected by the gain correction.
- Warning
- Array values are expected to be in the range [0, 1]. Applying the gain correction outside of this range may lead to unexpected results.
Example
Result
◆ gain() [2/3]
| void hmap::gain | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | factor | ||
| ) |
Apply a gain correction to the array elements without a mask.
This overload applies the gain correction to the entire array without using a mask. The gain correction is performed using the specified gain factor.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the gain correction is applied. factor Gain factor, expected to be greater than 0. It determines the strength of the gain correction.
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ gamma_correction() [1/2]
Apply gamma correction to the input array.
This function applies gamma correction to the input array, which adjusts the brightness and contrast based on a specified gamma factor. Gamma correction is used to correct or adjust the tonal range of an image or data to achieve a desired visual effect.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the gamma correction is applied. gamma Gamma factor, expected to be greater than 0. It determines the level of correction applied. A gamma value less than 1 will lighten the image, while a value greater than 1 will darken it. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask controls which parts of the array are affected by the gamma correction.
- Warning
- Array values are expected to be in the range [0, 1]. Applying gamma correction outside of this range may result in incorrect or unintended modifications.
Example
Result
◆ gamma_correction() [2/2]
| void hmap::gamma_correction | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | gamma | ||
| ) |
Apply gamma correction to the input array without a mask.
This overload applies gamma correction to the entire array without using a mask. The gamma correction is performed using the specified gamma factor.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the gamma correction is applied. gamma Gamma factor, expected to be greater than 0. It determines the level of correction applied. A gamma value less than 1 will lighten the image, while a value greater than 1 will darken it.
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ gamma_correction_local() [1/2]
Apply a "local" gamma correction to the input array.
This function performs gamma correction by first normalizing the values locally within a specified neighborhood around each pixel. The normalization is achieved using minimum and maximum filters before applying the gamma correction based on the specified gamma factor. This method allows for localized adjustments of contrast and brightness in the input array.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the local gamma correction is applied. gamma Gamma factor, expected to be greater than 0. It determines the level of correction applied after local normalization. A gamma value less than 1 will lighten the local regions, while a value greater than 1 will darken them. ir Filter radius that defines the size of the local neighborhood used for normalization. k Smoothing factor used to control the degree of smoothing applied during normalization. The default value is 0.1. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask controls which parts of the array are affected by the local gamma correction.
Example
Result
◆ gamma_correction_local() [2/2]
| void hmap::gamma_correction_local | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | gamma, | ||
| int | ir, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | k = 0.1f |
||
| ) |
Apply a "local" gamma correction with a mask to the input array.
This overload applies local gamma correction to the input array using a mask. The gamma correction is performed after normalizing values locally within the specified neighborhood defined by the filter radius. The optional mask allows for selective application of the correction.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the local gamma correction is applied. gamma Gamma factor, expected to be greater than 0. It determines the level of correction applied after local normalization. A gamma value less than 1 will lighten the local regions, while a value greater than 1 will darken them. ir Filter radius that defines the size of the local neighborhood used for normalization. p_mask Filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask controls which parts of the array are affected by the local gamma correction. k Smoothing factor used to control the degree of smoothing applied during normalization. The default value is 0.1.
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ kuwahara() [1/2]
Applies the Kuwahara filter to an array with optional per-pixel masking.
This overloaded version of the Kuwahara filter allows applying the filter with a per-pixel mask. The mask determines the blending ratio for each pixel, allowing selective smoothing.
- Parameters
-
array The input/output array to apply the filter on. The array is modified in place. ir The radius of the region to analyze for each pixel. Larger values result in stronger smoothing. mix_ratio A blending factor between the original and filtered arrays when p_maskisnullptr. Ignored ifp_maskis provided.
Example
Result
◆ kuwahara() [2/2]
Applies the Kuwahara filter to an array with optional per-pixel masking.
This overloaded version of the Kuwahara filter allows applying the filter with a per-pixel mask. The mask determines the blending ratio for each pixel, allowing selective smoothing.
- Parameters
-
array The input/output array to apply the filter on. The array is modified in place. ir The radius of the region to analyze for each pixel. Larger values result in stronger smoothing. p_mask A pointer to an array representing the mask. The values in the mask range from 0.0 to 1.0, specifying the blending ratio for each pixel. If nullptr, the filter is applied without masking.mix_ratio A blending factor between the original and filtered arrays when p_maskisnullptr. Ignored ifp_maskis provided.
If no mask is provided:
- The function behaves like the single-argument version of
kuwahara.
Example
Result

◆ laplace() [1/2]
Applies an iterative 8-neighbor Laplacian smoothing filter on an array.
This function performs isotropic Laplacian diffusion on a 2D array using an explicit finite-difference scheme. Each cell is updated according to the local Laplacian computed from its 8 surrounding neighbors:
\[ A_{i,j}^{t+1} = A_{i,j}^{t} + \sigma \cdot \left( \sum_{(p,q)\in N_{8}(i,j)} A_{p,q}^{t} - 8A_{i,j}^{t} \right) \]
where ( N_{8}(i,j) ) denotes the 8 neighboring cells.
Boundary cells are handled by clamping neighbor indices to the valid range, effectively replicating edge values at the borders.
- Parameters
-
array The 2D array to be smoothed (modified in place). sigma Diffusion coefficient (small positive value, e.g. 0.05–0.25). iterations Number of diffusion iterations to apply.
Example
Result
◆ laplace() [2/2]
| void hmap::laplace | ( | Array & | array, |
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | sigma = 0.125f, |
||
| int | iterations = 3 |
||
| ) |
Apply a low-pass Laplace filter with a mask.
This overload applies the Laplace filter to the input array using an optional mask. The mask determines which parts of the array are affected by the filter. The filtering intensity and the number of iterations control the extent of the smoothing effect.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the Laplace filter is applied. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask specifies which parts of the array are affected by the filter. sigma Filtering intensity, expected to be in the range [0, 1]. It controls the strength of the filtering effect. A value closer to 1 results in more smoothing. The default value is 0.2. iterations Number of iterations to apply the filter. More iterations will increase the smoothing effect. The default value is 3.
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ laplace1d()
| void hmap::laplace1d | ( | std::vector< float > & | v, |
| float | sigma = 0.5f, |
||
| int | iterations = 1 |
||
| ) |
Apply a low-pass Laplace filter to a vector.
This function applies a low-pass Laplace filter to a 1D vector to smooth out high-frequency noise and detail. The filtering intensity and the number of iterations control the extent of the smoothing effect.
- Parameters
-
v Input vector to which the Laplace filter is applied. sigma Filtering intensity, expected to be in the range [0, 1]. It determines the strength of the filtering effect. A value closer to 1 results in more smoothing. iterations Number of iterations to apply the filter. More iterations will increase the smoothing effect. The default value is 1.
◆ laplace_edge_preserving() [1/2]
| void hmap::laplace_edge_preserving | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | talus, | ||
| float | sigma = 0.2f, |
||
| int | iterations = 3 |
||
| ) |
Apply a low-pass anisotropic Laplace filter to the input array.
This function applies an anisotropic Laplace filter to the input array. Anisotropic diffusion, also known as edge-preserving smoothing, helps to reduce noise while preserving edges. The effect of the filter is controlled by the talus limit, filtering intensity, and the number of iterations.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the anisotropic Laplace filter is applied. talus Talus limit for edge sensitivity. Gradients above this value are less affected by the filtering, preserving important edges in the data. sigma Filtering intensity, expected to be in the range [0, 1]. It controls the strength of the filtering effect. A value closer to 1 results in more smoothing. The default value is 0.2. iterations Number of iterations to apply the filter. More iterations will increase the smoothing effect. The default value is 3.
Example
Result

◆ laplace_edge_preserving() [2/2]
| void hmap::laplace_edge_preserving | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | talus, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | sigma = 0.2f, |
||
| int | iterations = 3 |
||
| ) |
Apply a low-pass anisotropic Laplace filter with a mask.
This overload applies the anisotropic Laplace filter to the input array using an optional mask. The mask determines which parts of the array are affected by the filter. The effect of the filtering is controlled by the talus limit, filtering intensity, and the number of iterations.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the anisotropic Laplace filter is applied. talus Talus limit for edge sensitivity. Gradients above this value are less affected by the filtering, preserving important edges in the data. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask specifies which parts of the array are affected by the filter. sigma Filtering intensity, expected to be in the range [0, 1]. It controls the strength of the filtering effect. A value closer to 1 results in more smoothing. The default value is 0.2. iterations Number of iterations to apply the filter. More iterations will increase the smoothing effect. The default value is 3.
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ low_pass_high_order()
Apply a low-pass high-order filter to the input array.
This function applies a high-order low-pass filter to the input array. The filter can be of 5th, 7th, or 9th order, providing increasingly sharp filtering effects. The filtering intensity is controlled by the sigma parameter, which determines the strength of the filtering.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the high-order low-pass filter is applied. order Filter order, which can be 5, 7, or 9. Higher orders provide more refined filtering. sigma Filtering intensity, expected to be in the range [0, 1]. It controls the strength of the filtering effect. A value closer to 1 results in more smoothing. The default value is 1.0.
Example
Result
- See also
laplace
◆ make_binary()
Convert array values to binary using a threshold.
This function applies a binary filter to the input array, converting all values to either 0 or 1 based on a specified threshold. Values above the threshold are set to 1, while values equal to or below the threshold are set to 0.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be converted to binary. threshold Threshold value. Any array value greater than this threshold is set to 1, while values less than or equal to the threshold are set to 0. The default threshold is 0.0.
◆ maximum_local()
Return the local maxima based on a maximum filter with a square kernel.
This function identifies the local maxima in the input array using a maximum filter with a square kernel. The local maxima are determined based on the footprint radius specified by ir. The result is an array where each value represents the local maximum within the defined kernel size.
- Parameters
-
array Input array from which local maxima are to be extracted. ir Square kernel footprint radius. The size of the kernel used to determine the local maxima.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array containing the local maxima.
Example
Result
- See also
maximum_local_disk,minimum_local
◆ maximum_local_disk()
Return the local maxima based on a maximum filter using a disk kernel.
This function identifies the local maxima in the input array using a maximum filter with a disk-shaped kernel. The local maxima are determined based on the footprint radius specified by ir. The result is an array where each value represents the local maximum within the disk-shaped kernel.
- Parameters
-
array Input array from which local maxima are to be extracted. ir Disk kernel footprint radius. The size of the disk-shaped kernel used to determine the local maxima.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array containing the local maxima.
Example
Result

- See also
maximum_local,minimum_local_disk,minimum_local
◆ match_histogram()
Transform the input array elevation to match the histogram of a reference array.
This function performs histogram matching on the input array to adjust its elevation values so that the resulting histogram closely matches the histogram of a reference array. This process is useful for aligning the statistical properties of the input data with those of the reference data.
- Parameters
-
array Input array whose elevation values are to be transformed. array_reference Reference array whose histogram is used as the target for matching.
Example
Result
◆ mean_shift() [1/2]
| Array hmap::mean_shift | ( | const Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| float | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 1, |
||
| bool | talus_weighted = true |
||
| ) |
Applies the mean shift algorithm to the input array.
The mean shift algorithm iteratively adjusts each value in the input array by averaging nearby values within a specified radius (ir), using either simple or weighted mean computation. The process stops after the specified number of iterations or if convergence criteria are met.
- Parameters
-
array The input array to process. ir The radius of the neighborhood to consider for mean computation. threshold The value threshold for considering neighboring elements. Only elements with differences below this threshold are included. iterations The number of iterations to perform the mean shift process. talus_weighted If true, uses weighted mean based on differences between values and their neighbors. If false, uses unweighted mean.
- Returns
- A new array containing the result of the mean shift process.
Example
Result
◆ mean_shift() [2/2]
| Array hmap::mean_shift | ( | const Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| float | talus, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| int | iterations = 1, |
||
| bool | talus_weighted = true |
||
| ) |
◆ median_3x3() [1/2]
Apply a 3x3 median filter to the input array.
This function applies a 3x3 median filter to the input array to reduce noise while preserving edges. The median filter replaces each pixel with the median value of the 3x3 neighborhood surrounding it. An optional mask can be used to control which parts of the array are filtered.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the median filter is applied. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask determines which parts of the array are affected by the median filter.
Example
Result
◆ median_3x3() [2/2]
| void hmap::median_3x3 | ( | Array & | array | ) |
Apply a 3x3 median filter to the input array without a mask.
This overload applies a 3x3 median filter to the input array, affecting all pixels. The median filter replaces each pixel with the median value of the 3x3 neighborhood surrounding it.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the median filter is applied.
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ median_pseudo()
Computes a fast pseudo-median approximation of a local neighborhood in an array.
This function approximates the effect of a median filter by computing the local minimum, maximum, and mean values within a square neighborhood of radius ir, and averaging the results:
\[ \text{pseudo\_median}(x, y) = \frac{\text{min} + \text{max} + \text{mean}}{3} \]
This method is computationally cheaper than a true median filter and can approximate its noise-reduction and edge-preserving properties to some extent.
- Parameters
-
array Input array (e.g., image or 2D signal). ir Radius of the square neighborhood (kernel size will be \(2 \cdot ir + 1\)).
- Returns
- An Array containing the pseudo-median filtered output.
- Note
- This method works best on images with impulsive noise (e.g., salt-and-pepper), but is only an approximation and may behave differently from a true median filter on complex structures or edges.
Example
Result
- See also
- minimum_local, maximum_local, mean_local
◆ minimum_local()
Return the local minima based on a maximum filter with a square kernel.
This function identifies the local minima in the input array using a maximum filter with a square kernel. The local minima are determined based on the footprint radius specified by ir. The result is an array where each value represents the local minimum within the defined kernel size.
- Parameters
-
array Input array from which local minima are to be extracted. ir Square kernel footprint radius. The size of the kernel used to determine the local minima.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array containing the local minima.
Example
Result

- See also
minimum_local
◆ minimum_local_disk()
Return the local minima based on a maximum filter using a disk kernel.
This function calculates the local minima in the input array using a maximum filter with a disk-shaped kernel. The local minima are determined based on the footprint radius specified by ir. The result is an array where each value represents the local minimum within the disk-shaped kernel.
- Parameters
-
array Input array from which local minima are to be extracted. ir Disk kernel footprint radius. The size of the disk-shaped kernel used to determine the local minima.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array containing the local minima.
Example
Result

- See also
maximum_local,maximum_local_disk,minimum_local
◆ normal_displacement() [1/2]
| void hmap::normal_displacement | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | amount = 0.1f, |
||
| int | ir = 0, |
||
| bool | reverse = false |
||
| ) |
Apply a displacement to the terrain along the normal direction.
This function displaces the terrain along its normal direction, simulating effects like erosion or terrain modification. The amount of displacement and direction (normal or reversed) can be specified. Optionally, a mask can be used to control which parts of the terrain are affected.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the terrain. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask specifies which parts of the array are affected by the displacement. amount Amount of displacement to apply. The default value is 0.1. ir Pre-filtering radius. The radius used to smooth the terrain before applying displacement. The default value is 0. reverse If true, the displacement direction is reversed. The default value is false.
Example
Result
◆ normal_displacement() [2/2]
| void hmap::normal_displacement | ( | Array & | array, |
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | amount = 0.1f, |
||
| int | ir = 0, |
||
| bool | reverse = false |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ plateau() [1/2]
Apply a plateau-shape filter to the input array.
This function applies a plateau-shape filter to the input array, modifying the terrain to create flat, plateau-like regions. The filter's radius and flatness can be adjusted to control the extent and shape of the plateaus. An optional mask can be used to control which parts of the array are affected.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the plateau-shape filter is applied. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask specifies which parts of the array are affected by the filter. ir Plateau radius. The size of the area over which the plateau effect is applied. factor Gain factor that controls the flatness of the plateau. The higher the factor, the flatter the resulting plateau. The default value is 1.0.
Example
Result
◆ plateau() [2/2]
| void hmap::plateau | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| float | factor | ||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ recast_billow()
| void hmap::recast_billow | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | vref, | ||
| float | k | ||
| ) |
Transform heightmap to give a "billow" like appearance.
This function modifies the heightmap to produce a "billow" effect. The transformation is applied based on a reference elevation (vref) where the elevation is folded. The smoothing coefficient (k) controls the degree of smoothing applied during the transformation.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap to be transformed. vref Reference elevation where the heightmap values are folded. This value determines the baseline around which the billow effect is centered. k Smoothing coefficient that influences the degree of smoothness in the billow transformation. Higher values result in more smoothing.
Example
Result
◆ recast_canyon() [1/4]
Transform heightmap to give a "canyon" like appearance.
This function modifies the heightmap to create a "canyon" effect. The transformation is based on a canyon top elevation (vcut). The effect can be adjusted with a gamma factor to control the intensity of the canyon effect. Optional parameters include a filter mask for selective application and a noise array for additional variation.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap to be transformed. vcut Canyon top elevation. This value defines the threshold for canyon formation. gamma Gamma factor (> 0) that adjusts the intensity of the canyon effect. A higher value increases the effect. The default value is 4.0. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask specifies which parts of the heightmap are affected by the transformation. p_noise Optional noise array used to introduce variation in the canyon effect. If not provided, no additional noise is applied.
Example
Result

◆ recast_canyon() [2/4]
| void hmap::recast_canyon | ( | Array & | array, |
| const Array & | vcut, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | gamma = 4.f |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ recast_canyon() [3/4]
| void hmap::recast_canyon | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | vcut, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | gamma = 4.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise = nullptr |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ recast_canyon() [4/4]
| void hmap::recast_canyon | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | vcut, | ||
| float | gamma = 4.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise = nullptr |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ recast_cliff() [1/2]
Transform heightmap to add cliffs where gradients are steep enough.
This function modifies the heightmap to introduce cliffs based on a reference talus angle. Cliffs are added where the gradient exceeds the specified talus angle. The amplitude of the cliffs and the gain factor for steepness are adjustable. Additionally, a filter mask can be applied to control which parts of the heightmap are affected.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap to be modified. talus Reference talus angle. This angle determines the threshold above which cliffs are formed. ir Filter radius used to smooth the heightmap before applying the cliff effect. amplitude Amplitude of the cliffs. This value controls the height of the cliffs. gain Gain factor for the gain filter, influencing the steepness of the cliffs. Higher values result in steeper cliffs. The default value is 2.0. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask specifies which parts of the heightmap are affected by the cliff transformation.
Example
Result

◆ recast_cliff() [2/2]
| void hmap::recast_cliff | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | talus, | ||
| int | ir, | ||
| float | amplitude, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | gain = 2.f |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ recast_cliff_directional() [1/2]
| void hmap::recast_cliff_directional | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | talus, | ||
| int | ir, | ||
| float | amplitude, | ||
| float | angle, | ||
| float | gain = 2.f |
||
| ) |
Transform heightmap to add directional cliffs where gradients are steep enough.
This function modifies the heightmap to introduce cliffs in a specific direction, based on a reference talus angle. The cliffs are added where the gradient exceeds the specified talus angle, with the direction of the cliffs controlled by the specified angle. The amplitude of the cliffs and the gain factor for steepness are also adjustable. A filter mask can be used to specify which parts of the heightmap are affected.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap to be modified. talus Reference talus angle. This angle determines the threshold above which cliffs are formed. ir Filter radius used to smooth the heightmap before applying the cliff effect. amplitude Amplitude of the cliffs. This value controls the height of the cliffs. angle Angle (in degrees) determining the direction of the cliffs. gain Gain factor for the gain filter, influencing the steepness of the cliffs. Higher values result in steeper cliffs. The default value is 2.0. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask specifies which parts of the heightmap are affected by the cliff transformation.
Example
Result

This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ recast_cliff_directional() [2/2]
| void hmap::recast_cliff_directional | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | talus, | ||
| int | ir, | ||
| float | amplitude, | ||
| float | angle, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | gain = 2.f |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ recast_cracks()
| void hmap::recast_cracks | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | cut_min = 0.05f, |
||
| float | cut_max = 0.5f, |
||
| float | k_smoothing = 0.01f, |
||
| float | vmin = 0.f, |
||
| float | vmax = -1.f |
||
| ) |
◆ recast_escarpment() [1/2]
| void hmap::recast_escarpment | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir = 16, |
||
| float | ratio = 0.1f, |
||
| float | scale = 1.f, |
||
| bool | reverse = false, |
||
| bool | transpose_effect = false, |
||
| float | global_scaling = 0.f |
||
| ) |
Applies an escarpment effect to the given 2D array, modifying its values based on cumulative displacement with optional directional and transpositional transformations.
This function calculates cumulative displacement along the x-axis based on relative elevation differences between adjacent cells. The displacement is scaled and optionally reversed, then used to apply a warping effect to the array, simulating an escarpment feature. An optional global scaling factor can further adjust the displacement effect intensity.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the 2D array where the escarpment effect will be applied. ir Radius for the smoothing kernel used on the displacement, controlling the smoothness of the effect. Larger values result in smoother transitions. ratio The ratio influencing displacement; values > 1.0 increase displacement sensitivity to height differences. scale The scaling factor for the cumulative displacement, affecting the intensity of the effect. reverse If true, reverses the direction of the displacement effect. transpose_effect If true, transposes the array before and after applying the effect. global_scaling An additional scaling factor for the displacement; if set to 0, a default value is computed based on the array's range and size. Higher values increase the overall effect.
Example
Result

◆ recast_escarpment() [2/2]
| void hmap::recast_escarpment | ( | Array & | array, |
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| int | ir = 16, |
||
| float | ratio = 0.1f, |
||
| float | scale = 1.f, |
||
| bool | reverse = false, |
||
| bool | transpose_effect = false, |
||
| float | global_scaling = 0.f |
||
| ) |
Applies an escarpment effect to the given 2D array, with an optional mask to blend the effect.
This overload allows for a blending mask that controls the intensity of the escarpment effect at each point in the array. The mask values range between 0 and 1, where values closer to 1 fully apply the effect, and values closer to 0 reduce it. An optional global scaling factor can further adjust the displacement effect intensity.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the 2D array where the escarpment effect will be applied. p_mask Pointer to an optional mask array for blending the effect, where values range from 0 to 1. A nullptr applies the effect fully without blending. ir Radius for the smoothing kernel used on the displacement, controlling the smoothness of the effect. Larger values result in smoother transitions. ratio The ratio influencing displacement; values > 1.0 increase displacement sensitivity to height differences. scale The scaling factor for the cumulative displacement, affecting the intensity of the effect. reverse If true, reverses the direction of the displacement effect. transpose_effect If true, transposes the array before and after applying the effect. global_scaling An additional scaling factor for the displacement; if set to 0, a default value is computed based on the array's range and size. Higher values increase the overall effect.
Example
Result

◆ recast_peak() [1/2]
Transform heightmap to give a "peak" like appearance.
This function modifies the heightmap to create a "peak" effect, where the elevations are adjusted to emphasize peak-like features. The transformation is applied based on a filter radius (ir) and involves gamma correction and smoothing parameters. The effect can be selectively applied using a filter mask.
- Warning
- Array values are expected to be in the range [0, 1].
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap to be transformed. ir Filter radius used to smooth the heightmap before applying the peak effect. gamma Gamma factor (> 0) that adjusts the intensity of the peak effect. A higher value increases the effect. The default value is 2.0. For details on gamma correction, see gamma_correction.k Smoothing parameter (> 0) that controls the degree of smoothing applied during the transformation. Higher values result in more smoothing. The default value is 0.1. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask specifies which parts of the heightmap are affected by the peak transformation.
Example
Result

◆ recast_peak() [2/2]
| void hmap::recast_peak | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | gamma = 2.f, |
||
| float | k = 0.1f |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ recast_rocky_slopes() [1/2]
| void hmap::recast_rocky_slopes | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | talus, | ||
| int | ir, | ||
| float | amplitude, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | kw, | ||
| float | gamma = 0.5f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Transform heightmap by adding "rock-like" features at higher slopes.
This function modifies the heightmap to introduce rock-like features, particularly at locations with higher slopes. The transformation is controlled by parameters defining talus limit, filter radius, amplitude, and noise characteristics. The rock features are generated using a specified random seed and can be customized with optional noise and gamma correction. A filter mask can be applied to control which parts of the heightmap are affected.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap to be transformed. talus Talus limit that determines the threshold above which rock-like features are introduced based on slope steepness. ir Filter radius used to smooth the heightmap and define the area of influence for adding rock features. amplitude Amplitude of the rock features. This value controls the intensity of the rock-like appearance. seed Random number seed used to generate noise patterns for the rock features. Different seeds produce different rock patterns. kw Noise wavenumber with respect to a unit domain, influencing the frequency of rock features. Higher values result in more detailed rock textures. gamma Gamma correction coefficient applied to the rock features. This parameter adjusts the contrast of the rock features. The default value is 0.5. p_noise Optional reference to an input noise array used for generating rock features. If provided, it overrides the default noise generator. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask specifies which parts of the heightmap are affected by the rock feature transformation. bbox Bounding box defining the region of interest within the heightmap. This parameter specifies the coordinates of the bounding box in the format {xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax}. The default bounding box covers the entire domain.
Example
Result

◆ recast_rocky_slopes() [2/2]
| void hmap::recast_rocky_slopes | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | talus, | ||
| int | ir, | ||
| float | amplitude, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | kw, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | gamma = 0.5f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ recast_sag() [1/2]
| void hmap::recast_sag | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | vref, | ||
| float | k | ||
| ) |
Transform heightmap to give a "cliff" like appearance.
This function modifies the heightmap to create a "cliff" effect by folding the elevations around a reference height (vref). The transformation is influenced by a smoothing coefficient (k) and can be selectively applied using a filter mask.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap to be transformed. vref Reference elevation where the heightmap is folded to create the cliff-like appearance. Elevations near this value will be prominently altered. k Smoothing coefficient that controls the degree of smoothing applied during the transformation. A higher value results in smoother cliffs. The default value is not specified in this function; it must be provided by the user. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask specifies which parts of the heightmap are affected by the cliff transformation. If not provided, the transformation is applied to the entire heightmap.
Example
Result

◆ recast_sag() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ recurve() [1/2]
| void hmap::recurve | ( | Array & | array, |
| const std::vector< float > & | t, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | v | ||
| ) |
Apply a curve adjustment filter to the array.
This function applies a curve adjustment to the heightmap by mapping input values to output values according to a given correction curve. The curve is monotonically interpolated, and any values outside the defined input range are clipped. The filter can be selectively applied using a mask.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap to be adjusted. t Vector of input values for the correction curve. These values define the x-coordinates (input values) of the curve. v Vector of output values for the correction curve. These values define the y-coordinates (output values) of the curve corresponding to the input values in t.p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask specifies which parts of the heightmap are affected by the curve adjustment. If not provided, the curve adjustment is applied to the entire heightmap.
Example
Result
◆ recurve() [2/2]
| void hmap::recurve | ( | Array & | array, |
| const std::vector< float > & | t, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | v, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask | ||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ recurve_bexp() [1/3]
Apply a curve adjustment filter using a "bumpy exponential-shape" curve.
This function adjusts the heightmap using a "bumpy exponential-shape" curve, where the curve has an exponential decay defined by the parameter tau. The curve transformation is applied to the entire heightmap or selectively using a filter mask.
- Warning
- Array values are expected to be in the range [0, 1].
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap to be adjusted. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask specifies which parts of the heightmap are affected by the curve adjustment. If not provided, the adjustment is applied to the entire heightmap. tau Exponential decay parameter that defines the shape of the "bumpy" curve. Higher values of tauresult in a sharper curve. The default value is 0.5.
Example
Result
◆ recurve_bexp() [2/3]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ recurve_exp() [1/3]
Apply a curve adjustment filter using a "sharp exponential-shape" curve.
This function adjusts the heightmap using a "sharp exponential-shape" curve, where the curve has an exponential decay defined by the parameter tau. The curve transformation can be applied to the entire heightmap or selectively using a filter mask.
- Warning
- Array values are expected to be in the range [0, 1].
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap to be adjusted. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The mask specifies which parts of the heightmap are affected by the curve adjustment. If not provided, the adjustment is applied to the entire heightmap. tau Exponential decay parameter that defines the shape of the "sharp" curve. Higher values of tauresult in a steeper curve. The default value is 0.5.
Example
Result

◆ recurve_exp() [2/3]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ recurve_kura() [1/2]
| void hmap::recurve_kura | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | a, | ||
| float | b | ||
| ) |
Apply a curve adjustment filter using Kumaraswamy's cumulative distribution function (CDF).
This function transforms the heightmap using Kumaraswamy's CDF, which is defined by two shape parameters, a and b. The transformation applies a curve adjustment that can shape the data closer to 0 or 1 depending on the values of a and b. The adjustment can be applied to the entire heightmap or selectively using a filter mask.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap to be adjusted. a Parameter 'a' of Kumaraswamy's CDF, which drives the curve shape towards 0. b Parameter 'b' of Kumaraswamy's CDF, which drives the curve shape towards 1. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. If provided, the adjustment is applied according to this mask. If not provided, the entire heightmap is adjusted.
Example
Result

◆ recurve_kura() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ recurve_s() [1/2]
| void hmap::recurve_s | ( | Array & | array | ) |
Apply a curve adjustment filter using a smooth "S-shape" curve.
This function adjusts the heightmap using a smooth "S-shape" curve, which transforms the input values in a manner that creates an S-shaped distribution. The transformation can be applied to the entire heightmap or selectively using a filter mask.
- Warning
- Array values are expected to be in the range [0, 1].
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap to be adjusted. p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. If provided, the adjustment is applied according to this mask. If not provided, the entire heightmap is adjusted.
Example
Result

◆ recurve_s() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ recurve_smoothstep_rational() [1/2]
| void hmap::recurve_smoothstep_rational | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | n | ||
| ) |
Apply a curve adjustment filter using an nth-order smoothstep curve.
This function applies a curve adjustment to the heightmap using a smoothstep function of order n. The smoothstep function provides a smooth transition between 0 and 1, where n determines the smoothness of the transition. The adjustment can be applied to the entire heightmap or selectively using a filter mask.
- Warning
- Array values are expected to be in the range [0, 1].
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap to be adjusted. n Smoothstep order, which determines the degree of smoothness for the transition. nshould be a non-negative value (in [0, ∞[).p_mask Optional filter mask, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. If provided, the adjustment is applied according to this mask. If not provided, the entire heightmap is adjusted.
Example
Result

◆ recurve_smoothstep_rational() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ reverse_above_theshold() [1/4]
| void hmap::reverse_above_theshold | ( | Array & | array, |
| const Array & | threshold, | ||
| float | scaling = 1.f, |
||
| float | transition_extent = 0.f |
||
| ) |
Applies a smooth reversal of values above a given threshold.
This function modifies the elements of an array by "reversing" values that exceed a given threshold value, optionally blending the effect over a transition range.
For values above the threshold:
- The difference between the value and the threshold is scaled down proportionally to
scalingand modulated by a smooth transition (using smoothstep3) based ontransition_extent.
For values below the threshold:
- The values are linearly blended (
lerp) with the threshold value using a smooth transition factor, gradually reducing the reversal effect.
- Parameters
-
array Array to modify in place. threshold Array containing the per-element threshold values. scaling Multiplier applied to the difference above the threshold. transition_extent Width of the smooth transition zone for blending.
Example
Result
◆ reverse_above_theshold() [2/4]
| void hmap::reverse_above_theshold | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | threshold, | ||
| float | scaling = 1.f, |
||
| float | transition_extent = 0.f |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ reverse_above_theshold() [3/4]
| void hmap::reverse_above_theshold | ( | Array & | array, |
| const Array & | threshold, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | scaling = 1.f, |
||
| float | transition_extent = 0.f |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ reverse_above_theshold() [4/4]
| void hmap::reverse_above_theshold | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | threshold, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | scaling = 1.f, |
||
| float | transition_extent = 0.f |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ saturate() [1/2]
| void hmap::saturate | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | vmin, | ||
| float | vmax, | ||
| float | from_min, | ||
| float | from_max, | ||
| float | k = 0.f |
||
| ) |
Saturate the array values based on the input interval [vmin, vmax] (the output amplitude is not modified).
This function adjusts the heightmap values to fit within the specified range [vmin, vmax]. Values outside the range [from_min, from_max] are clamped to [vmin, vmax]. The output amplitude of the heightmap remains unchanged.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap to be saturated. vmin The lower bound of the range to remap to. vmax The upper bound of the range to remap to. from_min The lower bound of the range to remap from. from_max The upper bound of the range to remap from.
Example
Result
◆ saturate() [2/2]
◆ sharpen() [1/2]
Apply a sharpening filter based on the Laplace operator.
This function applies a sharpening filter to the input array using the Laplace operator. The sharpening effect can be controlled by adjusting the ratio parameter, which determines the balance between the sharpened and non-sharpened output. A ratio of 1 applies full sharpening, while a ratio of 0 applies no sharpening.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap or image to be sharpened. p_mask Optional filter mask, expected in the range [0, 1]. If provided, sharpening is applied according to this mask. If not provided, the entire array is sharpened. ratio Ratio of the sharpening effect. A value of 1 applies full sharpening, while a value of 0 applies no sharpening. Default is 1.
Example
Result
◆ sharpen() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ sharpen_cone() [1/2]
Apply a sharpening filter based on a smooth cone filter.
This function applies a sharpening filter to the input array using a smooth cone filter. The sharpening effect can be controlled by the scale parameter, and the size of the smoothing operation is determined by the ir parameter. The optional filter mask allows selective application of the sharpening effect.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap or image to be sharpened. p_mask Optional filter mask, expected in the range [0, 1]. If provided, sharpening is applied according to this mask. If not provided, the entire array is sharpened. ir Filter radius, which determines the size of the smoothing operation. scale Sharpening scale. Adjusts the intensity of the sharpening effect. Default is 0.5.
Example
Result

◆ sharpen_cone() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ shrink() [1/4]
| void hmap::shrink | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| int | iterations = 1 |
||
| ) |
Apply shrinking, or "deflating", to emphasize the ridges in the heightmap.
This function applies a shrinking filter to the input array, which accentuates the ridges by shrinking or deflating the terrain features. The filter radius ir determines the extent of the deflation. You can also apply the shrinking effect selectively using an optional filter mask. Additionally, an alternative method using a custom kernel is available.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap to be processed. ir Filter radius, which controls the extent of the shrinking effect. p_mask Optional filter mask, expected in the range [0, 1]. If provided, shrinking is applied according to this mask. If not provided, the entire array is processed. kernel Optional custom kernel to be used for the shrinking operation. If provided, this kernel will override the default filter radius.
Example
Result

- See also
ex_expand
◆ shrink() [2/4]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ shrink() [3/4]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ shrink() [4/4]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ shrink_directional()
| void hmap::shrink_directional | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| float | angle, | ||
| float | aspect_ratio, | ||
| float | anisotropy = 1.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_mask = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Apply directional shrinking, or "deflating", to emphasize the ridges in the terrain.
This function applies a directional shrinking filter to the input array, enhancing the ridges by shrinking or deflating the terrain features with respect to a specified direction. Parameters include filter radius ir, direction angle, aspect ratio, and anisotropy to control the shape and orientation of the filter. An optional filter mask can be used for selective application.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap to be processed. ir Filter radius, which controls the extent of the shrinking effect. angle Angle (in degrees) of the directional filter. aspect_ratio Pulse aspect ratio, which influences the shape of the filter. anisotropy Pulse width ratio between upstream and downstream sides. Default is 1. p_mask Optional filter mask, expected in the range [0, 1]. If provided, shrinking is applied according to this mask. If not provided, the entire array is processed.
Example
Result

◆ smooth_cone() [1/2]
| void hmap::smooth_cone | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir | ||
| ) |
Apply a convolution filter with a cone kernel to smooth the array.
This function performs convolution on the input array using a cone-shaped kernel. The cone radius ir determines the extent of the smoothing effect. An optional filter mask can be used for selective smoothing.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap or image to be smoothed. ir Cone radius, which controls the extent of the smoothing effect. The cone's half-width is half this radius. p_mask Optional filter mask, expected in the range [0, 1]. If provided, smoothing is applied according to this mask. If not provided, the entire array is processed.
Example
Result
◆ smooth_cone() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ smooth_cpulse() [1/2]
| void hmap::smooth_cpulse | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir | ||
| ) |
Apply filtering to the array using convolution with a cubic pulse kernel.
This function performs convolution on the input array using a cubic pulse kernel. It serves as an alternative to Gaussian smoothing, offering a more compact support with potentially faster computations. For direct comparison with Gaussian smoothing, the pulse radius ir should be set to twice the desired Gaussian half-width.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap or image to be smoothed. ir Pulse radius, where the half-width of the cubic pulse kernel is half of this value. p_mask Optional filter mask, expected in the range [0, 1]. If provided, filtering is applied according to this mask. If not provided, the entire array is processed.
Example
Result
- See also
smooth_gaussian
◆ smooth_cpulse() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ smooth_cpulse_edge_removing()
| void hmap::smooth_cpulse_edge_removing | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | talus, | ||
| float | talus_width, | ||
| int | ir | ||
| ) |
Smooths an array while attenuating edges using a gradient-based pulse.
This function first computes the gradient norm of the input array, applies a sigmoid filter to highlight or attenuate regions based on the local gradient magnitude, and then performs a constrained pulse smoothing pass that respects those gradient-based weights. This is useful for smoothing heightmaps or scalar fields while preserving significant edges such as ridges or cliffs.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the input array to be smoothed. The array is modified in-place. talus Threshold value used in the sigmoid function to control where edge attenuation starts. Lower values affect more regions. talus_width Width (steepness) of the sigmoid transition zone around the talus threshold. ir Radius of the smoothing kernel used in the constrained pulse smoothing step.
◆ smooth_flat()
| void hmap::smooth_flat | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir | ||
| ) |
Applies a smoothing average filter to the given 2D array in both dimensions.
This function creates a smoothing kernel of size (2 \times \text{ir} + 1) with uniform weights, then applies a 1D convolution along both the i (rows) and j (columns) dimensions of the array to achieve a 2D smoothing effect.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the 2D array to be smoothed. ir Radius of the smoothing kernel, determining its size as (2 \times \text{ir} + 1). Larger values produce more smoothing.
◆ smooth_gaussian() [1/2]
| void hmap::smooth_gaussian | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir | ||
| ) |
Apply Gaussian filtering to the array.
This function performs convolution on the input array using a Gaussian kernel, which smooths the array by averaging values within a Gaussian-weighted neighborhood. The ir parameter specifies the Gaussian half-width, which influences the extent of the smoothing effect. An optional filter mask can be provided for selective filtering.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap or image to be smoothed. ir Gaussian half-width, which determines the extent of the smoothing effect. p_mask Optional filter mask, expected in the range [0, 1]. If provided, filtering is applied according to this mask. If not provided, the entire array is processed.
Example
Result
◆ smooth_gaussian() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ smooth_fill() [1/2]
| void hmap::smooth_fill | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| float | k = 0.1f, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Apply cubic pulse smoothing to fill lower flat regions while preserving some sharpness.
This function applies a cubic pulse smoothing technique to the input array, specifically designed to fill in lower flat regions without significantly impacting sharp features. It provides a more computationally efficient alternative to the thermal_auto_bedrock method. The p_deposition_map output field captures the amount of smoothing applied.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap or image to be processed. ir Pulse radius, which determines the extent of the smoothing effect. k Transition smoothing parameter in the range [0, 1]. It controls the balance between smoothing and preserving sharpness. p_mask Optional filter mask, expected in the range [0, 1]. If provided, smoothing is applied according to this mask. If not provided, the entire array is processed. p_deposition_map [out] Optional reference to the deposition map. This output field records the amount of deposition or smoothing applied.
Example
Result
- See also
smooth_cpulse,thermal_auto_bedrock
◆ smooth_fill() [2/2]
| void hmap::smooth_fill | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | k = 0.1f, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ smooth_fill_holes() [1/2]
| void hmap::smooth_fill_holes | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir | ||
| ) |
Apply smoothing to fill holes (elliptic concave surfaces).
This function applies a smoothing filter to the input array to fill in holes or concave surfaces. The goal is to smooth out regions that are concave, providing a more uniform appearance.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap or image to be processed. ir Filter radius, which controls the extent of the smoothing effect. p_mask Optional filter mask, expected in the range [0, 1]. If provided, smoothing is applied according to this mask. If not provided, the entire array is processed.
Example
Result
- See also
smooth_fill_smear_peaks
◆ smooth_fill_holes() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ smooth_fill_smear_peaks() [1/2]
| void hmap::smooth_fill_smear_peaks | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir | ||
| ) |
Apply smoothing to smear peaks (elliptic convex surfaces).
This function applies a smoothing filter designed to reduce the prominence of peaks or convex surfaces in the input array. It smooths out convex regions, creating a more level surface.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap or image to be processed. ir Filter radius, which controls the extent of the smoothing effect. p_mask Optional filter mask, expected in the range [0, 1]. If provided, smoothing is applied according to this mask. If not provided, the entire array is processed.
Example
Result

- See also
smooth_fill_holes
◆ smooth_fill_smear_peaks() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ smoothstep_local() [1/2]
| void hmap::smoothstep_local | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir | ||
| ) |
Applies a localized smoothstep operation to the provided array.
This function modifies the input array using a localized smoothstep operation. It calculates the local minimum and maximum values within a radius (ir) and smooths the values in the array based on these bounds.
- Parameters
-
array The 2D array to be smoothed. ir The radius used to compute the local minimum and maximum values.
Example
Result
◆ smoothstep_local() [2/2]
Applies a localized smoothstep operation to the provided array with an optional mask.
If a mask is provided, the function blends the smoothed values with the original array using the mask. Otherwise, it directly applies the localized smoothstep operation.
- Parameters
-
array The 2D array to be smoothed. ir The radius used to compute the local minimum and maximum values. p_mask A pointer to an optional mask array. If provided, the smoothed array is blended with the original using this mask.
Example
Result

◆ steepen() [1/2]
| void hmap::steepen | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | scale, | ||
| int | ir = 8 |
||
| ) |
Steepen (or flatten) the array map.
This function applies a steepening effect to the input array, enhancing the contrast of the gradients or flattening features based on the given filter amplitude. The effect is controlled by the scale parameter, and the ir parameter defines the filtering radius for computing the array gradients.
- Parameters
-
array Input array representing the heightmap or image to be processed. scale Filter amplitude that determines the extent of steepening or flattening. p_mask Optional filter mask, expected in the range [0, 1]. If provided, steepening is applied according to this mask. If not provided, the entire array is processed. ir Filtering radius of the array gradients, which influences the extent of the effect.
Example
Result
◆ steepen() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ steepen_convective() [1/2]
| void hmap::steepen_convective | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | angle, | ||
| int | iterations = 1, |
||
| int | ir = 0, |
||
| float | dt = 0.1f |
||
| ) |
Steepen array values by applying a nonlinear convection operator in a given direction.
This function applies a nonlinear convection operator to the input array, simulating the effect described by Burger's equation. The steepening effect is applied in the specified direction (angle) and is controlled by several parameters including the number of iterations, smoothing radius, and time step. The input array values are expected to be in the range [-1, 1].
- Parameters
-
array Input array with elements expected to be in the range [-1, 1]. angle Steepening direction in degrees. iterations Number of iterations to perform the convection process. ir Smoothing radius applied to the array values before differentiation. dt Time step for the convection process, can be chosen smaller than 1 for finer tuning of the steepening effect. p_mask Optional filter mask, expected in the range [0, 1]. If provided, steepening is applied according to this mask. If not provided, the entire array is processed.
Example
Result
◆ steepen_convective() [2/2]
| void hmap::steepen_convective | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | angle, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| int | iterations = 1, |
||
| int | ir = 0, |
||
| float | dt = 0.1f |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ terrace() [1/2]
| void hmap::terrace | ( | Array & | array, |
| uint | seed, | ||
| int | nlevels, | ||
| float | gain = 0.9f, |
||
| float | noise_ratio = 0.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise = nullptr, |
||
| float | vmin = 0.f, |
||
| float | vmax = -1.f |
||
| ) |
Applies a terrace effect to the values in an array.
This function adjusts the values in the array by applying a terrace or stepped effect, often used for terrain generation or other natural-looking height variations. The terrace effect is controlled by several parameters such as the number of levels, gain, noise ratio, and optional min/max range. The noise is applied to levels for added randomness, and a gain function is applied to smooth the transitions.
- Parameters
-
array The array of values to modify with the terrace effect. seed Seed value for random number generation. nlevels Number of terrace levels to apply. gain Gain factor for controlling the sharpness of the terrace levels, in [0, 1]. noise_ratio Ratio of noise applied to each terrace level, except the first and last. p_noise Optional noise array to introduce additional variation per element. vmin Minimum value for terracing; if less than vmax, will be auto-determined.vmax Maximum value for terracing; if less than vmin, will be auto-determined.
- Note
- If
p_noiseis provided, each value inarrayis transformed using both the original value and the corresponding noise value fromp_noise.
Example
Result
◆ terrace() [2/2]
| void hmap::terrace | ( | Array & | array, |
| uint | seed, | ||
| int | nlevels, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | gain = 0.9f, |
||
| float | noise_ratio = 0.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise = nullptr, |
||
| float | vmin = 0.f, |
||
| float | vmax = -1.f |
||
| ) |
Applies a terrace effect to an array with optional masking.
This overloaded version of the terrace function modifies array based on the terrace levels, gain, noise ratio, and an optional mask array. If a mask is provided, the terrace effect is applied conditionally based on the mask values.
- Parameters
-
array The array of values to modify with the terrace effect. seed Seed value for random number generation. nlevels Number of terrace levels to apply. p_mask Optional mask array. If provided, blends the terrace effect with original values based on the mask. gain Gain factor for controlling the sharpness of the terrace levels, in [0, 1]. noise_ratio Ratio of noise applied to each terrace level, except the first and last. p_noise Optional noise array to introduce additional variation per element. vmin Minimum value for terracing; if less than vmax, will be auto-determined.vmax Maximum value for terracing; if less than vmin, will be auto-determined.
This function:
- If no mask is provided, directly applies the terrace effect using the first terrace overload.
- If a mask is provided, creates a temporary copy of
array, applies the terrace effect to it, and then interpolates betweenarrayand the modified copy based on mask values.
- Note
- The mask array allows for blending the terrace effect with the original array for more localized effects.
Example
Result

◆ tessellate()
| Array hmap::tessellate | ( | Array & | array, |
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | node_density = 0.001f, |
||
| const Array * | p_weight = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Apply tessellation to the array with random node placement.
This function applies tessellation to the input array, creating a denser mesh by randomly distributing nodes based on the specified node density. The seed parameter allows for controlling the randomness of the node placement, and the p_weight reference is used to adjust the density distribution.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which tessellation will be applied. seed Random seed number to initialize the node placement. node_density Node density as a ratio relative to the number of cells in the input array. Determines the number of nodes to be added. p_weight Optional reference to the density distribution array, expected in the range [0, 1]. If provided, tessellation is influenced by this distribution.
- Returns
- Array Output array after tessellation is applied.
Example
Result
◆ wrinkle() [1/2]
| void hmap::wrinkle | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | wrinkle_amplitude, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | wrinkle_angle = 0.f, |
||
| float | displacement_amplitude = 1.f, |
||
| int | ir = 0, |
||
| float | kw = 2.f, |
||
| uint | seed = 1, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Apply wrinkle effect to the array, creating wrinkled or bumpy features.
This function adds wrinkle-like features to the input array. The wrinkle_amplitude controls the intensity of the wrinkling effect, while other parameters such as displacement_amplitude, ir, kw, seed, octaves, and weight control various aspects of the underlying noise and wrinkle generation.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which wrinkles will be applied. wrinkle_amplitude Amplitude of the wrinkle effect. p_mask Optional filter mask, expected in the range [0, 1]. If provided, the wrinkle effect is applied according to this mask. If not provided, the entire array is processed. wrinkle_angle Overall rotation angle (in degree). displacement_amplitude Drives the displacement of the wrinkles. ir Smooth filter radius applied during wrinkle generation. kw Underlying primitive wavenumber, affecting the frequency of wrinkles. seed Random seed number for generating underlying primitive noise. octaves Number of octaves used in the underlying primitive noise. weight Weight of the underlying primitive noise. bbox Bounding box for the generated wrinkles, default is {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
Example
Result
◆ wrinkle() [2/2]
| void hmap::wrinkle | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | wrinkle_amplitude, | ||
| float | wrinkle_angle = 0.f, |
||
| float | displacement_amplitude = 1.f, |
||
| int | ir = 0, |
||
| float | kw = 2.f, |
||
| uint | seed = 1, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ make_xy_function_from_array()
| std::function< float(float, float)> hmap::make_xy_function_from_array | ( | const Array & | array, |
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Create a continuous 2D function from a sampled array.
This adaptor takes a discrete 2D array (indexed by i, j) defined over a bounding box and returns a continuous function \(f(x, y)\) that interpolates values at arbitrary 2D positions inside the bounding box.
- Parameters
-
array Input array containing sampled values on a regular grid. bbox Bounding box of the array in world coordinates, given as (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax).
- Returns
- A function
f(point)that returns the interpolated value at a 2D position.
◆ create_noise_function_from_type()
| std::unique_ptr< NoiseFunction > hmap::create_noise_function_from_type | ( | NoiseType | noise_type, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed | ||
| ) |
Create a noise function based on the specified noise type.
This function creates an instance of a noise function corresponding to the specified noise_type. It initializes the noise function with the given frequency scaling vector (kw) and random seed (seed).
- Parameters
-
noise_type The type of noise function to create (e.g., PERLIN, SIMPLEX2, etc.). kw The frequency scaling vector to be used for the noise function. seed The random seed for noise generation.
- Returns
- A
std::unique_ptrto the created noise function.
◆ merge_cloud()
Merges two point clouds into one.
This function combines two separate point clouds into a single cloud by appending the points from the second cloud to the first. The resulting cloud contains all points from both input clouds.
- Parameters
-
cloud1 The first point cloud to be merged. This cloud will be the base cloud to which the points from the second cloud are added. cloud2 The second point cloud whose points will be appended to the first cloud.
- Returns
- Cloud The resulting point cloud that includes all points from both
cloud1andcloud2.
◆ merge_clouds()
◆ random_cloud()
| Cloud hmap::random_cloud | ( | size_t | count, |
| uint | seed, | ||
| const PointSamplingMethod & | method = PointSamplingMethod::RND_LHS, |
||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a random cloud of points within a bounding box.
Points are sampled according to the given sampling method, optionally seeded for reproducibility.
- Parameters
-
count Number of points to generate. seed Random number generator seed. method Sampling method to use. Defaults to PointSamplingMethod::RND_RANDOM. bbox Bounding box in which to generate the points (a,b,c,d = xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax). Defaults to the unit square {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
- Returns
- A Cloud containing the generated points.
Example
Result




◆ random_cloud_density()
| Cloud hmap::random_cloud_density | ( | size_t | count, |
| const Array & | density, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a random cloud of points based on a spatial density map.
The probability of placing a point at a location is proportional to the density value at that location.
- Parameters
-
count Number of points to generate. density 2D array representing spatial density values. seed Random number generator seed. bbox Bounding box in which to generate the points (a,b,c,d = xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax). Defaults to the unit square {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
- Returns
- A Cloud containing the generated points.
Example
Result




◆ random_cloud_distance() [1/2]
| Cloud hmap::random_cloud_distance | ( | float | min_dist, |
| uint | seed, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a random cloud of points separated by at least a given minimum distance.
Points are distributed randomly but maintain a minimum separation, producing a blue-noise-like distribution.
- Parameters
-
min_dist Minimum allowed distance between any two points. seed Random number generator seed. bbox Bounding box in which to generate the points (a,b,c,d = xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax). Defaults to the unit square {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
- Returns
- A Cloud containing the generated points.
Example
Result




◆ random_cloud_distance() [2/2]
| Cloud hmap::random_cloud_distance | ( | float | min_dist, |
| float | max_dist, | ||
| const Array & | density, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a random cloud of points separated by a distance range, influenced by a density map.
Points maintain a separation between min_dist and max_dist, and are distributed according to the provided density map.
- Parameters
-
min_dist Minimum allowed distance between points. max_dist Maximum allowed distance between points. density 2D array representing spatial density values. seed Random number generator seed. bbox Bounding box in which to generate the points (a,b,c,d = xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax). Defaults to the unit square {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
- Returns
- A Cloud containing the generated points.
Example
Result




◆ random_cloud_distance_power_law()
| Cloud hmap::random_cloud_distance_power_law | ( | float | dist_min, |
| float | dist_max, | ||
| float | alpha, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a random cloud of points with distances drawn from a power-law distribution.
Distances between points follow a power-law distribution between dist_min and dist_max, with exponent alpha.
- Parameters
-
dist_min Minimum possible distance between points. dist_max Maximum possible distance between points. alpha Power-law exponent (larger alpha favors shorter distances). seed Random number generator seed. bbox Bounding box in which to generate the points (a,b,c,d = xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax). Defaults to the unit square {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
- Returns
- A Cloud containing the generated points.
Example
Result




◆ random_cloud_distance_weibull()
| Cloud hmap::random_cloud_distance_weibull | ( | float | dist_min, |
| float | lambda, | ||
| float | k, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a random cloud of points with distances drawn from a Weibull distribution.
Distances between points follow a Weibull distribution parameterized by lambda (scale) and k (shape).
- Parameters
-
dist_min Minimum possible distance between points. lambda Weibull distribution scale parameter. k Weibull distribution shape parameter. seed Random number generator seed. bbox Bounding box in which to generate the points (a,b,c,d = xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax). Defaults to the unit square {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
- Returns
- A Cloud containing the generated points.
Example
Result




◆ random_cloud_jittered()
| Cloud hmap::random_cloud_jittered | ( | size_t | count, |
| const glm::vec2 & | jitter_amount, | ||
| const glm::vec2 & | stagger_ratio, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a jittered grid cloud of points.
Points are placed on a grid and then offset by a jitter amount, optionally staggered for a more irregular pattern.
- Parameters
-
count Number of points to generate. jitter_amount Maximum jitter to apply in each axis (x, y). stagger_ratio Ratio of staggering between consecutive rows or columns. seed Random number generator seed. bbox Bounding box in which to generate the points (a,b,c,d = xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax). Defaults to the unit square {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
- Returns
- A Cloud containing the generated points.
Example
Result




◆ convert_length_to_pixel()
| int hmap::convert_length_to_pixel | ( | float | x, |
| int | nx, | ||
| bool | lim_inf = true, |
||
| bool | lim_sup = false, |
||
| float | scale = 1.f |
||
| ) |
Converts a length value to a pixel index in a discretized space.
This function maps a floating-point length x to an integer pixel index, considering the total number of pixels nx and a scaling factor scale. Optionally, it can enforce lower and upper limits on the output index.
- Parameters
-
x The length value to be converted. nx The number of pixels in the discretized space. lim_inf If nonzero, enforces a minimum index of 1. lim_sup If nonzero, enforces a maximum index of nx - 1.scale The scaling factor relating the length to the pixel space.
- Returns
- The computed pixel index.
◆ grid_xy_vector()
| void hmap::grid_xy_vector | ( | std::vector< float > & | x, |
| std::vector< float > & | y, | ||
| glm::ivec2 | shape, | ||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, |
||
| bool | endpoint = false |
||
| ) |
Return x and y coordinates of a regular grid, as two 1D vectors.
- Parameters
-
x[out] Vector x. y[out] Vector y. shape Shape. bbox Bounding box. endpoint Include or not the endpoint.
◆ dig_path()
| void hmap::dig_path | ( | Array & | z, |
| Path & | path, | ||
| int | width = 1, |
||
| int | decay = 2, |
||
| int | flattening_radius = 16, |
||
| bool | force_downhill = false, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, |
||
| float | depth = 0.f |
||
| ) |
Dig a path on a heightmap.
This function modifies a heightmap array by "digging" a path into it based on the provided path. The path is represented by a Path object, and the function adjusts the height values in the z array to create the appearance of a dug path. The width, border decay, and flattening radius parameters control the characteristics of the dig. Optionally, the path can be forced to have a monotonically decreasing elevation.
Example
Result
- Parameters
-
z Input array representing the heightmap to be modified. path The path to be dug into the heightmap, with coordinates with respect to a unit-square. The path will be processed to create the dig effect. width Radius of the path width in pixels. This determines how wide the dug path will be. decay Radius of the path border decay in pixels. This controls how quickly the effect of the path fades out towards the edges. flattening_radius Radius used to flatten the elevation of the path, creating a smooth transition. This is measured in pixels. force_downhill If true, the path's elevation will be forced to decrease monotonically, creating a downhill effect.bbox Bounding box specifying the region of the heightmap to consider for the digging operation. It defines the area where the path is applied. depth Optional depth parameter to specify the maximum depth of the dig. If not provided, the default depth of 0.f is used.
◆ dig_river() [1/2]
| void hmap::dig_river | ( | Array & | z, |
| const std::vector< Path > & | path_list, | ||
| float | riverbank_talus, | ||
| int | river_width = 0, |
||
| int | merging_width = 0, |
||
| float | depth = 0.f, |
||
| float | riverbed_talus = 0.f, |
||
| float | noise_ratio = 0.9f, |
||
| uint | seed = 0, |
||
| Array * | p_mask = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Modifies the elevation array to carve a river along a specified path.
This function adjusts the elevation values in the input array z to simulate a river along the provided path. It incorporates parameters for riverbed and riverbank slopes, noise effects, and merging behavior to create a realistic river profile.
- Parameters
-
z The input 2D array representing the elevation map. This array will be modified in place. path The path along which the river is to be carved, represented as a sequence of points, with coordinates with respect to a unit-square. riverbank_talus The slope of the riverbank, controlling how steep the river's edges are. merging_ir The merging radius, specifying how far the effects of multiple rivers combine. riverbed_talus The slope of the riverbed, controlling how steep the riverbed is (default: 0.0). noise_ratio The proportion of random noise applied to the river's shape for realism (default: 0.9). seed The seed for the random noise generator, ensuring reproducibility (default: 0).
Example
Result
◆ dig_river() [2/2]
| void hmap::dig_river | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Path & | path, | ||
| float | riverbank_talus, | ||
| int | river_width = 0, |
||
| int | merging_width = 0, |
||
| float | depth = 0.f, |
||
| float | riverbed_talus = 0.f, |
||
| float | noise_ratio = 0.9f, |
||
| uint | seed = 0, |
||
| Array * | p_mask = nullptr |
||
| ) |
◆ find_cut_path_dijkstra()
| Path hmap::find_cut_path_dijkstra | ( | const Array & | z, |
| DomainBoundary | start, | ||
| DomainBoundary | end, | ||
| float | dijk_elevation_ratio = 0.9f, |
||
| float | dijk_distance_exponent = 2.f, |
||
| float | dijk_upward_penalization = 100.f |
||
| ) |
Find a Dijkstra-based cut path between two domain boundaries.
Selects the lowest point on the start and end boundaries of heightmap z, then computes a path between them using a weighted Dijkstra search. The path cost combines elevation, distance, and uphill penalization. The result is returned as normalized (x, y) coordinates and elevation samples.
- Parameters
-
z Heightmap array. start Boundary where the path begins. end Boundary where the path ends. dijk_elevation_ratio Weight of elevation in the cost. dijk_distance_exponent Exponent applied to distance cost. dijk_upward_penalization Extra penalty for uphill moves.
- Returns
- Path containing normalized (x, y) points and elevations.
Example
Result
◆ find_cut_path_midpoint()
| Path hmap::find_cut_path_midpoint | ( | const Array & | z, |
| DomainBoundary | start, | ||
| DomainBoundary | end, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| int | midp_iterations = 4, |
||
| float | midp_sigma = 0.2f |
||
| ) |
◆ angle() [1/2]
Computes the angle between two points relative to the x-axis.
This function calculates the angle formed by the vector from p1 to p2 with respect to the x-axis. The angle is measured in radians and is oriented in the counter-clockwise direction.
- Parameters
-
p1 The starting point of the vector. p2 The ending point of the vector.
- Returns
- The angle in radians between the vector formed by
p1top2and the x-axis. The angle is in the range [-π, π].
◆ angle() [2/2]
Computes the angle formed by three points with the reference point as the origin.
Given three points ( p0 ), ( p1 ), and ( p2 ), this function calculates the angle formed between the vectors ( p0 \rightarrow p2 ) and ( p0 \rightarrow p1 ). The angle is oriented in the 2D plane and measured in radians.
- Parameters
-
p0 The reference point (origin of the angle measurement). p1 The first point defining the angle. p2 The second point defining the angle.
- Returns
- The angle between the vectors ( p0 \rightarrow p2 ) and ( p0 \rightarrow p1 ) in radians.
- Note
- The angle is calculated using the 2D vectors defined by ( p0 \rightarrow p1 ) and ( p0 \rightarrow p2 ). The result will be in the range ([-π, π]).
◆ cross_product()
Computes the 2D cross product of vectors formed by three points.
Given three points p0, p1, and p2 in 2D space, this function computes the scalar cross product of the vectors (p1 - p0) and (p2 - p0). In 2D, the cross product is a scalar value and is often used to determine the orientation of the three points or the signed area of the parallelogram they form.
- Parameters
-
p0 The first point, which serves as the common origin of the two vectors. p1 The second point, forming the first vector p1 - p0. p2 The third point, forming the second vector p2 - p0.
- Returns
- The scalar value of the 2D cross product.
- Positive if the points p0, p1, p2 are oriented counterclockwise.
- Negative if they are oriented clockwise.
- Zero if the points are collinear.
◆ curvature()
Calculates the curvature formed by three points in 2D space.
- Parameters
-
p1 The first point of the triangle. p2 The second point of the triangle. p3 The third point of the triangle.
- Returns
- The curvature. Returns 0 if the points are collinear.
◆ distance()
Calculates the distance between two points.
This function computes the Euclidean distance between two points in 2D space.
- Parameters
-
p1 The first point. p2 The second point.
- Returns
- The distance between the two points.
◆ interp_bezier()
| Point hmap::interp_bezier | ( | const Point & | p_start, |
| const Point & | p_ctrl_start, | ||
| const Point & | p_ctrl_end, | ||
| const Point & | p_end, | ||
| float | t | ||
| ) |
Performs a cubic Bezier interpolation.
Interpolates a point on a cubic Bezier curve defined by the control points p_start, p_ctrl_start, p_ctrl_end, and p_end, using the parameter t. The parameter t should be within the range [0, 1], where t = 0 corresponds to the start point p_start and t = 1 corresponds to the end point p_end.
- Parameters
-
p_start The first control point (start point). p_ctrl_start The second control point. p_ctrl_end The third control point. p_end The fourth control point (end point). t The interpolation parameter, ranging from 0 to 1.
- Returns
- The interpolated point on the Bezier curve.
Example
Result
◆ interp_bspline()
| Point hmap::interp_bspline | ( | const Point & | p0, |
| const Point & | p1, | ||
| const Point & | p2, | ||
| const Point & | p3, | ||
| float | t | ||
| ) |
Performs a cubic B-spline interpolation.
Interpolates a point on a cubic B-spline curve using the control points p0, p1, p2, and p3. The points p1 and p2 define the segment of the curve to be interpolated, while p0 and p3 are used as additional control points. The parameter t should be within the range [0, 1], where t = 0 corresponds to the start point p1 and t = 1 corresponds to the end point p2.
- Parameters
-
p0 The first control point (influence for the start point). p1 The second control point (start point of the segment). p2 The third control point (end point of the segment). p3 The fourth control point (influence for the end point). t The interpolation parameter, ranging from 0 to 1.
- Returns
- The interpolated point on the B-spline curve.
Example
Result

◆ interp_catmullrom()
| Point hmap::interp_catmullrom | ( | const Point & | p0, |
| const Point & | p1, | ||
| const Point & | p2, | ||
| const Point & | p3, | ||
| float | t | ||
| ) |
Performs a Catmull-Rom spline interpolation.
Interpolates a point on a Catmull-Rom spline defined by the points p0, p1, p2, and p3. The points p1 and p2 define the segment of the curve to be interpolated, while p0 and p3 are used as additional control points. The parameter t should be within the range [0, 1], where t = 0 corresponds to the start point p1 and t = 1 corresponds to the end point p2.
- Parameters
-
p0 The first control point (influence for the start point). p1 The second control point (start point of the segment). p2 The third control point (end point of the segment). p3 The fourth control point (influence for the end point). t The interpolation parameter, ranging from 0 to 1.
- Returns
- The interpolated point on the Catmull-Rom spline.
Example
Result

◆ interp_decasteljau()
Performs a De Casteljau algorithm-based interpolation for Bezier curves.
Interpolates a point on a Bézier curve defined by a set of control points using De Casteljau's algorithm. The algorithm is recursive and provides a stable and numerically robust method to evaluate Bézier curves at a given parameter t.
The parameter t should be within the range [0, 1], where t = 0 corresponds to the first control point and t = 1 corresponds to the last control point.
- Parameters
-
points A vector of control points defining the Bézier curve. t The interpolation parameter, ranging from 0 to 1.
- Returns
- The interpolated point on the Bézier curve.
Example
Result

◆ intersect_bounding_boxes()
| glm::vec4 hmap::intersect_bounding_boxes | ( | const glm::vec4 & | bbox1, |
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox2 | ||
| ) |
Determines the intersection of two bounding boxes.
This function calculates the intersection of two bounding boxes, bbox1 and bbox2. If they intersect, it returns the intersecting bounding box. If they are disjoint, it returns std::nullopt.
- Parameters
-
bbox1 The first bounding box defined as glm::vec4.bbox2 The second bounding box defined as glm::vec4.
- Returns
- An
std::optional<glm::vec4>containing the intersecting bounding box if an intersection exists;std::nulloptotherwise.
◆ is_point_within_bounding_box() [1/2]
| bool hmap::is_point_within_bounding_box | ( | Point | p, |
| glm::vec4 | bbox | ||
| ) |
Checks if a point is within a specified bounding box.
This function determines if a given point p lies within the rectangular bounding box defined by bbox.
- Parameters
-
p The point to check, represented as a Pointwithxandycoordinates.bbox The bounding box defined as a glm::vec4, whereaandbare the horizontal boundaries (min and max x), andcanddare the vertical boundaries (min and max y).
- Returns
trueif the point is within the bounding box;falseotherwise.
◆ is_point_within_bounding_box() [2/2]
| bool hmap::is_point_within_bounding_box | ( | float | x, |
| float | y, | ||
| glm::vec4 | bbox | ||
| ) |
Checks if a point is within a specified bounding box.
This function determines if a point with coordinates (x, y) lies within the rectangular bounding box defined by bbox.
- Parameters
-
x The x-coordinate of the point to check. y The y-coordinate of the point to check. bbox The bounding box defined as a glm::vec4, whereaandbare the horizontal boundaries (min and max x), andcanddare the vertical boundaries (min and max y).
- Returns
trueif the point is within the bounding box;falseotherwise.
◆ lerp() [1/4]
Linearly interpolates between two points.
This function performs linear interpolation between two points based on a given factor. The interpolation factor t should be in the range [0, 1], where 0 corresponds to the first point and 1 corresponds to the second point.
- Parameters
-
p1 The starting point. p2 The ending point. t The interpolation factor (0 <= t <= 1).
- Returns
- The interpolated point between
p1andp2.
- Note
- If
tis outside the range [0, 1], the function will still return a point outside the segment defined byp1andp2.
◆ midpoint()
| Point hmap::midpoint | ( | const Point & | p1, |
| const Point & | p2, | ||
| int | orientation, | ||
| float | distance_ratio, | ||
| float | t = 0.5f |
||
| ) |
Computes the midpoint displacement in 1D with a perpendicular displacement.
This function generates a midpoint between two points p1 and p2 based on a linear interpolation parameter t. It then displaces this midpoint in the direction perpendicular to the line segment formed by p1 and p2. The displacement distance is determined by the distance_ratio parameter and the orientation (which can be -1 or 1).
- Parameters
-
p1 The first point. p2 The second point. orientation Determines the direction of the perpendicular displacement. - A value of
1displaces the midpoint in the positive perpendicular direction. - A value of
-1displaces the midpoint in the negative perpendicular direction.
distance_ratio The ratio of the displacement distance relative to the length of the line segment p1p2.t The interpolation factor (default is 0.5) for computing the midpoint between p1andp2, before the displacement. - A value of
- Returns
- A
Pointrepresenting the displaced midpoint.
◆ sort_points()
| void hmap::sort_points | ( | std::vector< Point > & | points | ) |
Sorts a vector of points in ascending order based on their coordinates.
This function sorts the provided vector of Point objects first by the x-coordinate and then by the y-coordinate in ascending order. The sorting is done in-place.
- Parameters
-
points A vector of Pointobjects to be sorted. The vector is modified directly with the points arranged in ascending order.
◆ triangle_area()
Calculates the area of a triangle formed by three points in 2D space.
This function uses the determinant method to compute the absolute area of a triangle given three points (p1, p2, p3). It assumes the points are specified as 2D coordinates.
- Parameters
-
p1 The first point of the triangle. p2 The second point of the triangle. p3 The third point of the triangle.
- Returns
- The area of the triangle as a floating-point value. Returns 0 if the points are collinear.
◆ unit_square_bbox()
| glm::vec4 hmap::unit_square_bbox | ( | ) |
Constructs a 4D bounding box for a unit square.
This function returns a glm::vec4 object representing the bounding box of a unit square, with components (min_x, max_x, min_y, max_y) set to (0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f).
- Returns
- glm::vec4 A 4D vector representing the unit square's bounding box.
◆ bbox_to_ranges2d()
| std::array< std::pair< float, float >, 2 > hmap::bbox_to_ranges2d | ( | const glm::vec4 & | bbox | ) |
Converts a 2D bounding box into coordinate ranges.
This function takes a bounding box defined by four values (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax) stored in a glm::vec4 and returns an array of two ranges:
- ranges[0] = {xmin, xmax}
- ranges[1] = {ymin, ymax}
- Parameters
-
bbox Bounding box in the format {xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax}.
- Returns
- An array of two pairs:
- First pair: x-axis range (min, max)
- Second pair: y-axis range (min, max)
◆ expand_points_domain()
| void hmap::expand_points_domain | ( | std::vector< float > & | x, |
| std::vector< float > & | y, | ||
| std::vector< float > & | value, | ||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Expand grid by translating and copying the values of the current bounding box to the 8 first neighboring bounding boxes.
- Parameters
-
x xcoordinates.y ycoordinates.value values. bbox Bounding box.
◆ expand_points_at_domain_boundaries()
| void hmap::expand_points_at_domain_boundaries | ( | std::vector< float > & | x, |
| std::vector< float > & | y, | ||
| std::vector< float > & | value, | ||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, |
||
| float | boundary_value = 0.f |
||
| ) |
Expand the grid by adding points on the boundaries of the bounding box.
- Parameters
-
x xcoordinates.y ycoordinates.value values. bbox Bounding box. corner_value Value at the boundary points.
◆ expand_points_domain_corners()
| void hmap::expand_points_domain_corners | ( | std::vector< float > & | x, |
| std::vector< float > & | y, | ||
| std::vector< float > & | value, | ||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, |
||
| float | corner_value = 0.f |
||
| ) |
Expand the grid by adding four points at the corner of the bounding box.
- Parameters
-
x xcoordinates.y ycoordinates.value values. bbox Bounding box. corner_value Value at the four corner points.
◆ make_pointwise_function_from_array()
| std::function< float(const ps::Point< float, 2 > &)> hmap::make_pointwise_function_from_array | ( | const Array & | array, |
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox | ||
| ) |
Create a continuous 2D function from a sampled array.
This adaptor takes a discrete 2D array (indexed by i, j) defined over a bounding box and returns a continuous function \(f(x, y)\) that interpolates values at arbitrary 2D positions inside the bounding box.
The function maps a point \(p = (x, y)\) in world coordinates to array indices \((i, j)\) and interpolates the array values.
- Parameters
-
array Input array containing sampled values on a regular grid. bbox Bounding box of the array in world coordinates, given as (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax).
- Returns
- A function
f(point)that returns the interpolated value at a 2D position.
- Example
- Array heightmap = [...];glm::vec4 bbox = {0.0f, 100.0f, 0.0f, 100.0f};ps::Point<float, 2> p{25.5f, 42.3f};std::function< float(const ps::Point< float, 2 > &)> make_pointwise_function_from_array(const Array &array, const glm::vec4 &bbox)Create a continuous 2D function from a sampled array.Definition point_sampling.cpp:26
◆ random_points()
| std::array< std::vector< float >, 2 > hmap::random_points | ( | size_t | count, |
| uint | seed, | ||
| const PointSamplingMethod & | method = PointSamplingMethod::RND_RANDOM, |
||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates random 2D points within a bounding box using a sampling method.
- Parameters
-
count Number of points to generate. seed Random number generator seed. method Sampling method to use. Defaults to PointSamplingMethod::RND_RANDOM. bbox Bounding box in which to generate the points (a,b,c,d = xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax). Defaults to the unit square {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
- Returns
- A pair of float vectors {x_coords, y_coords}.
◆ random_points_density()
| std::array< std::vector< float >, 2 > hmap::random_points_density | ( | size_t | count, |
| const Array & | density, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates random 2D points within a bounding box based on a density map.
Points are sampled with probability proportional to the density values.
- Parameters
-
count Number of points to generate. density 2D array representing spatial density values. seed Random number generator seed. bbox Bounding box in which to generate the points (a,b,c,d = xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax). Defaults to the unit square {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
- Returns
- A pair of float vectors {x_coords, y_coords}.
◆ random_points_distance() [1/2]
| std::array< std::vector< float >, 2 > hmap::random_points_distance | ( | float | min_dist, |
| uint | seed, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates random 2D points with a minimum separation distance.
Produces a blue-noise-like distribution where no two points are closer than min_dist.
- Parameters
-
min_dist Minimum allowed distance between points. seed Random number generator seed. bbox Bounding box in which to generate the points (a,b,c,d = xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax). Defaults to the unit square {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
- Returns
- A pair of float vectors {x_coords, y_coords}.
◆ random_points_distance() [2/2]
| std::array< std::vector< float >, 2 > hmap::random_points_distance | ( | float | min_dist, |
| float | max_dist, | ||
| const Array & | density, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates random 2D points with distance constraints and a density map.
Points are separated by distances between min_dist and max_dist, and are sampled proportionally to the given density map.
- Parameters
-
min_dist Minimum allowed distance between points. max_dist Maximum allowed distance between points. density 2D array representing spatial density values. seed Random number generator seed. bbox Bounding box in which to generate the points (a,b,c,d = xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax). Defaults to the unit square {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
- Returns
- A pair of float vectors {x_coords, y_coords}.
◆ random_points_distance_power_law()
| std::array< std::vector< float >, 2 > hmap::random_points_distance_power_law | ( | float | dist_min, |
| float | dist_max, | ||
| float | alpha, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates random 2D points with distances drawn from a power-law distribution.
Distances between points follow a power-law distribution between dist_min and dist_max, with exponent alpha.
- Parameters
-
dist_min Minimum possible distance between points. dist_max Maximum possible distance between points. alpha Power-law exponent (larger alpha favors shorter distances). seed Random number generator seed. bbox Bounding box in which to generate the points (a,b,c,d = xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax). Defaults to the unit square {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
- Returns
- A pair of float vectors {x_coords, y_coords}.
◆ random_points_distance_weibull()
| std::array< std::vector< float >, 2 > hmap::random_points_distance_weibull | ( | float | dist_min, |
| float | lambda, | ||
| float | k, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates random 2D points with distances drawn from a Weibull distribution.
Distances between points follow a Weibull distribution parameterized by lambda (scale) and k (shape).
- Parameters
-
dist_min Minimum possible distance between points. lambda Weibull distribution scale parameter. k Weibull distribution shape parameter. seed Random number generator seed. bbox Bounding box in which to generate the points (a,b,c,d = xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax). Defaults to the unit square {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
- Returns
- A pair of float vectors {x_coords, y_coords}.
◆ random_points_jittered()
| std::array< std::vector< float >, 2 > hmap::random_points_jittered | ( | size_t | count, |
| const glm::vec2 & | jitter_amount, | ||
| const glm::vec2 & | stagger_ratio, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates jittered grid-based 2D points.
Points are placed on a regular grid, offset by jitter_amount, and optionally staggered according to stagger_ratio.
- Parameters
-
count Number of points to generate. jitter_amount Maximum jitter to apply in each axis (x, y). stagger_ratio Ratio of staggering between consecutive rows or columns. seed Random number generator seed. bbox Bounding box in which to generate the points (a,b,c,d = xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax). Defaults to the unit square {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
- Returns
- A pair of float vectors {x_coords, y_coords}.
◆ remove_points_outside_bbox()
| void hmap::remove_points_outside_bbox | ( | std::vector< float > & | x, |
| std::vector< float > & | y, | ||
| std::vector< float > & | value, | ||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Remove grid points that are outside a given bounding box.
- Parameters
-
x xcoordinates.y ycoordinates.value Values at points. bbox Bounding box.
◆ rescale_points_to_unit_square()
| void hmap::rescale_points_to_unit_square | ( | std::vector< float > & | x, |
| std::vector< float > & | y, | ||
| glm::vec4 | bbox | ||
| ) |
Rescale coordinate (x, y) so that they fit in a unit-square box based on a given initial bounding box.
- Parameters
-
x[in,out] xcoordinates (output).y[in,out] ycoordinates (output).bbox Initial bounding box.
◆ divergence_from_gradients()
Compute the divergence of a 2D gradient field.
Given two scalar fields representing the horizontal and vertical derivatives of a height map:
\[ p(x, y) = \frac{\partial h}{\partial x}, \qquad q(x, y) = \frac{\partial h}{\partial y} \]
this function returns the divergence:
\[ f(x, y) = \frac{\partial p}{\partial x}(x, y) + \frac{\partial q}{\partial y}(x, y) \]
The divergence is a key term for solving the Poisson equation \(\nabla^2 h = f\) when reconstructing a height field from gradients or from a normal map.
- Parameters
-
dx Array of horizontal derivatives ( \(\partial h / \partial x\)). Must have the same dimensions as dy.dy Array of vertical derivatives ( \(\partial h / \partial y\)). Must have the same dimensions as dx.
- Returns
- A new Array containing the divergence \(f(x, y)\) for each pixel. The returned array has the same size as the inputs.
◆ gradient1d()
| std::vector< float > hmap::gradient1d | ( | const std::vector< float > & | v | ) |
Compute the gradient of a 1D vector.
This function calculates the gradient of a 1D vector by computing the difference between successive elements.
- Parameters
-
v Input vector of floats.
- Returns
- std::vector<float> Vector of gradient values.
◆ gradient_angle()
Compute the polar angle of the gradient of a 2D array.
This function calculates the gradient angle of a 2D array, which represents the direction of the steepest ascent. The angle is measured in radians and falls within the range [-π, π]. The direction can be inverted if the downward flag is set to true.
- Parameters
-
array Input 2D array. downward If true, invert the direction of the gradient.
- Returns
- Array Gradient angles in radians.
Example
Result
◆ gradient_angle_circular_smoothing()
| Array hmap::gradient_angle_circular_smoothing | ( | const Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| bool | downward = false |
||
| ) |
Computes a smoothed gradient angle (aspect) field with circular unwrapping.
This function computes the gradient angle (aspect) of the input scalar field and applies a circular smoothing to remove discontinuities caused by the ±π wrap of the arctangent. The angle field is smoothed by converting the angle to a unit vector representation on the circle, applying a local smoothing kernel, and converting it back to an angle. This results in a continuous aspect map that is ideal for visualization or further processing.
- Parameters
-
array Input scalar field (e.g., a heightmap). ir Radius of the local smoothing kernel applied to the angle vectors. downward If set to true, angles are adjusted to point in the downslope direction (useful for hydrology or flow simulations). Iffalse, angles point in the upslope direction.
- Returns
- An Array containing the smoothed gradient angles in radians, in the range [-π, π].
- Note
- Regions with very low gradient magnitude may produce unstable angle values; these regions should typically be masked or treated separately.
- This function is suited for preserving continuous angular fields when the direction (not the orientation) of the gradient matters.
Example
Result

◆ gradient_norm()
Compute the gradient norm of a 2D array.
This function calculates the gradient norm (magnitude) of a 2D array. Optionally, the x and y gradients can be computed and stored in p_dx and p_dy respectively.
- Parameters
-
array Input 2D array. p_dx Pointer to an Array where the x-gradient will be stored (optional). p_dy Pointer to an Array where the y-gradient will be stored (optional).
- Returns
- Array Gradient norm (magnitude).
Example
Result
◆ gradient_norm_prewitt()
| Array hmap::gradient_norm_prewitt | ( | const Array & | array, |
| Array * | p_dx = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_dy = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Compute the gradient norm of a 2D array using the Prewitt filter.
This function calculates the gradient norm (magnitude) using the Prewitt filter for gradient computation. Optionally, the x and y gradients can be computed and stored in p_dx and p_dy respectively.
- Parameters
-
array Input 2D array. p_dx Pointer to an Array where the x-gradient will be stored (optional). p_dy Pointer to an Array where the y-gradient will be stored (optional).
- Returns
- Array Gradient norm (magnitude).
Example
Result

◆ gradient_norm_scharr()
| Array hmap::gradient_norm_scharr | ( | const Array & | array, |
| Array * | p_dx = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_dy = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Compute the gradient norm of a 2D array using the Scharr filter.
This function calculates the gradient norm (magnitude) using the Scharr filter for gradient computation. Optionally, the x and y gradients can be computed and stored in p_dx and p_dy respectively.
- Parameters
-
array Input 2D array. p_dx Pointer to an Array where the x-gradient will be stored (optional). p_dy Pointer to an Array where the y-gradient will be stored (optional).
- Returns
- Array Gradient norm (magnitude).
◆ gradient_norm_sobel()
| Array hmap::gradient_norm_sobel | ( | const Array & | array, |
| Array * | p_dx = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_dy = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Compute the gradient norm of a 2D array using the Sobel filter.
This function calculates the gradient norm (magnitude) using the Sobel filter for gradient computation. Optionally, the x and y gradients can be computed and stored in p_dx and p_dy respectively.
- Parameters
-
array Input 2D array. p_dx Pointer to an Array where the x-gradient will be stored (optional). p_dy Pointer to an Array where the y-gradient will be stored (optional).
- Returns
- Array Gradient norm (magnitude).
◆ gradient_talus() [1/2]
Compute the gradient talus slope of a 2D array.
The talus slope is defined as the largest elevation difference between a cell and its immediate neighbors. This function computes the talus slope for the given 2D array.
- Parameters
-
array Input 2D array.
- Returns
- Array Gradient talus slope.
◆ gradient_talus() [2/2]
Compute the gradient talus slope and store it in the provided array.
This overload computes the gradient talus slope of a 2D array and stores the result in the given talus array.
- Parameters
-
array Input 2D array. talus Output array where the gradient talus slope will be stored. This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ gradient_x() [1/2]
Compute the gradient in the x-direction of a 2D array.
This function calculates the gradient in the x-direction (i.e., horizontal gradient) for the given 2D array.
- Parameters
-
array Input 2D array.
- Returns
- Array Gradient in the x-direction.
◆ gradient_x() [2/2]
Compute the gradient in the x-direction of a 2D array and store it.
This overload calculates the gradient in the x-direction and stores the result in the provided dx array.
- Parameters
-
array Input 2D array. dx Output array where the gradient in the x-direction will be stored. This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ gradient_y() [1/2]
Compute the gradient in the y-direction of a 2D array.
This function calculates the gradient in the y-direction (i.e., vertical gradient) for the given 2D array.
- Parameters
-
array Input 2D array.
- Returns
- Array Gradient in the y-direction.
◆ gradient_y() [2/2]
Compute the gradient in the y-direction of a 2D array and store it.
This overload calculates the gradient in the y-direction and stores the result in the provided dy array.
- Parameters
-
array Input 2D array. dy Output array where the gradient in the y-direction will be stored. This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ laplacian()
Compute the Laplacian of a 2D array.
The Laplacian is a measure of the second-order spatial derivative of the input array. This function computes the Laplacian for the given 2D array.
- Parameters
-
array Input 2D array.
- Returns
- Array Laplacian of the input array.
◆ normal_map()
Generates a normal map from a given 2D array.
This function calculates the normal vectors for each element in the 2D array and returns them as a tensor. The normal map is commonly used in image processing and 3D graphics to represent surface orientations based on height values.
- Parameters
-
array A 2D array representing the height values from which normals are computed.
- Returns
- A tensor containing the normal vectors for each position in the input array.
◆ normal_map_to_heightmap()
Converts a normal map to a heightmap using direct summation of gradients.
This function computes a heightmap from a given normal map (nmap) by integrating gradients derived from the normal map in two passes. The result is the average of two independent integrations to reduce artifacts from directional bias.
- Parameters
-
nmap A 3D tensor representing the normal map. It should have three channels (X, Y, Z) and a shape of (width, height, 3). The values are assumed to be in the range [0, 1].
- Returns
- An
Arrayobject representing the computed heightmap with the same spatial dimensions as the input normal map (width, height).
- Note
- The algorithm assumes the normal map values are normalized between 0 and 1.
- Two heightmaps (
z1andz2) are computed using different traversal orders, and the final result is their average to reduce directional bias. - Example #include "highmap.hpp"int main(void){glm::ivec2 shape = {256, 256};glm::vec2 res = {4.f, 4.f};int seed = 1;hmap::Tensor nmap = hmap::normal_map(z1);// rebuild input elevation field from normal maphmap::Array z2 = hmap::normal_map_to_heightmap(nmap);// Poisson solverhmap::Array z3 = hmap::normal_map_to_heightmap_poisson(nmap);hmap::remap(z1);hmap::remap(z2);hmap::remap(z3);hmap::export_banner_png("ex_normal_map_to_heightmap.png",{z1, z2, z3},}Array normal_map_to_heightmap(const Tensor &nmap)Converts a normal map to a heightmap using direct summation of gradients.Definition normal_map.cpp:32Array normal_map_to_heightmap_poisson(const Tensor &nmap, int iterations=500, float omega=1.5f)Reconstruct a height/displacement map from a normal map by solving a Poisson equation with Gauss–Seid...Definition normal_map.cpp:65Tensor normal_map(const Array &array)Generates a normal map from a given 2D array.Definition normal_map.cpp:12
Result
◆ normal_map_to_heightmap_poisson()
| Array hmap::normal_map_to_heightmap_poisson | ( | const Tensor & | nmap, |
| int | iterations = 500, |
||
| float | omega = 1.5f |
||
| ) |
Reconstruct a height/displacement map from a normal map by solving a Poisson equation with Gauss–Seidel iteration.
The reconstruction is unique up to an additive constant. After solving, you may subtract the mean or normalize to a desired range.
- Parameters
-
nmap Input normal map as a 2D tensor. - Channel 0 = (N_x), channel 1 = (N_y), channel 2 = (N_z).
- Values are expected in [0,1] or [-1,1]; if stored in [0,1], they will be remapped internally to [-1,1].
iterations Number of Gauss–Seidel iterations to perform (default = 500). Higher values improve accuracy but increase runtime. omega Relaxation factor (1.0 = pure Gauss–Seidel; 1.0–2.0 = over-relaxation). Recommended: 1.2–1.5 for faster convergence.
- Returns
- * A 2D Array containing the reconstructed height map. Values are not normalized; apply scaling or centering if needed. Example** #include "highmap.hpp"int main(void){glm::ivec2 shape = {256, 256};glm::vec2 res = {4.f, 4.f};int seed = 1;hmap::Tensor nmap = hmap::normal_map(z1);// rebuild input elevation field from normal maphmap::Array z2 = hmap::normal_map_to_heightmap(nmap);// Poisson solverhmap::Array z3 = hmap::normal_map_to_heightmap_poisson(nmap);hmap::remap(z1);hmap::remap(z2);hmap::remap(z3);hmap::export_banner_png("ex_normal_map_to_heightmap.png",{z1, z2, z3},}
Result

◆ phase_field()
| Array hmap::phase_field | ( | const Array & | array, |
| float | kw, | ||
| int | width, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | noise_amp = 0.f, |
||
| int | prefilter_ir = -1, |
||
| float | density_factor = 1.f, |
||
| bool | rotate90 = false, |
||
| Array * | p_gnoise_x = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_gnoise_y = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Computes a phase field using spatially varying Gabor noise based on the input heightmap.
This function generates a 2D phase field by combining gradient angles from the input array and Gabor noise, which is spatially distributed with varying parameters. The resulting phase field can be used for procedural terrain generation or other simulations.
- Parameters
-
[in] array The input 2D heightmap array. [in] kw Wave number for the Gabor kernel, determining the frequency of the noise. [in] width Width of the Gabor kernel. [in] seed Random seed for reproducible Gabor noise generation. [in] noise_amp Noise amplitude added to the phase field. [in] prefilter_ir Kernel radius for pre-smoothing the input array. If negative, a default value is computed. [in] density_factor Factor controlling the density of the noise points. [in] rotate90 Boolean flag to rotate the gradient angles by 90 degrees. [out] p_gnoise_x Optional pointer to store the generated Gabor noise in the X direction. [out] p_gnoise_y Optional pointer to store the generated Gabor noise in the Y direction.
- Returns
- A 2D array representing the computed phase field.
- Example #include "highmap.hpp"int main(void){glm::ivec2 shape = {256, 256};glm::vec2 kw = {2.f, 2.f};int seed = 0;hmap::remap(z);float kp = 4.f;int width = 64;float density = 4.f;bool rotate90 = true;hmap::Array phi0 = hmap::phase_field(z, kp, width, ++seed, -1, density);hmap::Array phi1 =hmap::phase_field(z, kp, width, ++seed, -1, density, rotate90);hmap::remap(phi0);hmap::remap(phi1);hmap::export_banner_png("ex_phase_field.png",{z, phi0, phi1},}Array phase_field(const Array &array, float kw, int width, uint seed, float noise_amp=0.f, int prefilter_ir=-1, float density_factor=1.f, bool rotate90=false, Array *p_gnoise_x=nullptr, Array *p_gnoise_y=nullptr)Computes a phase field using spatially varying Gabor noise based on the input heightmap.Definition phase_field.cpp:16
Result

◆ solve_poisson_gauss_seidel()
| void hmap::solve_poisson_gauss_seidel | ( | const Array & | rhs, |
| Array & | h, | ||
| int | iterations = 500, |
||
| float | omega = 1.0f |
||
| ) |
Solve the Poisson equation ∇²h = rhs using Gauss–Seidel iteration.
This function assumes Dirichlet boundary conditions (height = 0 at the edges). The algorithm updates interior points according to:
\[ h(x, y) = (1 - \omega) h(x, y) + \omega \cdot 0.25 \big( h(x+1, y) + h(x-1, y) + h(x, y+1) + h(x, y-1) - rhs(x, y) \big) \]
- Parameters
-
rhs Right-hand side (divergence of gradients). h Height field to update; initialized to 0 or an estimate. iterations Number of Gauss–Seidel iterations to run. omega Relaxation parameter (1 = standard Gauss–Seidel, 1 < omega < 2 = over-relaxation).
◆ unwrap_phase()
Unwraps a 2D phase array to correct discontinuities in phase data.
This function unwraps phase values in the given array, ensuring that discontinuities exceeding \( \pi \) are adjusted to provide a continuous phase result.
- Parameters
-
alpha A 2D array of wrapped phase values.
- Returns
- A 2D array of unwrapped phase values.
Example
Result

◆ basin_id()
| Array hmap::basin_id | ( | const Array & | z, |
| FlowDirectionMethod | fd_method = FlowDirectionMethod::FDM_D8, |
||
| bool | remove_lakes = true |
||
| ) |
Label drainage basins using a priority-flood algorithm.
Starting from boundary cells, this function floods a 2D scalar field inward using a height-ordered priority queue and assigns each cell to a basin. Each boundary cell initializes a unique basin.
Connectivity is 8-neighbor. Spill elevations between basins are detected but not yet recorded.
- Parameters
-
z Input 2D elevation array.
- Returns
- Array of basin identifiers with the same shape as
z.
Example
Result
◆ d8_compute_ndip()
Computes the number of drainage paths for each cell based on the D8 flow direction model.
This function calculates the number of neighboring cells that have flow directions pointing to the current cell according to the D8 model. The result is an array where each cell contains the count of its incoming flow directions.
- Parameters
-
d8 Input array representing the flow directions according to the D8 model. Each cell value indicates the direction of flow according to the D8 convention.
- Returns
- Array An array where each cell contains the number of incoming flow directions pointing to it.
◆ find_flow_apex()
| void hmap::find_flow_apex | ( | const Array & | z, |
| std::vector< int > & | is, | ||
| std::vector< int > & | js | ||
| ) |
Identifies flow apex (source) cells using D8 flow routing.
A flow apex is defined as a cell with zero inflow neighbors (no upstream contributors) in the D8 flow graph. These cells correspond to drainage sources, ridge heads, or local flow origins.
- Parameters
-
z Input elevation field. is Output x-coordinates of flow apex cells. js Output y-coordinates of flow apex cells.
◆ find_flow_sinks() [1/2]
| void hmap::find_flow_sinks | ( | const Array & | z, |
| std::vector< int > & | is, | ||
| std::vector< int > & | js | ||
| ) |
Identifies the indices of flow sinks within the heightmap.
This function locates the cells in the heightmap that are flow sinks (cells with no outflow) and returns their indices. Flow sinks are cells that do not direct flow to any other cell.
- Parameters
-
z Input array representing the heightmap values. is Output vector containing the row indices iof the flow sinks.js Output vector containing the column indices jof the flow sinks.
Example
◆ find_flow_sinks() [2/2]
| std::vector< glm::ivec2 > hmap::find_flow_sinks | ( | const Array & | z | ) |
◆ flooding_uniform_level()
Compute water depth for a uniform flooding level.
Subtracts terrain elevation from a reference water level and clamps negative values to zero.
- Parameters
-
z Input elevation array. zref Reference water level.
- Returns
- Water depth array (0 where terrain is above zref).
Example
Result

◆ flooding_from_boundaries()
| Array hmap::flooding_from_boundaries | ( | const Array & | z, |
| float | zref, | ||
| bool | from_east = true, |
||
| bool | from_west = true, |
||
| bool | from_north = true, |
||
| bool | from_south = true |
||
| ) |
Compute flooding starting from the lowest boundary points.
Finds the lowest elevation on the selected boundaries and simulates flooding from those points up to a reference water level.
- Parameters
-
z Input elevation array. zref Reference water level. from_east Include east boundary. from_west Include west boundary. from_north Include north boundary. from_south Include south boundary.
- Returns
- Water depth array.
Example
Result

◆ flooding_from_point() [1/2]
| Array hmap::flooding_from_point | ( | const Array & | z, |
| int | i, | ||
| int | j, | ||
| float | depth_min = std::numeric_limits<float>::max() |
||
| ) |
Flood terrain starting from a single seed point.
Fills areas below a reference level by propagating from the given cell until higher ground is reached.
- Parameters
-
z Input elevation array. i Seed point X index. j Seed point Y index. depth_min Water depth at the source point (if max, uses 0).
- Returns
- Water depth array.
Example
Result

◆ flooding_from_point() [2/2]
| Array hmap::flooding_from_point | ( | const Array & | z, |
| const std::vector< int > & | i, | ||
| const std::vector< int > & | j, | ||
| float | depth_min = std::numeric_limits<float>::max() |
||
| ) |
Flood terrain starting from multiple seed points.
Merges flooding results from each point below the reference level.
- Parameters
-
z Input elevation array. i List of X indices for seeds. j List of Y indices for seeds. depth_min Water depth at the source point (if max, uses 0).
- Returns
- Water depth array.
Example
Result

◆ flooding_lake_system()
Estimate lake water depths on a terrain by filling depressions.
This function identifies depressions in a terrain elevation model and simulates the flooding of these areas to produce a lake system. It uses a rough depression-filling algorithm to compute the water surface, then subtracts the original elevations to obtain the water depth at each cell.
- Parameters
-
z Input 2D array representing terrain elevations (height field). surface_threshold The minimum number of pixels a component must have to be retained. Components smaller than this threshold will be removed. The default value is 0 (no filtering).
- Returns
- A 2D array representing the water depth for each cell. Values are zero where no lake is present and positive where water accumulates in depressions.
- See also
- depression_filling
Example
Result
◆ flow_accumulation_d8()
Computes the flow accumulation for each cell using the D8 flow direction model.
This function calculates the flow accumulation for each cell in the heightmap based on the D8 flow direction model [Zhou2019]. Flow accumulation represents the total amount of flow that accumulates at each cell from upstream cells.
- Parameters
-
z Input array representing the heightmap values.
- Returns
- Array An array where each cell contains the computed flow accumulation.
Example
Result
- See also
- flow_direction_d8
◆ flow_accumulation_dinf()
Computes the flow accumulation for each cell using the Multiple Flow Direction (MFD) model.
This function calculates the flow accumulation for each cell based on the MFD model [Qin2007]. Flow accumulation represents the total amount of flow that accumulates at each cell from upstream cells. The flow-partition exponent is locally defined using a reference talus value, where smaller values of talus_ref will lead to narrower flow streams. The maximum talus value of the heightmap can be used as a reference.
- Parameters
-
z Input array representing the heightmap values. talus_ref Reference talus used to locally define the flow-partition exponent. Small values will result in thinner flow streams.
- Returns
- Array An array where each cell contains the computed flow accumulation.
Example
Result

- See also
- flow_direction_dinf, flow_accumulation_d8
◆ flow_direction_d8()
Computes the flow direction from each cell to its downslope neighbor using the D8 model.
This function calculates the direction of flow for each cell in the heightmap using the D8 flow direction model [Greenlee1987]. The D8 model defines eight possible flow directions as follows:
5 6 7 4 . 0 3 2 1 *
- Parameters
-
z Input array representing the heightmap values.
- Returns
- Array An array where each cell contains the flow direction according to the D8 nomenclature.
- See also
- flow_accumulation_d8
◆ flow_direction_dinf()
Computes the flow direction and weights for each direction using the Multiple Flow Direction (MFD) model.
This function calculates the flow direction for each cell and provides the weight for each possible flow direction using the MFD model [Qin2007]. The flow-partition exponent is determined using a reference talus value. Smaller values of talus_ref will lead to thinner flow streams. The maximum talus value of the heightmap can be used as a reference.
- Parameters
-
z Input array representing the heightmap values. talus_ref Reference talus used to locally define the flow-partition exponent. Smaller values will result in thinner flow streams.
- Returns
- std::vector<Array> A vector of arrays, each containing the weights for flow directions at every cell.
◆ flow_direction_dinf_flat()
| std::vector< float > hmap::flow_direction_dinf_flat | ( | const Array & | z, |
| float | talus_ref | ||
| ) |
◆ flow_direction_dinf_angle()
Computes the flow direction using the Multiple Flow Direction (MFD) model.
◆ flow_fixing()
| Array hmap::flow_fixing | ( | const Array & | z, |
| float | riverbed_talus = 0.f, |
||
| int | iterations = 5, |
||
| int | prefilter_ir = 8, |
||
| bool | carve_riverbed = true, |
||
| bool | smooth_river_bottom = true, |
||
| float | talus_riverbank = 0.01f, |
||
| uint | seed = 0, |
||
| float | riverbank_noise_ratio = 0.f, |
||
| float | merging_distance = 8.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr |
||
| ) |
◆ flow_stream()
| Path hmap::flow_stream | ( | const Array & | z, |
| const glm::ivec2 | ij_start, | ||
| const float | elevation_ratio = 0.5f, |
||
| const float | distance_exponent = 2.f, |
||
| const float | upward_penalization = 100.f |
||
| ) |
Computes the optimal flow path from a starting point to the boundary of a given elevation array.
This function finds the flow path on a grid represented by the input array z, starting from the given point ij_start. It identifies the best path to the boundary, minimizing upward elevation penalties while accounting for distance and elevation factors.
- Parameters
-
z The input 2D array representing elevation values. ij_start The starting point as a 2D vector of indices (i, j) within the array. elevation_ratio Weight for elevation difference in the cost function (default: 0.5). distance_exponent Exponent for the distance term in the cost function (default: 2.0). upward_penalization Penalty factor for upward elevation changes (default: 100.0).
- Returns
- A Path object representing the optimal flow path with normalized x and y coordinates and corresponding elevations.
The output path consists of:
- Normalized x-coordinates along the path.
- Normalized y-coordinates along the path.
- Elevation values corresponding to each point on the path.
Example
Result

◆ generate_riverbed()
| Array hmap::generate_riverbed | ( | const Path & | path, |
| glm::ivec2 | shape, | ||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, |
||
| bool | bezier_smoothing = false, |
||
| float | depth_start = 0.01f, |
||
| float | depth_end = 1.f, |
||
| float | slope_start = 64.f, |
||
| float | slope_end = 32.f, |
||
| float | shape_exponent_start = 1.f, |
||
| float | shape_exponent_end = 10.f, |
||
| float | k_smoothing = 0.5f, |
||
| int | post_filter_ir = 0, |
||
| Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_noise_r = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Generates a 2D array representing a riverbed based on a specified path.
This function calculates a scalar depth field (dz) for a riverbed shape using a path, which can optionally be smoothed with Bezier curves. It supports noise perturbation and post-filtering to adjust the riverbed's features.
- Parameters
-
path The input path defining the riverbed's trajectory. shape The dimensions of the output array (width, height). bbox The bounding box for the output grid in world coordinates. bezier_smoothing Flag to enable or disable Bezier smoothing of the path. depth_start The depth at the start of the riverbed. depth_end The depth at the end of the riverbed. slope_start The slope multiplier at the start of the riverbed. slope_end The slope multiplier at the end of the riverbed. shape_exponent_start The shape exponent at the start of the riverbed. shape_exponent_end The shape exponent at the end of the riverbed. k_smoothing The smoothing factor for the riverbed shape adjustments. post_filter_ir The radius of the post-filtering operation for smoothing the output. p_noise_x Optional pointer to a noise array for perturbing the x-coordinates. p_noise_y Optional pointer to a noise array for perturbing the y-coordinates. p_noise_r Optional pointer to a noise array for perturbing the radial function.
- Returns
- A 2D array representing the calculated riverbed depth field.
- Note
- The function requires the path to have at least two points. If the path has fewer points, an empty array is returned with the given shape.
Example
Result

◆ merge_water_depths()
Merge two water depth fields.
Computes the maximum (or smoothed maximum) of two depth arrays.
- Parameters
-
depth1 First water depth array. depth2 Second water depth array. k_smooth Smoothing parameter (0 = sharp max).
- Returns
- Combined water depth array.
◆ water_depth_from_mask()
| Array hmap::water_depth_from_mask | ( | const Array & | z, |
| const Array & | mask, | ||
| float | mask_threshold = 0.f, |
||
| int | iterations_max = 10000, |
||
| float | tolerance = 1e-2f, |
||
| float | omega = 1.8f |
||
| ) |
Compute water depth over a masked terrain using harmonic interpolation.
This function estimates the water depth above a terrain surface by solving a Laplace equation on the domain defined by mask. The solution is obtained using the harmonic interpolation method with Successive Over-Relaxation (SOR). The resulting water depth is given by the difference between the interpolated surface and the original terrain elevation.
- Parameters
-
z Input 2D array representing the terrain elevations (height field). mask Mask array of the same shape as z. Values greater thanmask_thresholddefine regions where water can accumulate, while lower values represent boundaries or fixed terrain.mask_threshold Threshold used to convert maskinto a binary field (0 or 1) for identifying water/terrain boundaries.iterations_max Maximum number of SOR iterations used in the harmonic interpolation. tolerance Convergence criterion: the algorithm stops if the maximum absolute update between iterations is less than this value. omega Relaxation factor for the SOR solver (1 < omega < 2 recommended).
- Returns
- A 2D array containing the computed water depth at each grid cell. Depth values are non-negative where water is present and zero where the mask indicates no water.
- See also
- harmonic_interpolation
Example
Result
◆ water_depth_dry_out()
| void hmap::water_depth_dry_out | ( | Array & | water_depth, |
| float | dry_out_ratio = 0.5f, |
||
| const Array * | p_mask = nullptr, |
||
| float | depth_max = std::numeric_limits<float>::max() |
||
| ) |
Apply a drying factor to a water depth field.
This function reduces the water depth values in-place by multiplying them by a given dry_out_ratio. If a mask is provided, the drying is applied only where the mask is non-zero, allowing selective drying of specific regions.
- Parameters
-
water_depth Reference to the 2D array containing water depth values. The array is modified in-place. dry_out_ratio Multiplicative factor (typically between 0 and 1) used to scale down the water depth. A value of 1 leaves the depth unchanged, while 0 removes all water. p_mask Optional pointer to a mask array of the same shape as water_depth. Drying is applied only where the mask has non-zero values. Ifnullptr, the factor is applied uniformly to all cells.depth_max Maximum water depth, computed automatically by default.
Example
Result
◆ water_depth_increase()
| Array hmap::water_depth_increase | ( | const Array & | water_depth, |
| const Array & | z, | ||
| float | additional_depth | ||
| ) |
Simulates the increase in water depth over a terrain.
This function propagates additional water depth over a terrain elevation map (z), starting from cells that already contain water. The propagation occurs only in the upward direction (i.e., to higher elevation cells) and considers 8-neighbor connectivity. It effectively models how water would expand when its level rises by additional_depth.
- Parameters
-
water_depth Input array representing the base water depth. z Elevation array corresponding to the same grid as water_depth.additional_depth The additional water depth to simulate (e.g., a flooding increment).
- Returns
- An Array representing the updated water depth distribution after propagation.
- Note
- The algorithm uses a simple flood-fill–like approach with an upward constraint, ensuring that water spreads only to neighboring cells at higher elevation.
◆ water_mask() [1/2]
Generates a binary mask representing water presence.
This version of the function converts the given water depth array into a binary mask where non-zero values indicate the presence of water.
- Parameters
-
water_depth Input array representing water depth values.
- Returns
- A binary Array where each cell is 1 if water is present, 0 otherwise.
Example
Result
◆ water_mask() [2/2]
Computes a gradient-based water mask using an extended water depth model.
This function computes a smooth mask indicating regions that would be newly flooded when the water depth is artificially increased by a specified additional amount. It uses water_depth_increase() to simulate the spread of water over the terrain.
- Parameters
-
water_depth Input array representing the current water depth. z Elevation array corresponding to the same grid as water_depth.additional_depth The amount of additional water depth to simulate.
- Returns
- An Array representing the normalized water extension mask, where values range from 0 to 1.
Example
Result

◆ add_filename_suffix()
| std::filesystem::path hmap::add_filename_suffix | ( | const std::filesystem::path & | file_path, |
| const std::string & | suffix | ||
| ) |
◆ make_unique_temp_dir()
| std::filesystem::path hmap::make_unique_temp_dir | ( | const std::string & | prefix | ) |
Create a unique temporary directory.
Creates and returns a unique directory inside the system temporary directory using the given prefix.
- Parameters
-
prefix Directory name prefix.
- Returns
- Path to the created temporary directory.
- Note
- The caller is responsible for deleting the directory.
◆ zfill()
| std::string hmap::zfill | ( | const std::string & | str, |
| int | n_zero | ||
| ) |
◆ upperbound_right()
| size_t hmap::upperbound_right | ( | const std::vector< float > & | v, |
| float | value | ||
| ) |
◆ argsort()
| std::vector< size_t > hmap::argsort | ( | const std::vector< float > & | v | ) |
◆ reindex_vector() [1/3]
| void hmap::reindex_vector | ( | std::vector< T > & | v, |
| std::vector< size_t > & | idx | ||
| ) |
◆ shuffle_vector()
| void hmap::shuffle_vector | ( | std::vector< T > & | values, |
| std::uint32_t | seed | ||
| ) |
◆ shuffled_vector()
| std::vector< T > hmap::shuffled_vector | ( | const std::vector< T > & | values, |
| std::uint32_t | seed | ||
| ) |
◆ vector_unique_values()
| void hmap::vector_unique_values | ( | std::vector< float > & | v | ) |
◆ make_histogram()
| std::string hmap::make_histogram | ( | const std::vector< float > & | values, |
| int | bin_count, | ||
| int | hist_height | ||
| ) |
◆ bilinear_interp()
|
inline |
Compute the bilinear interpolated value from four input values.
This function calculates the interpolated value at a point within a grid using bilinear interpolation based on four surrounding values.
- Parameters
-
f00 Value at (u, v) = (0, 0). f10 Value at (u, v) = (1, 0). f01 Value at (u, v) = (0, 1). f11 Value at (u, v) = (1, 1). u The interpolation parameter in the x-direction, expected in [0, 1). v The interpolation parameter in the y-direction, expected in [0, 1).
- Returns
- float The bilinear interpolated value.
◆ cubic_interpolate()
|
inline |
◆ harmonic_interpolation()
| Array hmap::harmonic_interpolation | ( | const Array & | array, |
| const Array & | mask_fixed_values, | ||
| int | iterations_max = 500, |
||
| float | tolerance = 1e-5f, |
||
| float | omega = 1.8f |
||
| ) |
Perform harmonic interpolation on a 2D array using the Successive Over-Relaxation (SOR) method.
This function solves the discrete Laplace equation on a regular grid by iteratively updating the values of an input array. Values marked as fixed in the mask_fixed_values remain unchanged throughout the process. The algorithm stops when either the maximum number of iterations is reached or the change between successive iterations falls below the specified tolerance.
- Parameters
-
array Input 2D array providing the initial guess for the solution. mask_fixed_values Mask of the same shape as array. Cells with a value greater than zero indicate fixed points that must remain unchanged during interpolation.iterations_max Maximum number of SOR iterations to perform. tolerance Convergence criterion: the algorithm stops if the maximum absolute update between iterations is less than this value. omega Relaxation factor (1 < omega < 2 recommended). Values closer to 2 accelerate convergence, but overly large values may cause divergence.
- Returns
- A new 2D array containing the interpolated solution.
- Note
- The algorithm updates only the interior points (indices
[1..nx-2, 1..ny-2]). - Cells where
mask_fixed_values(i, j) > 0remain unchanged. - A relaxation factor of 1 corresponds to the standard Jacobi/Gauss-Seidel update.
- The algorithm updates only the interior points (indices
◆ interpolate2d()
| Array hmap::interpolate2d | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| const std::vector< float > & | x, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | y, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | values, | ||
| InterpolationMethod2D | interpolation_method, | ||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generic 2D interpolation function.
This function performs interpolation on a 2D grid using the specified interpolation method. It can optionally apply noise and stretching to the input data before interpolation.
- Parameters
-
shape Output array shape. x x coordinates of the input values. y y coordinates of the input values. values Input values at (x, y). interpolation_method Interpolation method (see InterpolationMethod2D). p_noise_x Pointer to the input noise array in the x direction (optional). p_noise_y Pointer to the input noise array in the y direction (optional). p_stretching Pointer to the local wavenumber multiplier array (optional). bbox Domain bounding box (default: {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}).
- Returns
- Array Output array with interpolated values.
◆ interpolate2d_nearest()
| Array hmap::interpolate2d_nearest | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| const std::vector< float > & | x, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | y, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | values, | ||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
2D interpolation using the nearest neighbor method.
This function performs 2D interpolation by assigning the value of the nearest point to each point in the output grid.
- Parameters
-
shape Output array shape. x x coordinates of the input values. y y coordinates of the input values. values Input values at (x, y). p_noise_x Pointer to the input noise array in the x direction (optional). p_noise_y Pointer to the input noise array in the y direction (optional). p_stretching Pointer to the local wavenumber multiplier array (optional). bbox Domain bounding box (default: {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}).
- Returns
- Array Output array with interpolated values.
◆ interpolate2d_delaunay()
| Array hmap::interpolate2d_delaunay | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| const std::vector< float > & | x, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | y, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | values, | ||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
2D interpolation using the Delaunay triangulation method.
This function performs 2D interpolation by generating a Delaunay triangulation of the input points and interpolating the values within each triangle.
- Parameters
-
shape Output array shape. x x coordinates of the input values. y y coordinates of the input values. values Input values at (x, y). p_noise_x Pointer to the input noise array in the x direction (optional). p_noise_y Pointer to the input noise array in the y direction (optional). p_stretching Pointer to the local wavenumber multiplier array (optional). bbox Domain bounding box (default: {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}).
- Returns
- Array Output array with interpolated values.
◆ interpolate_array_bicubic() [1/2]
| void hmap::interpolate_array_bicubic | ( | const Array & | source, |
| Array & | target, | ||
| bool | endpoint = false, |
||
| bool | pixel_centered = true |
||
| ) |
◆ interpolate_array_bicubic() [2/2]
| void hmap::interpolate_array_bicubic | ( | const Array & | source, |
| Array & | target, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox_source, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox_target, | ||
| bool | endpoint = false, |
||
| bool | pixel_centered = true |
||
| ) |
◆ interpolate_array_bilinear() [1/2]
| void hmap::interpolate_array_bilinear | ( | const Array & | source, |
| Array & | target, | ||
| bool | endpoint = false, |
||
| bool | pixel_centered = true |
||
| ) |
◆ interpolate_array_bilinear() [2/2]
| void hmap::interpolate_array_bilinear | ( | const Array & | source, |
| Array & | target, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox_source, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox_target, | ||
| bool | endpoint = false, |
||
| bool | pixel_centered = true |
||
| ) |
◆ interpolate_array_nearest() [1/2]
| void hmap::interpolate_array_nearest | ( | const Array & | source, |
| Array & | target, | ||
| bool | endpoint = false |
||
| ) |
◆ interpolate_array_nearest() [2/2]
| void hmap::interpolate_array_nearest | ( | const Array & | source, |
| Array & | target, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox_source, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox_target, | ||
| bool | endpoint = false |
||
| ) |
◆ flatten_heightmap() [1/2]
| void hmap::flatten_heightmap | ( | VirtualArray & | h_source1, |
| const VirtualArray & | h_source2, | ||
| const CoordFrame & | t_source1, | ||
| const CoordFrame & | t_source2, | ||
| const ComputeMode & | cm | ||
| ) |
◆ flatten_heightmap() [2/2]
| void hmap::flatten_heightmap | ( | const std::vector< const VirtualArray * > & | h_sources, |
| VirtualArray & | h_target, | ||
| const std::vector< const CoordFrame * > & | t_sources, | ||
| const CoordFrame & | t_target, | ||
| const ComputeMode & | cm | ||
| ) |
◆ interpolate_heightmap()
| void hmap::interpolate_heightmap | ( | const VirtualArray & | h_source, |
| VirtualArray & | h_target, | ||
| const CoordFrame & | t_source, | ||
| const CoordFrame & | t_target, | ||
| const ComputeMode & | cm | ||
| ) |
◆ get_kernel()
| Array hmap::get_kernel | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| KernelType | kernel_type | ||
| ) |
Generate a kernel of the specified type.
This function creates a kernel based on the given shape and kernel type. It supports various types of kernels including biweight, cubic pulse, cone, and more. The resulting kernel is returned as an array.
- Parameters
-
shape The dimensions of the kernel to be generated. kernel_type The type of kernel to generate (e.g., BIWEIGHT, CUBIC_PULSE, etc.).
- Returns
- Array The generated kernel array.
◆ biweight()
| Array hmap::biweight | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape | ) |
Generates a biweight kernel array.
This function creates a biweight kernel, which is a type of kernel function used in statistics for smoothing and interpolation.
For more details on the biweight kernel, refer to the Wikipedia page: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kernel_%28statistics%29.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape specifying the dimensions of the kernel.
- Returns
- Array A new array containing the biweight kernel.
◆ blackman()
| Array hmap::blackman | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape | ) |
Generates a Blackman window array with the specified shape.
The Blackman window is commonly used in signal processing for smoothing or tapering. This function creates a 2D array of values representing the Blackman window, calculated based on the given shape dimensions.
- Parameters
-
shape A 2D vector representing the dimensions of the array.
- Returns
- An
Arrayobject containing the Blackman window values of the specified shape.
◆ cone() [1/2]
| Array hmap::cone | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape | ) |
Generates a cone-shaped kernel array.
This function creates a cone-shaped kernel. The maximum value of the kernel is 1, and the shape of the kernel is determined by the provided array dimensions.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape specifying the dimensions of the kernel.
- Returns
- Array A new array containing the cone-shaped kernel.
◆ cone_talus()
| Array hmap::cone_talus | ( | float | height, |
| float | talus | ||
| ) |
Generates a cone-shaped kernel with specified height and talus.
This function creates a cone-shaped kernel with a given height and talus. The output array's shape is adjusted accordingly based on the specified height and talus.
- Parameters
-
height Height of the cone. This determines the peak value of the kernel. talus The slope of the cone, which affects the rate at which the kernel value decreases.
- Returns
- Array A new array containing the cone-shaped kernel with the specified height and talus.
◆ cone_smooth()
| Array hmap::cone_smooth | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape | ) |
Generates a cone-shaped kernel with a smooth landing.
This function creates a cone-shaped kernel where the kernel smoothly transitions to zero at the bottom, resulting in a smooth derivative at the cone base.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape specifying the dimensions of the kernel.
- Returns
- Array A new array containing the smooth cone-shaped kernel.
◆ cubic_pulse() [1/2]
| Array hmap::cubic_pulse | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape | ) |
◆ cubic_pulse_1d()
| std::vector< float > hmap::cubic_pulse_1d | ( | int | nk | ) |
Generates a 1D cubic pulse kernel.
- Parameters
-
nk The number of samples in the 1D kernel.
- Returns
- std::vector<float> A vector containing the cubic pulse kernel values.
◆ cubic_pulse_directional()
| Array hmap::cubic_pulse_directional | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | angle, | ||
| float | aspect_ratio, | ||
| float | anisotropy | ||
| ) |
Generates a "directional" cubic pulse kernel.
This function creates a cubic pulse kernel with directional properties. The kernel's shape can be adjusted based on the provided angle, aspect ratio, and anisotropy. This allows for creating kernels that are elongated or compressed in specific directions, making them suitable for applications requiring directional smoothing or filtering.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape specifying the dimensions of the kernel. angle Angle (in degrees) defining the direction of the pulse elongation. aspect_ratio Pulse aspect ratio, which controls the kernel's elongation or compression. anisotropy Pulse width ratio between upstream and downstream sides of the pulse.
- Returns
- Array A new array containing the directional cubic pulse kernel.
◆ cubic_pulse_truncated()
| Array hmap::cubic_pulse_truncated | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | slant_ratio, | ||
| float | angle | ||
| ) |
Generates a truncated cubic pulse kernel.
This function creates a cubic pulse kernel that is truncated based on the specified slant ratio and angle. The truncation slope determines how the kernel's values decrease as they approach the edge of the kernel, creating a "cut-off" effect.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape specifying the dimensions of the kernel. slant_ratio Truncation slope that affects the kernel's cut-off behavior. angle Angle (in degrees) that defines the orientation of the truncation.
- Returns
- Array A new array containing the truncated cubic pulse kernel.
Example
Result
◆ cupola()
Generate a 2D radial cupola kernel.
Values are computed from the normalized radial distance to the center: constant 1 inside radius rc, then smoothly decreasing to 0 at radius 1.
- Parameters
-
shape Size of the output array (width, height). rc Radius of the inner flat region (normalized, < 1).
- Returns
- Generated cupola-shaped Array.
◆ disk() [1/2]
| Array hmap::disk | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape | ) |
Generates a disk-shaped kernel footprint.
This function creates a disk-shaped kernel, which is a circular kernel where the values are radially symmetric around the center.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape specifying the dimensions of the kernel.
- Returns
- Array A new array containing the disk-shaped kernel.
◆ disk_smooth()
Generates a smooth, disk-shaped kernel footprint with soft edges.
This function creates a 2D, disk-shaped kernel with radially symmetric values centered in the array. Values inside the cutoff radius r_cutoff are set to 1.0. Between r_cutoff and the normalized radius 1.0, the values smoothly fall off to zero using a parabolic profile to ensure soft transitions at the disk boundary.
The generated array is useful for constructing smooth low-pass filters or spatial masks with circular support.
- Parameters
-
shape The dimensions of the output array (width, height). r_cutoff Normalized cutoff radius in the range [0.0, 1.0]. Inside this radius, the kernel has a flat value of 1.0; outside, it decays smoothly to 0.0.
- Returns
- A 2D array of size
shapecontaining the smooth disk-shaped kernel.
- Note
- Coordinates are normalized such that the radius 1.0 corresponds to the maximum possible distance from the center in either dimension.
- See also
- disk()
◆ gabor()
| Array hmap::gabor | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | kw, | ||
| float | angle, | ||
| bool | quad_phase_shift = false |
||
| ) |
Generates a Gabor kernel of the specified shape.
This function creates a Gabor kernel, which is a type of sinusoidal kernel modulated by a Gaussian envelope. The Gabor kernel is useful for texture analysis and feature extraction. The kernel's frequency and orientation are defined by the wavenumber and angle parameters, respectively.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape specifying the dimensions of the kernel. kw Kernel wavenumber, which determines the frequency of the sinusoidal component. angle Kernel angle (in degrees) that defines the orientation of the sinusoidal component.
- Returns
- Array A new array containing the Gabor kernel.
Example
Result

◆ gabor_dune()
| Array hmap::gabor_dune | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | kw, | ||
| float | angle, | ||
| float | xtop, | ||
| float | xbottom | ||
| ) |
Generates a modified dune-like Gabor kernel.
This function creates a modified Gabor kernel that has a dune-like profile. The dune profile modifies the standard Gabor kernel to include a top and foot for the dune, giving it a specific shape. The xtop and xbottom parameters control the relative locations of the top and foot of the dune profile, respectively.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape specifying the dimensions of the kernel. kw Kernel wavenumber, which determines the frequency of the sinusoidal component. angle Kernel angle (in degrees) that defines the orientation of the sinusoidal component. xtop Relative location of the top of the dune profile (in [0, 1]). xbottom Relative location of the foot of the dune profile (in [0, 1]).
- Returns
- Array A new array containing the modified dune-like Gabor kernel.
Example
Result

◆ hann()
| Array hmap::hann | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape | ) |
Generates a Hann window array with the specified shape.
The Hann window is commonly used in signal processing for smoothing or tapering. This function creates a 2D array of values representing the Hann window, calculated based on the given shape dimensions.
- Parameters
-
shape A 2D vector representing the dimensions of the array.
- Returns
- An
Arrayobject containing the Hann window values of the specified shape.
◆ lorentzian()
Generate a Lorentzian kernel.
The Lorentzian kernel is characterized by its peak and tails that decay with the distance from the center. The width of the kernel is determined using the provided footprint threshold.
- Parameters
-
shape The dimensions of the kernel. footprint_threshold Determines the width of the Lorentzian kernel. Default is 0.1.
- Returns
- Array The Lorentzian kernel array.
◆ lorentzian_compact()
| Array hmap::lorentzian_compact | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape | ) |
Generate a modified Lorentzian kernel with compact support.
This version of the Lorentzian kernel is modified to have compact support, meaning it is non-zero only within a certain range. This modification is useful for specific applications requiring compact kernels.
- Parameters
-
shape The dimensions of the kernel.
- Returns
- Array The modified Lorentzian kernel with compact support.
◆ sinc_radial()
| Array hmap::sinc_radial | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | kw | ||
| ) |
Generates a radial sinc function array with the specified shape and wave number.
This function creates a 2D array of values representing the radial sinc function, calculated based on the given shape and wave number. The sinc function is defined as sin(x) / x and is useful in signal processing and analysis.
- Parameters
-
shape A 2D vector representing the dimensions of the array. kw The wave number used to scale the radial sinc function.
- Returns
- An
Arrayobject containing the radial sinc function values of the specified shape.
◆ sinc_separable()
| Array hmap::sinc_separable | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | kw | ||
| ) |
Generates a separable sinc function array with the specified shape and wave number.
This function creates a 2D array of values representing the separable sinc function, calculated as the product of 1D sinc functions along each dimension of the array. The sinc function is defined as sin(x) / x and is useful in signal processing and analysis.
- Parameters
-
shape A 2D vector representing the dimensions of the array. kw The wave number used to scale the separable sinc function.
- Returns
- An
Arrayobject containing the separable sinc function values of the specified shape.
◆ smooth_cosine() [1/2]
| Array hmap::smooth_cosine | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape | ) |
Generate a smooth cosine kernel.
The smooth cosine kernel is a type of kernel function that smoothly transitions between values, based on a cosine function.
- Parameters
-
shape The dimensions of the kernel.
- Returns
- Array The smooth cosine kernel array.
◆ square()
| Array hmap::square | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape | ) |
Generate a square-shaped kernel.
The square kernel is a simple, isotropic kernel where the values are constant within the square region. The maximum value within the kernel is 1.
- Parameters
-
shape The dimensions of the kernel.
- Returns
- Array The square-shaped kernel array.
◆ tricube()
| Array hmap::tricube | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape | ) |
Generate a tricube kernel.
The tricube kernel is a type of kernel function that is often used in statistical applications. It has a specific shape defined by the tricube polynomial.
- Parameters
-
shape The dimensions of the kernel.
- Returns
- Array The tricube kernel array.
Reference See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kernel_%28statistics%29 for details on the tricube kernel.
◆ abs()
Return the absolute value of the array elements.
- Parameters
-
array Input array.
- Returns
- Array Output array.
◆ abs_smooth() [1/4]
Return the smooth absolute value of the array elements.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. k Smoothing coefficient. vshift Reference value for the "zero" value of the absolute value (default is zero).
- Returns
- Array Output array.
Example
Result
◆ abs_smooth() [2/4]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ abs_smooth() [3/4]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ abs_smooth() [4/4]
| float hmap::abs_smooth | ( | float | a, |
| float | mu | ||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ almost_unit_identity() [1/2]
Return the almost unit identity function.
Function that maps the unit interval to itself with zero derivative at 0 and "one" derivative at 1 (see Inigo Quilez's articles).
- Parameters
-
array Input array.
- Returns
- Array Output array.
◆ almost_unit_identity() [2/2]
| float hmap::almost_unit_identity | ( | float | x | ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ almost_unit_identity_c2() [1/2]
| float hmap::almost_unit_identity_c2 | ( | float | x | ) |
Return the almost unit identity function (with a second-order derivative equals 0 at x = 1 also to avoid discontinuities in some cases)
- Parameters
-
x Input.
- Returns
- float Output.
◆ almost_unit_identity_c2() [2/2]
◆ approx_hypot()
|
inline |
Return the approximate hypothenuse of two numbers.
- Parameters
-
a a b a
- Returns
- float ~sqrt(a**2 + b**2)
◆ approx_rsqrt()
|
inline |
Return the approximate inverse square root of a number.
- Parameters
-
a a
- Returns
- float ~1/sqrt(a)
◆ atan()
Return the arctan of the array elements.
- Parameters
-
array Input array.
- Returns
- Array Reference to the current object.
◆ atan2()
Computes the element-wise arctangent of two arrays, considering the signs of both inputs.
This function calculates the arctangent of the ratio y/x for each corresponding element in the input arrays, while taking into account the quadrant of the angle. The output values are in radians and range from -π to π.
- Parameters
-
y A 2D array representing the numerator values. x A 2D array representing the denominator values.
- Returns
- A 2D array where each element is the result of
atan2(y(i, j), x(i, j)).
◆ ceil_div()
| int hmap::ceil_div | ( | int | a, |
| int | b | ||
| ) |
Integer ceiling division.
- Parameters
-
a Numerator (>= 0) b Denominator (> 0)
- Returns
- ceil(a / b)
◆ cos()
Return the cosine of the array elements.
- Parameters
-
array Input array.
- Returns
- Array Reference to the current object.
◆ exp()
Return the exponantial of the array elements.
- Parameters
-
array Input array.
- Returns
- Array Reference to the current object.
◆ gain() [3/3]
| float hmap::gain | ( | float | x, |
| float | factor | ||
| ) |
◆ gaussian_decay()
Return the Gaussian of the array elements.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. sigma Gaussian half-width.
- Returns
- Array Reference to the current object.
Example
Result
◆ get_distance_function()
| std::function< float(float, float)> hmap::get_distance_function | ( | DistanceFunction | dist_fct | ) |
Return the requested distance function.
- Parameters
-
dist_fct Distance function type.
- Returns
- Distance function.
◆ get_phasor_profile_function()
| std::function< float(float)> hmap::get_phasor_profile_function | ( | PhasorProfile | phasor_profile, |
| float | delta, | ||
| float * | p_profile_avg = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Generates a function representing a phasor profile based on the specified type and parameters.
This function returns a callable object (std::function) that computes the value of the specified phasor profile for a given phase angle (phi). Optionally, it can compute the average value of the profile over the range [-π, π].
- Parameters
-
phasor_profile The type of phasor profile to generate. delta A parameter that can influence the profile (depending on the profile choice). p_profile_avg Optional pointer to a float. If not nullptr, it will store the average value of the profile over the range [-π, π].
- Returns
- A
std::function<float(float)>that computes the phasor profile for a given phase angle.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argumentIftheprovided`phasor_profile`isinvalid.
- Note
- The average value is computed using numerical integration over 50 sample points within [-π, π].
◆ get_radial_profile_function()
| std::function< float(float)> hmap::get_radial_profile_function | ( | RadialProfile | radial_profile, |
| float | delta | ||
| ) |
Returns a normalized radial profile function.
The returned function maps x ∈ [0,1] to a value in [0,1], with f(0) = 0 and f(1) = 1. It is typically used for radial or distance-based falloff in procedural heightmaps.
- Parameters
-
radial_profile Radial profile type. delta Shape parameter used by some profiles.
- Returns
- Radial profile evaluation function.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argumentIftheprofileisinvalid.
◆ highest_power_of_2()
| int hmap::highest_power_of_2 | ( | int | n | ) |
Computes the highest power of 2 less than or equal to the given number.
- Parameters
-
n The input integer for which the highest power of 2 is to be determined.
- Returns
- The highest power of 2 less than or equal to
n.
◆ is_equal()
Returns a binary mask of elements equal to value.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to test for non-zero values. value Value.
- Returns
- Array Binary mask array.
◆ is_non_zero()
Returns a binary mask of non-zero elements.
Creates an array of the same shape where each element is 1.0f if the corresponding input value is non-zero, otherwise 0.0f.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to test for non-zero values.
- Returns
- Array Binary mask array.
◆ is_zero()
Returns a binary mask of zero elements.
Creates an array of the same shape where each element is 1.0f if the corresponding input value is non-zero, otherwise 0.0f.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to test for non-zero values.
- Returns
- Array Binary mask array.
◆ lerp() [2/4]
Return the linear interpolation between two arrays by a parameter t.
- Parameters
-
array1 First array. array2 Second array. t Interpolation parameter (in [0, 1]).
- Returns
- Array Interpolated array.
◆ lerp() [3/4]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ lerp() [4/4]
| float hmap::lerp | ( | float | a, |
| float | b, | ||
| float | t | ||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ log10()
Return the log10 of the array elements.
- Parameters
-
array Input array.
- Returns
- Array Reference to the current object.
◆ pow()
Return the array elements raised to the power 'exp'.
- Parameters
-
exp Exponent.
- Returns
- Array Reference to the current object.
◆ radial_displacement_to_xy()
| void hmap::radial_displacement_to_xy | ( | const Array & | dr, |
| Array & | dx, | ||
| Array & | dy, | ||
| float | smoothing = 1.f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Interpret the input array dr as a radial displacement and convert it to a pair of displacements dx and dy in cartesian coordinates.
- Parameters
-
dr Radial displacement. dx Displacent in x direction (output). dy Displacent in y direction (output). smoothing Smoothing parameter to avoid discontinuity at the origin. center Origin center. bbox Domain bounding box.
Example
Result
◆ rotate_displacement()
Rotates a scalar displacement field into directional X and Y components.
This function converts a scalar displacement map into two directional components (dx and dy) according to a given rotation angle. It is typically used to orient procedural displacements, such as those applied to terrain heightmaps or noise-based distortion fields.
- Parameters
-
delta Input scalar displacement field. angle Rotation angle in degrees (counterclockwise). dx Output array receiving the X-axis displacement component. dy Output array receiving the Y-axis displacement component.
◆ sigmoid() [1/2]
| float hmap::sigmoid | ( | float | x, |
| float | width = 1.f, |
||
| float | vmin = 0.f, |
||
| float | vmax = 1.f, |
||
| float | x0 = 0.f |
||
| ) |
Computes the sigmoid function for a scalar value.
This function applies a generalized sigmoid transformation:
\[ y = v_{\min} + \frac{v_{\max} - v_{\min}} {1 + \exp\left(-\frac{x - x_0}{\text{width}}\right)} \]
- Parameters
-
x Input value. width Controls the steepness of the sigmoid curve. Higher values make the slope gentler. Default is 1.f.vmin Minimum value of the output range. Default is 0.f.vmax Maximum value of the output range. Default is 1.f.x0 The center point (x-offset) of the sigmoid curve. Default is 0.f.
- Returns
- The transformed scalar value in the range
[vmin, vmax].
Example
Result
◆ sigmoid() [2/2]
| Array hmap::sigmoid | ( | const Array & | array, |
| float | width = 1.f, |
||
| float | vmin = 0.f, |
||
| float | vmax = 1.f, |
||
| float | x0 = 0.f |
||
| ) |
Computes the sigmoid function element-wise for an array.
This function applies the same generalized sigmoid transformation as the scalar version:
\[ y = v_{\min} + \frac{v_{\max} - v_{\min}} {1 + \exp\left(-\frac{x - x_0}{\text{width}}\right)} \]
Each element in the input array is independently transformed.
- Parameters
-
array Input array of values. width Controls the steepness of the sigmoid curve. Higher values make the slope gentler. Default is 1.f.vmin Minimum value of the output range. Default is 0.f.vmax Maximum value of the output range. Default is 1.f.x0 The center point (x-offset) of the sigmoid curve. Default is 0.f.
- Returns
- A new array with each element transformed by the sigmoid function.
Example
Result

◆ sin()
Return the sine of the array elements.
- Parameters
-
array Input array.
- Returns
- Array Reference to the current object.
◆ smoothstep3() [1/2]
Return the 3rd order smoothstep function of the array elements.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. vmin Lower bound. vmax Upper bound.
- Returns
- Array Output array.
Example
Result

◆ smoothstep3() [2/2]
| float hmap::smoothstep3 | ( | float | x | ) |
Return the 3rd order smoothstep function.
- Parameters
-
x Input.
- Returns
- float Output.
◆ smoothstep3_lower() [1/2]
| float hmap::smoothstep3_lower | ( | float | x | ) |
Return the 3rd order smoothstep function, with zero derivative only at 0.
- Parameters
-
x Input.
- Returns
- float Output.
◆ smoothstep3_lower() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ smoothstep3_upper() [1/2]
| float hmap::smoothstep3_upper | ( | float | x | ) |
Return the 3rd order smoothstep function, with zero derivative only at 1.
- Parameters
-
x Input.
- Returns
- float Output.
◆ smoothstep3_upper() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ smoothstep5() [1/3]
Return the 5rd order smoothstep function of the array elements.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. vmin Lower bound. vmax Upper bound.
- Returns
- Array Output array.
Example
Result

◆ smoothstep5() [2/3]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ smoothstep5() [3/3]
| float hmap::smoothstep5 | ( | float | x | ) |
Return the 5rd order smoothstep function.
- Parameters
-
x Input.
- Returns
- float Output.
◆ smoothstep5_lower() [1/2]
| float hmap::smoothstep5_lower | ( | float | x | ) |
Return the 5rd order smoothstep function, with zero derivative only at 0.
- Parameters
-
x Input.
- Returns
- float Output.
◆ smoothstep5_lower() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ smoothstep5_upper() [1/2]
| float hmap::smoothstep5_upper | ( | float | x | ) |
Return the 5rd order smoothstep function, with zero derivative only at 1.
- Parameters
-
x Input.
- Returns
- float Output.
◆ smoothstep5_upper() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ smoothstep7() [1/2]
| float hmap::smoothstep7 | ( | float | x | ) |
Return the 7th order smoothstep function.
- Parameters
-
x Input.
- Returns
- float Output.
◆ smoothstep7() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ sqrt()
Return the square root of the array elements.
- Parameters
-
array Input array.
- Returns
- Array Reference to the current object.
◆ sqrt_safe()
◆ border()
Apply a border algorithm to the input array using a square structure.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the border algorithm is applied. ir Radius of the square kernel used for the border algorithm.
- Returns
- Array Output array with the border applied.
Example
Result

◆ closing()
Apply a closing algorithm to the input array using a square structure.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the closing algorithm is applied. ir Radius of the square kernel used for the closing algorithm.
- Returns
- Array Output array with the closing applied.
Example
Result

◆ dilation()
Apply a dilation algorithm to the input array using a square structure.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the dilation algorithm is applied. ir Radius of the square kernel used for the dilation algorithm.
- Returns
- Array Output array with the dilation applied.
Example
Result

◆ dilation_expand_border_only()
Expand non-zero regions of an array by morphological dilation, while preserving the original non-zero values.
This function performs a local-maximum (dilation) operation on the input array with a given radius ir, then copies back the original non-zero values so they remain unchanged. Only the surrounding background is filled with expanded values, effectively “growing” the borders of non-zero regions.
- Parameters
-
array Input 2D array where non-zero cells represent regions of interest and zero cells represent background. ir Radius of the dilation (in grid cells). Defines how far the non-zero values can expand into the background.
- Returns
- A new 2D array where the borders of non-zero regions have been expanded outward by up to
ircells, while the original non-zero values are kept intact.
◆ distance_transform()
Return the Euclidean distance transform.
Exact transform based on Meijster et al. algorithm [Meijster2000].
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be transformed, will be converted into binary: 1 wherever input is greater than 0, 0 elsewhere. return_squared_distance Whether the distance returned is squared or not.
- Returns
- Array Reference to the output array.
Example
Result
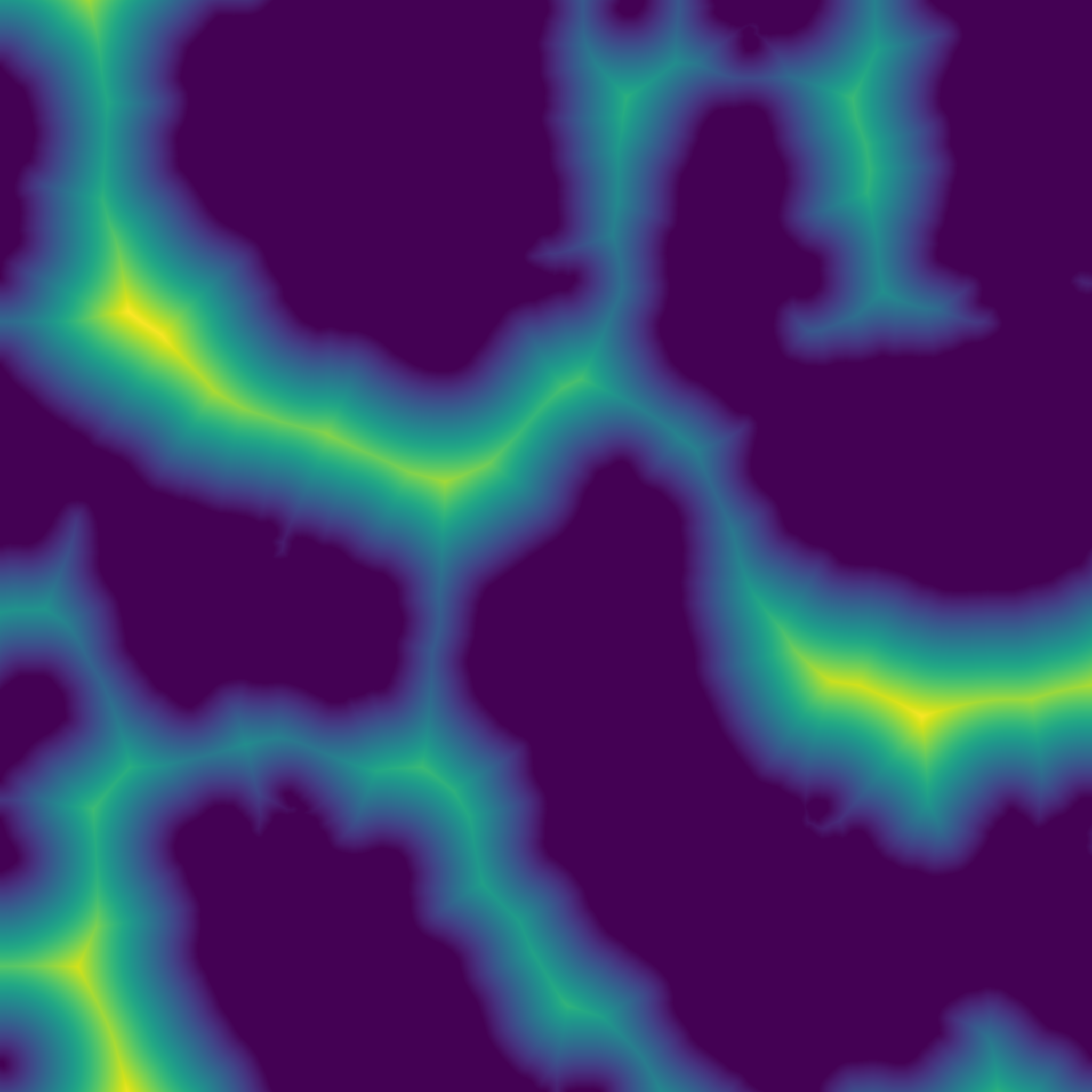
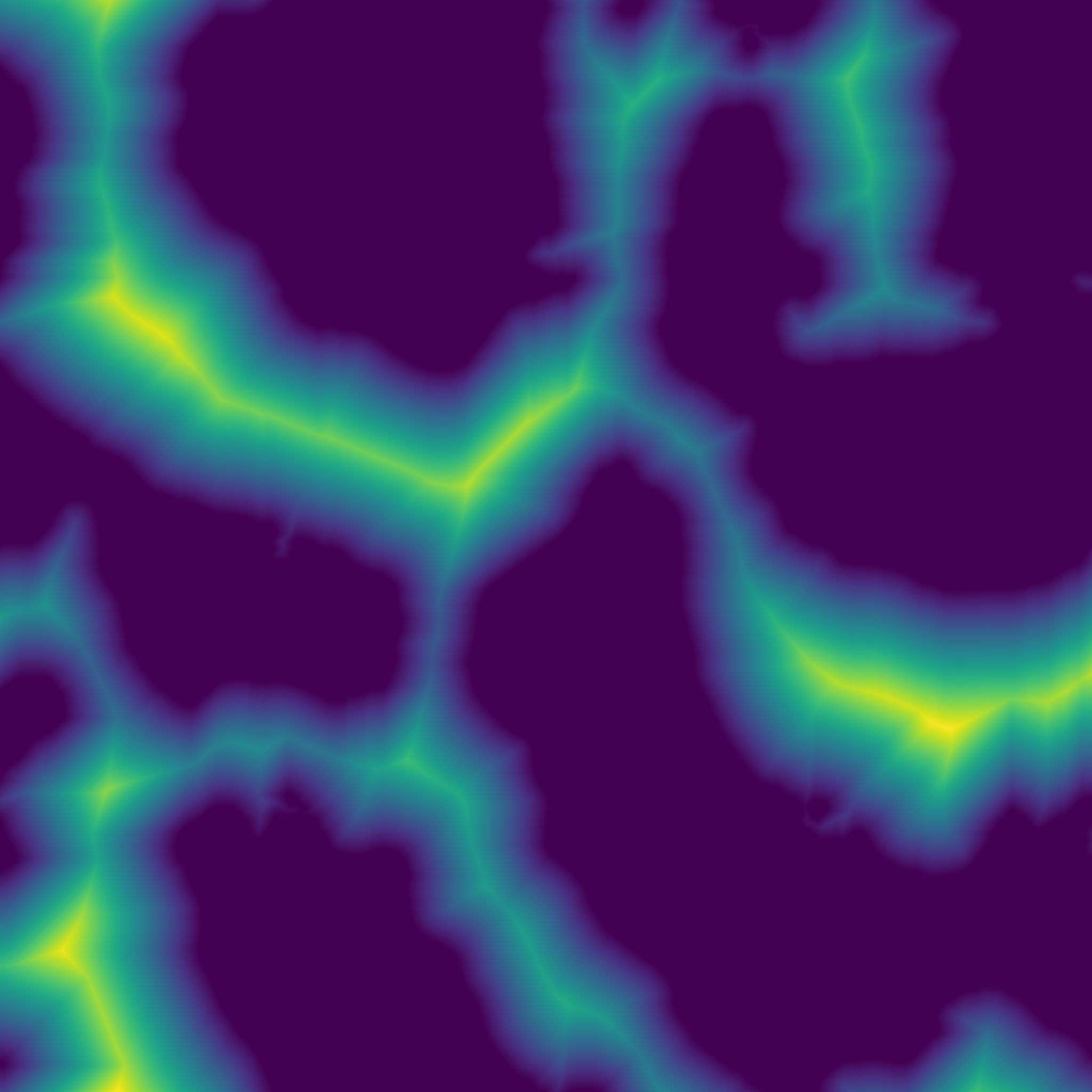
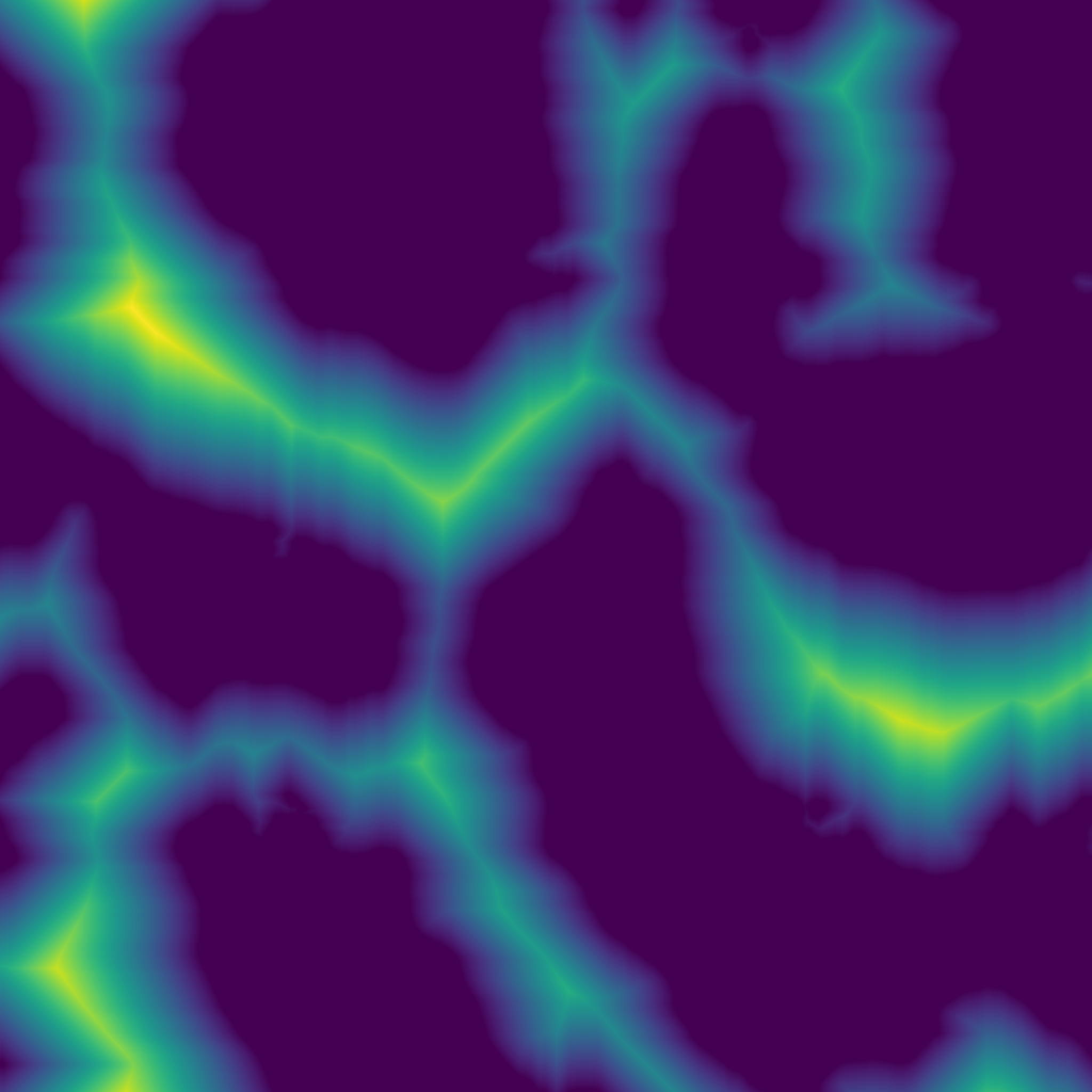
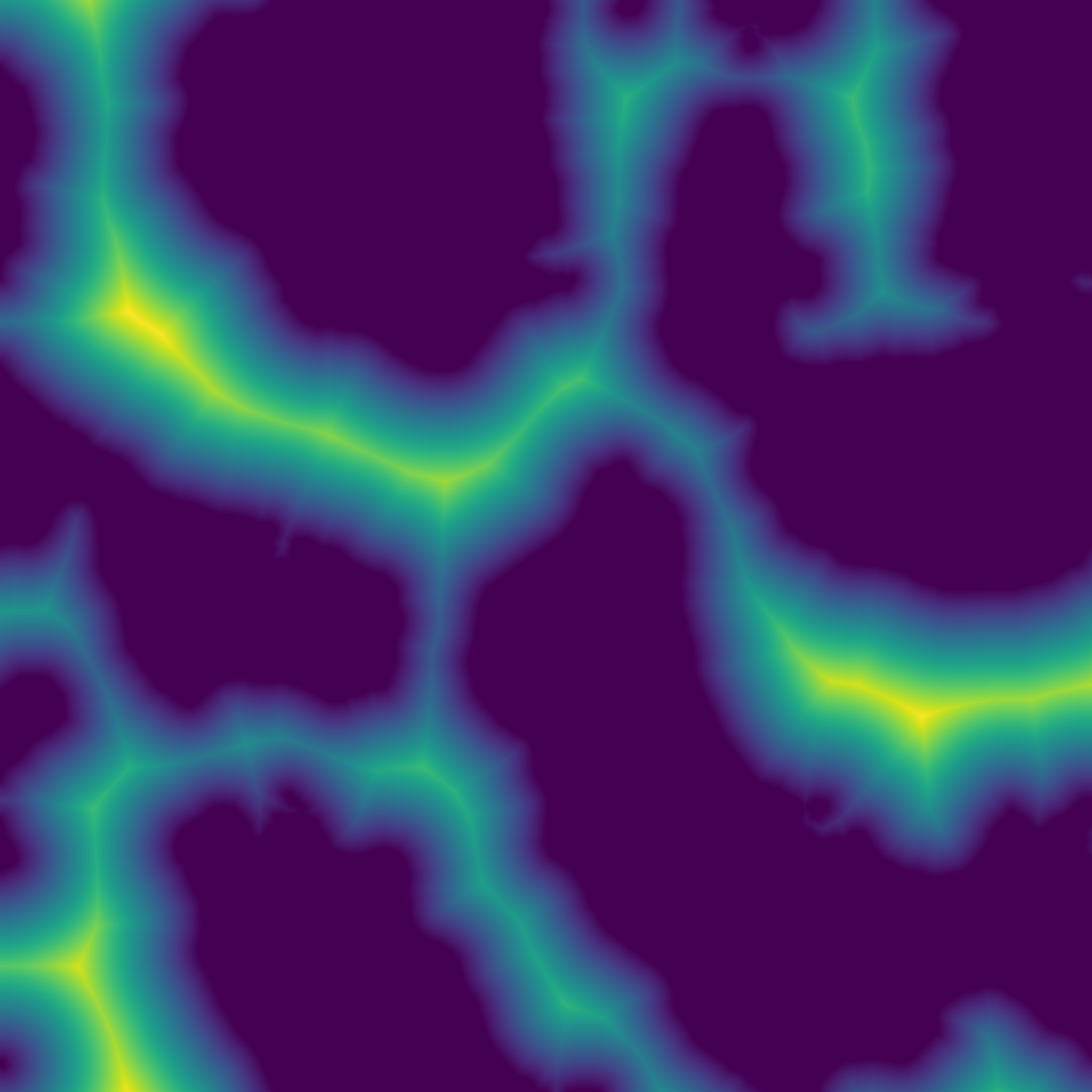
◆ distance_transform_approx()
Calculates an approximate distance transform of the input array.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to calculate the distance transform for. return_squared_distance Optional parameter to return squared distances. Defaults to false.
- Returns
- Array containing the approximate distance transform of the input array.
Example
Result





◆ distance_transform_manhattan()
| Array hmap::distance_transform_manhattan | ( | const Array & | array, |
| bool | return_squared_distance = false |
||
| ) |
Calculates the Manhattan distance transform of an array.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. return_squared_distance If true, returns the squared Manhattan distance instead of the actual distance.
- Returns
- Array containing the Manhattan distance transform of the input array.
Example
Result





◆ distance_transform_with_closest()
| Array hmap::distance_transform_with_closest | ( | const Array & | array, |
| Mat< glm::ivec2 > & | closest, | ||
| bool | return_squared_distance = false |
||
| ) |
Return the Euclidean distance transform.
Exact transform based on Meijster et al. algorithm [Meijster2000].
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be transformed, will be converted into binary: 1 wherever input is greater than 0, 0 elsewhere. return_squared_distance Whether the distance returned is squared or not.
- Returns
- Array Reference to the output array.
◆ erosion()
Apply an erosion algorithm to the input array using a square structure.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the erosion algorithm is applied. ir Radius of the square kernel used for the erosion algorithm.
- Returns
- Array Output array with the erosion applied.
Example
Result

◆ flood_fill()
| void hmap::flood_fill | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | i, | ||
| int | j, | ||
| float | fill_value = 1.f, |
||
| float | background_value = 0.f |
||
| ) |
Apply a flood fill algorithm to the input array.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be filled. i Seed point row index. j Seed point column index. fill_value Filling value. background_value Background value.
Example
Result
◆ morphological_black_hat()
Apply a morphological black hat algorithm to the input array using a square structure.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the black hat algorithm is applied. ir Radius of the square kernel used for the black hat algorithm.
- Returns
- Array Output array with the black hat applied.
Example
Result

◆ morphological_gradient()
Apply a morphological gradient algorithm to the input array using a square structure.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the gradient algorithm is applied. ir Radius of the square kernel used for the gradient algorithm.
- Returns
- Array Output array with the gradient applied.
Example
Result

◆ morphological_top_hat()
Apply a morphological top hat algorithm to the input array using a square structure.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the top hat algorithm is applied. ir Radius of the square kernel used for the top hat algorithm.
- Returns
- Array Output array with the top hat applied.
Example
Result

◆ opening()
Apply an opening algorithm to the input array using a square structure.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to which the opening algorithm is applied. ir Radius of the square kernel used for the opening algorithm.
- Returns
- Array Output array with the opening applied.
Example
Result

◆ relative_distance_from_skeleton()
| Array hmap::relative_distance_from_skeleton | ( | const Array & | array, |
| int | ir_search, | ||
| bool | zero_at_borders = true, |
||
| int | ir_erosion = 1 |
||
| ) |
Computes the relative distance of each non-zero cell in a binary array from the skeleton and border.
This function calculates a relative distance measure for each non-zero cell in the input array. The measure is defined as the ratio of the cell's distance to the nearest border and the combined distances to the nearest skeleton and border cells. The skeleton is computed using the Zhang-Suen skeletonization algorithm.
- Parameters
-
array The input binary array for which the relative distance map is to be calculated. Non-zero values are considered for processing. ir_search The search radius for finding the nearest skeleton and border cells. zero_at_borders If true, the borders of the skeletonized image will be set to zero. ir_erosion The erosion radius applied to the skeleton.
- Returns
- An array representing the relative distance map, where each cell has a value between 0 and 1. A value closer to 1 indicates proximity to the skeleton, while a value closer to 0 indicates proximity to the border.
- Note
- The skeleton is computed using the Zhang-Suen skeletonization algorithm.
Example
Result
◆ signed_curvature_from_distance()
Computes the signed curvature of the distance transform.
Computes the Euclidean distance transform of a binary array, optionally smooths it, then returns the divergence of the normalized gradient: κ = div( ∇d / ||∇d|| ). Positive values indicate convex regions, negative values concave regions.
- Parameters
-
array Binary input (non-zero = foreground). prefilter_ir Optional smoothing radius (0 = no smoothing).
- Returns
- Curvature field of the distance transform.
Example
Result




◆ signed_distance_transform()
Computes a signed distance transform using curvature sign.
First computes the unsigned Euclidean distance transform, then assigns its sign from the curvature of the smoothed distance field: sign = sign( div( ∇d / ||∇d|| ) ).
- Parameters
-
array Binary input (non-zero = foreground). prefilter_ir Optional smoothing radius for curvature evaluation.
- Returns
- Signed distance transform.
◆ skeleton()
Computes the skeleton of a binary image using the Zhang-Suen skeletonization algorithm.
This function processes a binary input array to extract its skeleton by iteratively thinning the image until no further changes occur. It optionally sets the borders of the resulting skeletonized image to zero.
- Parameters
-
array The input binary array to be skeletonized. Values should typically be 0 or 1. zero_at_borders If true, the borders of the resulting array will be set to zero.
- Returns
- The skeletonized version of the input array.
- Note
- This implementation is based on the algorithm described at https://github.com/krishraghuram/Zhang-Suen-Skeletonization.
Example
Result
◆ downscale_transform()
| void hmap::downscale_transform | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | kc, | ||
| std::function< void(Array &x)> | unary_op, | ||
| bool | apply_prefiltering = false |
||
| ) |
Applies a downscaling transformation to a 2D array using Fourier-based filtering.
This function performs a series of operations on a 2D array to isolate and transform its low-frequency components. It uses a Fourier transform for filtering, downscales the array for efficient processing, applies a user-defined unary operation, and then restores the transformed low-frequency content to the original resolution.
- Parameters
-
array A reference to the input 2D array to be transformed. The array may be resized internally. kc The cutoff wavenumber for isolating low-frequency components during filtering. unary_op A user-defined function that applies a transformation to the downscaled array.
- The function ensures that the input array is square for Fourier operations by resampling it if necessary.
- A smooth low-pass filter is applied in the frequency domain, and the filtered array is downscaled to a coarse resolution.
- The user-defined transformation (
unary_op) is applied to the downscaled array. - The transformed low-frequency content is upsampled and reintegrated into the original array.
- If the input array was not square, the final result is resampled back to its original shape.
- Example #include "highmap.hpp"int main(void){glm::vec2 kw = {2.f, 2.f};int seed = 2;{128, 128},kw,seed);{256, 256},kw,seed);{512, 512},kw,seed);{1024, 1024},kw,seed);auto z0 = z1024; // keep for referencefloat kc = 64.f;auto lambda = [](hmap::Array &x){int nparticles = 5000;uint seed = 0;hmap::hydraulic_particle(x, nparticles, seed);};// apply the erosion to each array with different resolutions// (results should be the same)hmap::downscale_transform(z128, kc, lambda);hmap::downscale_transform(z256, kc, lambda);hmap::downscale_transform(z512, kc, lambda);hmap::downscale_transform(z1024, kc, lambda);// interpolation in finer resolution to generate a single output imageauto z1 = z128.resample_to_shape({1024, 1024});auto z2 = z256.resample_to_shape({1024, 1024});auto z3 = z512.resample_to_shape({1024, 1024});auto z4 = z1024.resample_to_shape({1024, 1024});hmap::export_banner_png("ex_downscale_transform.png",{z0, z1, z2, z3, z4},true);}Array resample_to_shape(glm::ivec2 new_shape) constReturn a resampled array of shape new_shape using bilinear interpolation.Definition methods.cpp:317void downscale_transform(Array &array, float kc, std::function< void(Array &x)> unary_op, bool apply_prefiltering=false)Applies a downscaling transformation to a 2D array using Fourier-based filtering.Definition downscale_transform.cpp:15
Result
◆ downscale_transform_multi()
| void hmap::downscale_transform_multi | ( | Array & | array, |
| std::vector< float > | kc_list, | ||
| std::function< void(Array &x, const int current_index)> | unary_op, | ||
| bool | apply_prefiltering = false |
||
| ) |
◆ upscale_amplification()
| void hmap::upscale_amplification | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | upscaling_levels, | ||
| float | persistence, | ||
| std::function< void(Array &x, float current_scaling)> | unary_op | ||
| ) |
Applies an upscaling amplification process to an array, followed by a unary operation.
This function progressively upscales the given array by powers of 2 (starting from the initial shape), performs a user-defined unary operation on the upscaled array at each level, and finally returns the array to its original resolution using bilinear interpolation.
- Parameters
-
array A reference to the array that will be upscaled and processed. upscaling_levels The number of upscaling levels to apply. The function will resample the array for each level. persistence A scaling factor applied at each level to adjust the impact of the unary operation. Higher persistence values will amplify the effects at each level. unary_op A user-defined unary operation to apply to the array at each upscaling level. The operation takes a reference to the array.
- Note
- The function first applies bicubic resampling to upscale the array, then applies the user-provided
unary_opat each upscaling level. After all levels are processed, the array is resampled back to its initial shape using bilinear interpolation.
◆ add_kernel()
Add a kernel to a specified position in an array.
This function adds the values of a smaller kernel array to the input array, centered at the specified indices (i, j). The kernel is added element-wise.
- Parameters
-
array The input array to which the kernel is added. kernel The kernel array to be added. i The row index in the input array where the kernel is centered. j The column index in the input array where the kernel is centered.
◆ add_kernel_maximum_smooth()
| void hmap::add_kernel_maximum_smooth | ( | Array & | array, |
| const Array & | kernel, | ||
| float | k_smooth, | ||
| int | i, | ||
| int | j | ||
| ) |
Adds a smoothed maximum value from a kernel to a specified position in a 2D array.
This function applies a truncated kernel to the given array at position (ic, jc), where the kernel is truncated to ensure it fits within the array's bounds. The maximum value between the current array value and the kernel value is computed using a smoothing factor, and the result is stored back in the array.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the 2D array (heightmap) where the kernel is applied. kernel The kernel array containing values to be applied to the array. k_smooth The smoothing factor used in the maximum_smooth function. ic The x-coordinate of the center in the array where the kernel is applied. jc The y-coordinate of the center in the array where the kernel is applied.
The kernel is truncated to ensure it fits within the bounds of the array. After applying the kernel, the values in the array are updated with the result of the maximum_smooth function.
◆ detrend_reg()
Apply linear regression for detrending of a 2D array.
This function performs detrending on the input array by applying linear regression separately to each row and column, removing trends from the data.
- Parameters
-
array Input 2D array to be detrended.
- Returns
- Array The detrended output array.
Example
Result
◆ hstack()
Horizontally stack two arrays side by side.
This function concatenates two arrays along their columns, forming a new array with the columns of the first array followed by the columns of the second array.
- Parameters
-
array1 The first array to stack. array2 The second array to stack.
- Returns
- Array The resulting array obtained by horizontally stacking
array1andarray2.
◆ inpainting_diffusion()
Perform diffusion-based inpainting to fill a specified region of an array.
This function fills the region defined by a mask in the input array using diffusion-based inpainting, which propagates known values to missing regions.
- Parameters
-
array Input array with missing regions. mask Mask specifying the region to be inpainted. iterations Number of diffusion iterations to perform.
- Returns
- Array The array with the inpainted region.
Example
Result
◆ linspace()
| std::vector< float > hmap::linspace | ( | float | start, |
| float | stop, | ||
| int | num, | ||
| bool | endpoint = true |
||
| ) |
Generate a vector of evenly spaced numbers over a specified interval.
This function creates a vector containing evenly spaced values from start to stop. The number of values is specified by num, and endpoint determines whether to include the end value in the output.
- See also
- linspace_jitted
- Parameters
-
start Starting value of the interval. stop End value of the interval. num Number of values to generate. endpoint If true, include the end value in the output vector.
- Returns
- std::vector<float> Vector of evenly spaced values.
◆ linspace_jitted()
| std::vector< float > hmap::linspace_jitted | ( | float | start, |
| float | stop, | ||
| int | num, | ||
| float | ratio, | ||
| int | seed, | ||
| bool | endpoint = true |
||
| ) |
Generate a vector of jittered (noised) numbers over a specified interval.
This function creates a vector with values spaced over an interval but with added noise, controlled by the ratio parameter. The noise is applied to an evenly spaced grid. The seed parameter controls the randomness.
- See also
- linspace
- Parameters
-
start Starting value of the interval. stop End value of the interval. num Number of values to generate. ratio Jittering ratio applied to the evenly spaced grid. seed Random seed for generating jittered values. endpoint If true, include the end value in the output vector.
- Returns
- std::vector<float> Vector of jittered values.
◆ fill_array_using_xy_function() [1/2]
| void hmap::fill_array_using_xy_function | ( | Array & | array, |
| glm::vec4 | bbox, | ||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param, | ||
| const Array * | p_noise_x, | ||
| const Array * | p_noise_y, | ||
| const Array * | p_stretching, | ||
| std::function< float(float, float, float)> | fct_xy | ||
| ) |
Fill an array using a scalar function based on (x, y) coordinates.
This function populates an array with values computed from a scalar function that depends on (x, y) coordinates. Additional input arrays can affect the function's computation, such as control parameters, noise, and stretching.
- Parameters
-
array The array to be filled with computed values. bbox The bounding box of the domain specified as {xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax}. p_ctrl_param Pointer to an array of control parameters affecting the scalar function. p_noise_x Pointer to an array of noise values along the x-direction for domain warping. p_noise_y Pointer to an array of noise values along the y-direction for domain warping. p_stretching Pointer to an array of local wavenumber multipliers for adjusting the function. fct_xy The scalar function to compute values at (x, y) with an initial value.
Example
Result
◆ fill_array_using_xy_function() [2/2]
| void hmap::fill_array_using_xy_function | ( | Array & | array, |
| glm::vec4 | bbox, | ||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param, | ||
| const Array * | p_noise_x, | ||
| const Array * | p_noise_y, | ||
| const Array * | p_stretching, | ||
| std::function< float(float, float, float)> | fct_xy, | ||
| int | subsampling | ||
| ) |
Fill an array using a scalar function based on (x, y) coordinates with subsampling.
This function is similar to the one above but includes a subsampling parameter to optimize performance. The array is subsampled during computation based on the subsampling factor, which determines how frequently the scalar function is applied.
- Parameters
-
array The array to be filled with computed values. bbox The bounding box of the domain specified as {xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax}. p_ctrl_param Pointer to an array of control parameters affecting the scalar function. p_noise_x Pointer to an array of noise values along the x-direction for domain warping. p_noise_y Pointer to an array of noise values along the y-direction for domain warping. p_stretching Pointer to an array of local wavenumber multipliers for adjusting the function. fct_xy The scalar function to compute values at (x, y) with an initial value. subsampling The factor by which the array is subsampled during computation.
Example
Result

This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ find_vertical_cut_path()
| void hmap::find_vertical_cut_path | ( | const Array & | error, |
| std::vector< int > & | path_i | ||
| ) |
Find the vertical cut path with the minimum cost using Dijkstra's algorithm.
This function identifies the vertical cut path in an array from the bottom to the top that has the minimum cumulative cost. The path is determined using Dijkstra's algorithm.
- Parameters
-
error Input array containing error or cost values. path_i Output vector of indices representing the cut path.
◆ generate_mask()
| Array hmap::generate_mask | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| std::vector< int > | cut_path_i, | ||
| int | ir | ||
| ) |
Generate a smooth mask based on a cut path.
This function creates a mask based on the vertical cut path indices obtained from the find_vertical_cut_path function. The mask is smoothed using a specified filtering radius.
- Parameters
-
shape Shape of the mask to be generated. cut_path_i Vector of vertical cut path indices. ir Filtering radius for smoothing the mask.
- Returns
- Array The generated smooth mask.
◆ get_random_patch()
| Array hmap::get_random_patch | ( | const Array & | array, |
| glm::ivec2 | patch_shape, | ||
| std::mt19937 & | gen, | ||
| bool | patch_flip = false, |
||
| bool | patch_rotate = false, |
||
| bool | patch_transpose = false, |
||
| std::vector< Array * > * | p_secondary_arrays = nullptr, |
||
| std::vector< Array > * | p_secondary_patches = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Extracts a random sub-array (patch) from the input array, with optional transformations.
This function selects a random patch from the specified input array and applies optional transformations such as flipping, rotation, and transposition. Additionally, if a list of secondary arrays is provided, corresponding patches are extracted and transformed in the same way.
- Parameters
-
array The main input array from which the patch is extracted. patch_shape The shape (dimensions) of the patch to be extracted. gen Random number generator for selecting patch location. patch_flip If true, allows the patch to be flipped vertically or horizontally. patch_rotate If true, allows the patch to be rotated by 90 degrees. patch_transpose If true, allows the patch to be transposed. p_secondary_arrays Optional pointer to a list of secondary arrays. If provided, patches will be extracted and transformed from each array in the list, with the same transformations as the primary patch. p_secondary_patches Optional pointer to a list for storing the transformed patches from each secondary array.
- Returns
- The extracted and transformed patch from the main input array.
◆ random_vector()
| std::vector< float > hmap::random_vector | ( | float | min, |
| float | max, | ||
| int | num, | ||
| int | seed | ||
| ) |
Generate a vector filled with random values within a specified range.
This function creates a vector with random values uniformly distributed between min and max. The number of values and the randomness is controlled by the seed parameter.
- Parameters
-
min Lower bound of the random values. max Upper bound of the random values. num Number of random values to generate. seed Random seed for generating values.
- Returns
- std::vector<float> Vector of random values.
◆ rescale_vector()
| void hmap::rescale_vector | ( | std::vector< float > & | vec, |
| float | vmin, | ||
| float | vmax | ||
| ) |
Rescales the values of a vector to a specified range.
This function linearly rescales all elements in vec so that their new values lie within the range [vmin, vmax]. The rescaling is based on the current minimum and maximum values found in the input vector.
Special cases:
- If
vecis empty, the function does nothing. - If
vmin == vmax, all elements are set tovmax. - If all elements of
vecare equal, they are replaced by that constant value.
- Parameters
-
vec Reference to the vector of float values to rescale (modified in place). vmin Desired minimum value after rescaling. vmax Desired maximum value after rescaling.
◆ rescaled_vector()
| std::vector< float > hmap::rescaled_vector | ( | const std::vector< float > & | vec, |
| float | vmin, | ||
| float | vmax | ||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ swap()
◆ vstack()
Vertically stack two arrays.
This function concatenates two arrays along their rows, resulting in a new array where the rows of the second array are stacked below the rows of the first array.
- Parameters
-
array1 The first array to be stacked. array2 The second array to be stacked.
- Returns
- Array The resulting array with
array1stacked on top ofarray2.
◆ get_primitive_base()
| Array hmap::get_primitive_base | ( | const PrimitiveType & | primitive_type, |
| const glm::ivec2 & | shape, | ||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a primitive shape as a 2D array.
- Parameters
-
primitive_type Type of primitive to generate. shape Output array resolution. p_noise_x Optional X-direction noise modulation. p_noise_y Optional Y-direction noise modulation. center Center position of the primitive (normalized). bbox Bounding box of the primitive (normalized).
- Returns
- The generated primitive as an Array.
◆ biquad_pulse()
| Array hmap::biquad_pulse | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | gain = 1.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return a 'biquadratic pulse'.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. gain Gain (the higher, the steeper). p_ctrl_param Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the gain parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array Perlin billow noise.
Example
Result
◆ bump()
| Array hmap::bump | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | gain = 1.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return a bump.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. gain Gain (the higher, the steeper the bump). p_ctrl_param Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the gain parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. center Primitive reference center. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array Perlin billow noise.
Example
Result
◆ bump_lorentzian()
| Array hmap::bump_lorentzian | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | shape_factor = 0.5f, |
||
| float | radius = 0.5f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a 2D Lorentzian bump pattern.
This function fills an array with values computed from a normalized Lorentzian-shaped bump function. The bump is centered at a given position, has a specified radius, and can vary in width depending on a control parameter. Optional noise arrays can be applied to perturb the x and y coordinates before evaluation.
The Lorentzian function is normalized so that it returns 1.0 at the center and smoothly decays to 0.0 at the radius boundary. Outside the radius, the value is exactly 0.
- Parameters
-
shape Dimensions of the output array (width, height). width_factor Scaling factor controlling the bump width relative to the control parameter. radius Radius of the bump in the coordinate space of bbox.p_ctrl_param Optional pointer to an array of per-pixel control parameters. If provided, it modulates the width of the Lorentzian bump. p_noise_x Optional pointer to an array of x-offset noise values. Values are added to the x coordinate before evaluation. p_noise_y Optional pointer to an array of y-offset noise values. Values are added to the y coordinate before evaluation. center Center of the bump in the coordinate space of bbox.bbox Bounding box (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax) defining the coordinate space for the array.
- Returns
- A new Array object of size
shapecontaining the bump pattern.
- Note
- The function normalizes the Lorentzian curve so that the maximum value is 1 at the center and smoothly decays to 0 at the boundary defined by
radius.
- See also
- fill_array_using_xy_function
Example
Result

◆ caldera() [1/2]
| Array hmap::caldera | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | radius, | ||
| float | sigma_inner, | ||
| float | sigma_outer, | ||
| float | z_bottom, | ||
| const Array * | p_noise, | ||
| float | noise_amp_r, | ||
| float | noise_ratio_z, | ||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return a caldera-shaped heightmap.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. radius Crater radius at the ridge. sigma_inner Inner half-width. sigma_outer Outer half-width. z_bottom Bottom elevation (ridge is at elevation 1).p_noise Displacement noise. noise_amp_r Radial noise absolute scale (in pixels). noise_ratio_z Vertical noise relative scale (in [0, 1]). center Primitive reference center. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array.
Example
Result
◆ caldera() [2/2]
| Array hmap::caldera | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | radius, | ||
| float | sigma_inner, | ||
| float | sigma_outer, | ||
| float | z_bottom, | ||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ checkerboard()
| Array hmap::checkerboard | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return a checkerboard heightmap.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. kw Noise wavenumber with respect to a unit domain. p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array New array.
Example
Result
◆ cone() [2/2]
| Array hmap::cone | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | slope, | ||
| float | apex_elevation = 1.f, |
||
| bool | smooth_profile = false, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a synthetic conical mountain heightmap.
This function creates a simple cone-shaped elevation field centered at a given position. The cone profile follows a linear slope until it reaches the talus angle, resembling volcanic cones or alluvial fans. Optional displacement noise fields can be applied to perturb the cone shape.
- Parameters
-
shape Output array shape (resolution in x and y). slope Slope angle of the cone (controls steepness of the sides). center Center of the cone in normalized coordinates (default = {0.5f, 0.5f}). p_noise_x Optional pointer to external displacement noise field (X-axis). p_noise_y Optional pointer to external displacement noise field (Y-axis). bbox Bounding box of the generation domain in normalized coordinates (default = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}).
- Returns
- Array containing the generated conical heightmap.
Example
Result

◆ cone_complex()
| Array hmap::cone_complex | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | alpha, | ||
| float | radius = 0.5f, |
||
| bool | smooth_profile = true, |
||
| float | valley_amp = 0.2f, |
||
| int | valley_nb = 5, |
||
| float | valley_decay_ratio = 0.5f, |
||
| float | valley_angle0 = 15.f, |
||
| const ErosionProfile & | erosion_profile = ErosionProfile::TRIANGLE_GRENIER, |
||
| float | erosion_delta = 0.01f, |
||
| float | radial_waviness_amp = 0.05f, |
||
| float | radial_waviness_kw = 2.f, |
||
| float | bias_angle = 30.f, |
||
| float | bias_amp = 0.75f, |
||
| float | bias_exponent = 1.f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a complex conical heightfield with valleys, directional bias, and radial waviness.
This function procedurally constructs an island-like cone shape inside a 2D array. The height at each position is determined from the normalized radial distance to the center, with optional modulation by valleys, directional bias, and radial waviness. An erosion profile is applied to shape the valleys, and an optional control map can modulate the valley amplitude locally. The resulting height values are clamped to [0, 1].
- Parameters
-
shape Output array dimensions (width, height). alpha Exponent controlling the steepness of the cone slope. radius Effective radius of the island (in coordinate space units). valley_amp Global amplitude of valley depressions. valley_nb Number of valleys around the island. valley_decay_ratio Controls how valley amplitude decays toward the center. valley_angle0 Angular offset of the first valley (in degrees). erosion_profile Erosion profile type used for shaping valley cross-sections. erosion_delta Smoothing parameter for the erosion profile function. radial_waviness_amp Amplitude of radial sinusoidal perturbations (coastal waviness). radial_waviness_kw Frequency multiplier for radial waviness. bias_angle Direction (in degrees) of the slope bias (e.g. wind or sun exposure). bias_amp Amplitude of the directional bias effect. bias_exponent Controls how bias strength varies with radius. center Center position of the cone in coordinate space. p_ctrl_param Optional control array; its values modulate the local valley amplitude. If nullptr, the valley amplitude is uniform. p_noise_x Optional X-displacement noise field for coordinate perturbation. p_noise_y Optional Y-displacement noise field for coordinate perturbation. bbox Bounding box defining the world coordinates covered by the array.
- Returns
- A 2D Array containing the generated heightfield values in the range [0, 1].
Example
Result

◆ cone_sigmoid()
| Array hmap::cone_sigmoid | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | alpha, | ||
| float | radius = 0.5f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a smooth conical heightmap using a sigmoid-based profile.
This function creates a 2D array representing a cone shape centered at a given position. The height decreases radially from the apex according to a sigmoid-shaped falloff, producing a smooth, rounded cone rather than a sharp linear one. Optionally, displacement noise can be applied along the X and Y axes to perturb the cone surface.
- Parameters
-
shape Dimensions of the output array (width, height). alpha Peak elevation value of the cone (controls maximum height). radius Radius of the cone base, expressed in normalized [0, 1] units relative to the bounding box. center Normalized coordinates of the cone’s center (default = {0.5, 0.5}). p_noise_x Optional pointer to an array representing horizontal displacement noise (nullptr for none). p_noise_y Optional pointer to an array representing vertical displacement noise (nullptr for none). bbox Bounding box of the generated region in (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax) order.
- Returns
- A 2D Array object containing the generated conical heightmap.
Example
Result

◆ constant()
◆ crater()
| Array hmap::crater | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | radius, | ||
| float | depth, | ||
| float | lip_decay, | ||
| float | lip_height_ratio = 0.5f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return a crater-shaped heightmap.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. radius Crater radius. lip_decay Ejecta lip decay. lip_height_ratio Controls the ejecta lip relative height, in [0, 1]. depth Crater depth. p_ctrl_param Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the lip_height_ratio parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array New array.
Example
Result
◆ cubic_pulse() [2/2]
| Array hmap::cubic_pulse | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| const Array * | p_noise_x, | ||
| const Array * | p_noise_y, | ||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a cubic pulse array.
◆ dendry() [1/2]
| Array hmap::dendry | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| Array & | control_function, | ||
| float | eps = 0.05, |
||
| int | resolution = 1, |
||
| float | displacement = 0.075, |
||
| int | primitives_resolution_steps = 3, |
||
| float | slope_power = 2.f, |
||
| float | noise_amplitude_proportion = 0.01, |
||
| bool | add_control_function = true, |
||
| float | control_function_overlap = 0.5f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, |
||
| int | subsampling = 1 |
||
| ) |
Dendry is a locally computable procedural function that generates branching patterns at various scales (see [Gaillard2019]).
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. kw Noise wavenumber with respect to a unit domain. seed Random seed number. control_array Control array (can be of any shape, different from shape).eps Epsilon used to bias the area where points are generated in cells. resolution Number of resolutions in the noise function. displacement Maximum displacement of segments. primitives_resolution_steps Additional resolution steps in the ComputeColorPrimitives function. slope_power Additional parameter to control the variation of slope on terrains. noise_amplitude_proportion Proportion of the amplitude of the control function as noise. add_control_function Add control function to the output. control_function_overlap Extent of the extension added at the domain frontiers of the control array. p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array New array.
Example
Result
◆ dendry() [2/2]
| Array hmap::dendry | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| NoiseFunction & | noise_function, | ||
| float | noise_function_offset = 0.f, |
||
| float | noise_function_scaling = 1.f, |
||
| float | eps = 0.05, |
||
| int | resolution = 1, |
||
| float | displacement = 0.075, |
||
| int | primitives_resolution_steps = 3, |
||
| float | slope_power = 2.f, |
||
| float | noise_amplitude_proportion = 0.01, |
||
| bool | add_control_function = true, |
||
| float | control_function_overlap = 0.5f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
◆ diffusion_limited_aggregation()
| Array hmap::diffusion_limited_aggregation | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | scale, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | seeding_radius = 0.4f, |
||
| float | seeding_outer_radius_ratio = 0.2f, |
||
| float | slope = 8.f, |
||
| float | noise_ratio = 0.2f |
||
| ) |
Generates a diffusion-limited aggregation (DLA) pattern.
This function simulates the diffusion-limited aggregation process to generate a pattern within a grid of specified dimensions. The DLA process models particles that undergo a random walk until they stick to a seed, gradually forming complex fractal structures.
- Parameters
-
shape The dimensions of the grid where the DLA pattern will be generated. It is represented as a glm::ivec2object, where the first element is the width and the second element is the height.scale A scaling factor that influences the density of the particles in the DLA pattern. seeding_radius The radius within which initial seeding of particles occurs. This radius defines the area where the first particles are placed. seeding_outer_radius_ratio The ratio between the outer seeding radius and the initial seeding radius. It determines the outer boundary for particle seeding. slope Slope of the talus added to the DLA pattern. noise_ratio A parameter that controls the amount of randomness or noise introduced in the talus formation process. seed The seed for the random number generator, ensuring reproducibility of the pattern. The same seed will generate the same pattern.
- Returns
- A 2D array representing the generated DLA pattern. The array is of the same size as specified by
shape.
Example
Result
◆ disk() [2/2]
| Array hmap::disk | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | radius, | ||
| float | slope = 1.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a disk-shaped heightmap with optional modifications.
This function creates a 2D array representing a disk shape with a specified radius, slope, and other optional parameters such as control parameters, noise, and stretching for additional customization.
- Parameters
-
shape Dimensions of the output array (width, height). radius Radius of the disk, in normalized coordinates (0.0 to 1.0). slope Slope of the disk edge transition. A larger value makes the edge transition sharper. Defaults to 1.0. p_ctrl_param Optional pointer to an Arraycontrolling custom parameters for the disk generation.p_noise_x Optional pointer to an Arrayfor adding noise in the x-direction.p_noise_y Optional pointer to an Arrayfor adding noise in the y-direction.p_stretching Optional pointer to an Arrayfor stretching the disk horizontally or vertically.center Center of the disk in normalized coordinates (0.0 to 1.0). Defaults to {0.5, 0.5}. bbox Bounding box for the disk in normalized coordinates {x_min, x_max, y_min, y_max}. Defaults to {0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0}.
- Returns
- A 2D array representing the generated disk shape.
- Example #include "highmap.hpp"int main(void){glm::ivec2 shape = {256, 256};float radius = 0.2f;float slope = 6.f;z1.infos();// with control arrayglm::vec2 kw = {4.f, 4.f};int seed = 1;shape,kw,seed);hmap::remap(ctrl_array, 0.8f, 1.2f);}
Result
◆ gabor_noise()
| Array hmap::gabor_noise | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | kw, | ||
| float | angle, | ||
| int | width, | ||
| float | density, | ||
| uint | seed | ||
| ) |
Return a sparse Gabor noise.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. kw Kernel wavenumber, with respect to a unit domain. angle Kernel angle (in degree). width Kernel width (in pixels). density Spot noise density. seed Random seed number.
- Returns
- Array New array.
Example
Result

◆ gaussian_pulse()
| Array hmap::gaussian_pulse | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | sigma, | ||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return a gaussian_decay pulse kernel.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. sigma Gaussian sigma (in pixels). p_ctrl_param Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the half-width parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. center Primitive reference center. center Primitive reference center. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array
Example
Result
◆ island_land_mask()
| Array hmap::island_land_mask | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | radius, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | displacement = 0.2f, |
||
| NoiseType | noise_type = NoiseType::SIMPLEX2S, |
||
| float | kw = 4.f, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.f, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| const glm::vec2 & | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a 2D island mask by perturbing a radial boundary with noise.
Creates a binary mask of a single connected island using radial distance from a center point and adding an FBM-based angular displacement.
- Parameters
-
shape Output array size (width, height). radius Base island radius. seed Noise seed. displacement Amplitude of boundary perturbation. noise_type Type of underlying noise function. kw Angular frequency for sampling the noise. octaves Number of FBM octaves. weight Base amplitude of the FBM. persistence Amplitude falloff per octave. lacunarity Frequency multiplier per octave. center Center of the island in normalized coordinates. bbox Bounding box for coordinate remapping.
- Returns
- Binary mask where 1.f indicates land and 0.f indicates water.
Example
Result
◆ multisteps()
| Array hmap::multisteps | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | angle, | ||
| float | r = 1.2f, |
||
| int | nsteps = 8, |
||
| float | elevation_exponent = 0.7f, |
||
| float | shape_gain = 4.f, |
||
| float | scale = 0.5f, |
||
| float | outer_slope = 0.1f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const glm::vec2 & | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generate a multi-step height profile along a rotated axis.
Constructs an Array where values follow a sequence of geometric steps blended with an optional linear transition. Steps are rotated by the given angle, can be shaped with an exponent, and may be modulated by optional control and noise fields.
- Parameters
-
shape Output array resolution. angle Rotation angle in degrees. r Geometric ratio between successive step widths. nsteps Number of steps. elevation_exponent Exponent shaping step heights. shape_gain Gain used to reshape intra-step transitions. scale Scale of the step axis. outer_slope Slope outside the [0,1] axis interval. p_ctrl_param Optional control parameter array. p_noise_x Optional x-axis noise array. p_noise_y Optional y-axis noise array. center Center of the step axis. bbox Bounding box of the domain.
- Returns
- Generated Array.
Example
Result
◆ noise()
| Array hmap::noise | ( | NoiseType | noise_type, |
| glm::ivec2 | shape, | ||
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return an array filled with coherence noise.
- Parameters
-
noise_type Noise type. shape Array shape. kw Noise wavenumbers {kx, ky} for each directions. seed Random seed number. p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array.
Example
Result

◆ noise_fbm()
| Array hmap::noise_fbm | ( | NoiseType | noise_type, |
| glm::ivec2 | shape, | ||
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return an array filled with coherence fbm noise.
- Parameters
-
noise_type Noise type. shape Array shape. kw Noise wavenumbers {kx, ky} for each directions. seed Random seed number. octaves Number of octaves. weigth Octave weighting. persistence Octave persistence. lacunarity Defines the wavenumber ratio between each octaves. p_ctrl_param Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the weight parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array Fractal noise.
Example
Result
◆ noise_iq()
| Array hmap::noise_iq | ( | NoiseType | noise_type, |
| glm::ivec2 | shape, | ||
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| float | gradient_scale = 0.05f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return an array filled with coherence fbm noise.
- Parameters
-
noise_type Noise type. shape Array shape. kw Noise wavenumbers {kx, ky} for each directions. seed Random seed number. octaves Number of octaves. weigth Octave weighting. persistence Octave persistence. lacunarity Defines the wavenumber ratio between each octaves. gradient_scale Gradient scale. p_ctrl_param Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the weight parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array Fractal noise.
Example
Result







◆ noise_jordan()
| Array hmap::noise_jordan | ( | NoiseType | noise_type, |
| glm::ivec2 | shape, | ||
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| float | warp0 = 0.4f, |
||
| float | damp0 = 1.f, |
||
| float | warp_scale = 0.4f, |
||
| float | damp_scale = 1.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return an array filled with coherence fbm noise.
- Parameters
-
noise_type Noise type. shape Array shape. kw Noise wavenumbers {kx, ky} for each directions. seed Random seed number. octaves Number of octaves. weigth Octave weighting. persistence Octave persistence. lacunarity Defines the wavenumber ratio between each octaves. warp0 Initial warp scale. damp0 Initial damp scale. warp_scale Warp scale. damp_scale Damp scale. p_ctrl_param Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the weight parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array Fractal noise.
Example
Result







◆ noise_parberry()
| Array hmap::noise_parberry | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| float | mu = 1.02f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return an array filled with coherent fbm Parberry variant of Perlin noise.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. kw Noise wavenumbers {kx, ky} for each directions. seed Random seed number. octaves Number of octaves. weigth Octave weighting. persistence Octave persistence. lacunarity Defines the wavenumber ratio between each octaves. mu Gradient magnitude exponent. p_ctrl_param Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the weight parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array Fractal noise.
Example
Result







◆ noise_pingpong()
| Array hmap::noise_pingpong | ( | NoiseType | noise_type, |
| glm::ivec2 | shape, | ||
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return an array filled with coherence fbm pingpong noise.
- Parameters
-
noise_type Noise type. shape Array shape. kw Noise wavenumbers {kx, ky} for each directions. seed Random seed number. octaves Number of octaves. weigth Octave weighting. persistence Octave persistence. lacunarity Defines the wavenumber ratio between each octaves. p_ctrl_param Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the weight parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array Fractal noise.
Example
Result







◆ noise_ridged()
| Array hmap::noise_ridged | ( | NoiseType | noise_type, |
| glm::ivec2 | shape, | ||
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| float | k_smoothing = 0.1f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return an array filled with coherence fbm ridged noise.
- Parameters
-
noise_type Noise type. shape Array shape. kw Noise wavenumbers {kx, ky} for each directions. seed Random seed number. octaves Number of octaves. weigth Octave weighting. persistence Octave persistence. lacunarity Defines the wavenumber ratio between each octaves. k_smoothing Smoothing parameter. p_ctrl_param Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the weight parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array Fractal noise.
Example
Result







◆ noise_swiss()
| Array hmap::noise_swiss | ( | NoiseType | noise_type, |
| glm::ivec2 | shape, | ||
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| float | warp_scale = 0.1f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return an array filled with coherence fbm swiss noise.
- Parameters
-
noise_type Noise type. shape Array shape. kw Noise wavenumbers {kx, ky} for each directions. seed Random seed number. octaves Number of octaves. weigth Octave weighting. persistence Octave persistence. lacunarity Defines the wavenumber ratio between each octaves. warp_scale Warp scale. p_ctrl_param Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the weight parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array Fractal noise.
Example
Result







◆ paraboloid()
| Array hmap::paraboloid | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | angle, | ||
| float | a, | ||
| float | b, | ||
| float | v0 = 0.f, |
||
| bool | reverse_x = false, |
||
| bool | reverse_y = false, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return a paraboloid.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. angle Rotation angle. a Curvature parameter, first principal axis. b Curvature parameter, second principal axis. v0 Value at the paraboloid center. reverse_x Reverse coefficient of first principal axis. reverse_y Reverse coefficient of second principal axis. p_base_elevation Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the weight parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. center Primitive reference center. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Output array.
Example
Result
◆ peak()
| Array hmap::peak | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | radius, | ||
| const Array * | p_noise, | ||
| float | noise_r_amp, | ||
| float | noise_z_ratio, | ||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return a peak-shaped heightmap.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. radius Peak outer radius. p_noise Reference to the input noise array used for domain warping (NOT in pixels, with respect to a unit domain). noise_amp_r Radial noise absolute scale (in pixels). noise_ratio_z Vertical noise relative scale (in [0, 1]). bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array.
Example
Result
◆ phasor()
| Array hmap::phasor | ( | PhasorProfile | phasor_profile, |
| glm::ivec2 | shape, | ||
| float | kw, | ||
| const Array & | angle, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | profile_delta = 0.1f, |
||
| float | density_factor = 1.f, |
||
| float | kernel_width_ratio = 2.f, |
||
| float | phase_smoothing = 2.f |
||
| ) |
Generates a phasor noise field based on a Gabor noise model and phase profile.
This function creates a phasor noise array using a Gabor kernel approach, applying a specified phase profile, smoothing, and density settings. The output is influenced by the shape, frequency, and various noise characteristics, allowing fine control over the generated noise field.
- Parameters
-
phasor_profile The phase profile to apply. Determines the type of phasor function used (e.g., bulky cosine, peaky cosine). shape The dimensions of the output array as a 2D vector (width x height). kw The wave number (frequency) of the Gabor kernel. angle An array specifying the angle field for the Gabor kernel orientation. seed A seed value for the random number generator used to create jittered spawn points for Gabor kernels. profile_delta A parameter for adjusting the delta in the phase profile function. density_factor A scaling factor for the density of Gabor kernel spawn points. kernel_width_ratio The ratio of the kernel width to the phase field resolution. phase_smoothing A factor for controlling the blending of the phase profile. Larger values result in smoother transitions.
- Returns
- An
Arraycontaining the generated phasor noise field.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argumentIfaninvalid`phasor_profile`isprovided.
- Note
- If the kernel width is too small (less than 4), the function returns a zeroed array.
The function performs the following steps:
- Generates Gabor kernel spawn points using jittered random sampling.
- Constructs Gabor kernels based on the input angle field and applies them to noise arrays.
- Computes a phase field from the Gabor noise using
atan2. - Applies the specified phase profile using the
get_phasor_profile_function. - Smooths the phase field if
phase_smoothingis greater than zero.
Example
Result
◆ phasor_fbm()
| Array hmap::phasor_fbm | ( | PhasorProfile | phasor_profile, |
| glm::ivec2 | shape, | ||
| float | kw, | ||
| const Array & | angle, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | profile_delta = 0.1f, |
||
| float | density_factor = 1.f, |
||
| float | kernel_width_ratio = 2.f, |
||
| float | phase_smoothing = 2.f, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f |
||
| ) |
Generates a fractal Brownian motion (fBm) noise field using layered phasor profiles.
- Parameters
-
phasor_profile The phase profile to apply for each noise layer (e.g., bulky cosine, peaky cosine). shape The dimensions of the output array as a 2D vector (width x height). kw The base wave number (frequency) for the first noise layer. angle An array specifying the angle field for the Gabor kernel orientation in each layer. seed A seed value for the random number generator used in all noise layers. profile_delta A parameter for adjusting the delta in the phase profile function. density_factor A scaling factor for the density of Gabor kernel spawn points in each layer. kernel_width_ratio The ratio of the kernel width to the phase field resolution. phase_smoothing A factor for controlling the blending of the phase profile. Larger values result in smoother transitions. octaves The number of noise layers (octaves) to generate. weight A factor for controlling amplitude adjustments based on the previous layer's values. persistence A factor controlling how amplitude decreases across successive octaves. Values <1 cause rapid decay. lacunarity A factor controlling how frequency increases across successive octaves. Values >1 cause rapid growth.
- Returns
- An
Arraycontaining the generated fBm noise field.
- Exceptions
-
std::invalid_argumentIfaninvalid`phasor_profile`isprovidedtothe underlying phasorfunction.
Example
Result

◆ rectangle()
| Array hmap::rectangle | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | rx, | ||
| float | ry, | ||
| float | angle, | ||
| float | slope = 1.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a rectangle-shaped heightmap with optional modifications.
This function creates a 2D array representing a rectangle with specified dimensions, rotation, and optional parameters for customization such as control parameters, noise, and stretching.
- Parameters
-
shape Dimensions of the output array (width, height). rx Half-width of the rectangle, in normalized coordinates (0.0 to 1.0). ry Half-height of the rectangle, in normalized coordinates (0.0 to 1.0). angle Rotation angle of the rectangle in radians. Positive values rotate counterclockwise. slope Slope of the rectangle edge transition. A larger value makes the edge transition sharper. Defaults to 1.0. p_ctrl_param Optional pointer to an Arraycontrolling custom parameters for the rectangle generation.p_noise_x Optional pointer to an Arrayfor adding noise in the x-direction.p_noise_y Optional pointer to an Arrayfor adding noise in the y-direction.p_stretching Optional pointer to an Arrayfor stretching the rectangle horizontally or vertically.center Center of the rectangle in normalized coordinates (0.0 to 1.0). Defaults to {0.5, 0.5}. bbox Bounding box for the rectangle in normalized coordinates {x_min, x_max, y_min, y_max}. Defaults to {0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0}.
- Returns
- A 2D array representing the generated rectangle shape.
- Example #include "highmap.hpp"int main(void){glm::ivec2 shape = {256, 256};float rx = 0.1f;float ry = 0.2f;float angle = 15.f;float slope = 6.f;z1.infos();// with control arrayglm::vec2 kw = {4.f, 4.f};int seed = 1;shape,kw,seed);hmap::remap(ctrl_array, 0.8f, 1.2f);hmap::export_banner_png("ex_rectangle.png",{z1, z2},false);}Array rectangle(glm::ivec2 shape, float rx, float ry, float angle, float slope=1.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f})Generates a rectangle-shaped heightmap with optional modifications.Definition primitives.cpp:225
- Example
Result
◆ rift()
| Array hmap::rift | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | angle, | ||
| float | slope, | ||
| float | width, | ||
| bool | sharp_bottom = false, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return a rift function (Heaviside with an optional talus slope at the transition).
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. angle Overall rotation angle (in degree). slope Step slope (assuming a unit domain). width Rift width (assuming a unit domain). sharp_bottom Decide whether the rift bottom is sharp or not. p_ctrl_param Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the width parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local coordinate multiplier. center Primitive reference center. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array New array.
Example
Result
◆ slope()
| Array hmap::slope | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | angle, | ||
| float | slope, | ||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return an array corresponding to a slope with a given overall.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. angle Overall rotation angle (in degree). slope Slope (assuming a unit domain). p_ctrl_param Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the slope parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local coordinate multiplier. center Primitive reference center. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array New array.
Example
Result

◆ smooth_cosine() [2/2]
| Array hmap::smooth_cosine | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| const Array * | p_noise_x, | ||
| const Array * | p_noise_y, | ||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a smooth cosine array.
◆ step()
| Array hmap::step | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | angle, | ||
| float | slope, | ||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return a step function (Heaviside with an optional talus slope at the transition).
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. angle Overall rotation angle (in degree). slope Step slope (assuming a unit domain). p_ctrl_param Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the slope parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local coordinate multiplier. center Primitive reference center. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array New array.
Example
Result
◆ swirl()
| void hmap::swirl | ( | Array & | dx, |
| Array & | dy, | ||
| float | amplitude = 1.f, |
||
| float | exponent = 1.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generate displacements dx and dy to apply a swirl effect to another primitve.
- Parameters
-
dx[out] 'x' displacement (unit domain scale). dy[out] 'y' displacement (unit domain scale). amplitude Displacement amplitude. exponent Distance exponent. p_noise eference to the input noise array. bbox Domain bounding box.
Example
Result
◆ wave_dune()
| Array hmap::wave_dune | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | kw, | ||
| float | angle, | ||
| float | xtop, | ||
| float | xbottom, | ||
| float | phase_shift = 0.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return a dune shape wave.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. kw Wavenumber with respect to a unit domain. angle Overall rotation angle (in degree). xtop Relative location of the top of the dune profile (in [0, 1]). xbottom Relative location of the foot of the dune profile (in [0, 1]). phase_shift Phase shift (in radians). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array New array.
◆ wave_sine()
| Array hmap::wave_sine | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | kw, | ||
| float | angle, | ||
| float | phase_shift = 0.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return a sine wave.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. kw Wavenumber with respect to a unit domain. angle Overall rotation angle (in degree). phase_shift Phase shift (in radians). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array New array.
Example
Result


◆ wave_square()
| Array hmap::wave_square | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | kw, | ||
| float | angle, | ||
| float | phase_shift = 0.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return a square wave.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. kw Wavenumber with respect to a unit domain. angle Overall rotation angle (in degree). phase_shift Phase shift (in radians). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array New array.
Example
Result


◆ wave_triangular()
| Array hmap::wave_triangular | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | kw, | ||
| float | angle, | ||
| float | slant_ratio, | ||
| float | phase_shift = 0.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return a triangular wave.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. kw Wavenumber with respect to a unit domain. angle Overall rotation angle (in degree). slant_ratio Relative location of the triangle apex, in [0, 1]. phase_shift Phase shift (in radians). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array New array.
Example
Result


◆ white()
Return an array filled with white noise.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. a Lower bound of random distribution. b Upper bound of random distribution. seed Random number seed.
- Returns
- Array White noise.
Example
Result
- See also
white_sparse
◆ white_density_map()
Return an array filled 1 with a probability based on a density map.
- Parameters
-
density_map Density map. seed Random number seed.
- Returns
- Array New array.
Example
Result
◆ white_sparse()
Return an array sparsely filled with white noise.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. a Lower bound of random distribution. b Upper bound of random distribution. density Array filling density, in [0, 1]. If set to 1, the function is equivalent to white.seed Random number seed.
- Returns
- Array Sparse white noise.
Example
Result
- See also
white
◆ white_sparse_binary()
◆ worley_double()
| Array hmap::worley_double | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | ratio = 0.5f, |
||
| float | k = 0.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return an array filled with the maximum of two Worley (cellular) noises.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. kw Noise wavenumbers {kx, ky} for each directions, with respect to a unit domain. seed Random seed number. ratio Amplitude ratio between each Worley noise. k Transition smoothing parameter. p_ctrl_param Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the ratio parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. p_stretching Local wavenumber multiplier. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array Noise.
Example
Result
◆ chop()
| void hmap::chop | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | vmin | ||
| ) |
Set to zero any value lower than vmin.
This function processes the input array and sets any value that is less than the specified lower bound vmin to zero. This operation effectively "chops
off" values that fall below the threshold, which can be useful for filtering out unwanted low values in data processing tasks.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be processed. Values lower than vminwill be set to zero.vmin Lower bound threshold. Values below this threshold will be set to zero.
Example
Result

◆ chop_max_smooth()
| void hmap::chop_max_smooth | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | vmax | ||
| ) |
Set to zero any value lower than vmax and apply a linear decrease slope between vmax / 2 and vmax.
This function processes the input array and sets any value below the upper bound vmax to zero. Additionally, it applies a linear decrease slope to values that fall between vmax / 2 and vmax. This creates a smooth transition where values gradually approach zero as they get closer to vmax, providing a more nuanced adjustment compared to a sharp cutoff.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be processed. Values below vmaxwill be adjusted, with a linear decrease applied betweenvmax / 2andvmax.vmax Upper bound threshold. Values below this threshold will be zeroed, with linear decrease applied in the specified range.
Example
Result

◆ clamp() [1/2]
Clamp array elements to a target range.
This function restricts the values in the input array to be within a specified range. Values below vmin are set to vmin, and values above vmax are set to vmax. This operation ensures that all elements of the array remain within the defined bounds.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be clamped. vmin Lower bound of the clamping range (default is 0). vmax Upper bound of the clamping range (default is 1).
Example
Result
◆ clamp() [2/2]
Clamps the values of an array according to the specified mode.
This function modifies the input array in place based on one of three clamping modes:
- ClampMode::POSITIVE_ONLY Keeps only positive values and clamps them to a maximum value
vmax. All negative values are set to 0. - ClampMode::NEGATIVE_ONLY Keeps only negative values, reverses their sign (making them positive), and clamps them to a maximum value
vmax. Positive values are set to 0. - ClampMode::BOTH Keeps both positive and negative values, clamping them symmetrically between
-vmaxandvmax.
- Parameters
-
array Reference to the array whose values will be clamped. vmax The maximum absolute value used for clamping. mode The clamping mode to apply (see ClampMode).
◆ clamp_min() [1/2]
| void hmap::clamp_min | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | vmin | ||
| ) |
◆ clamp_min() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ clamp_min_smooth() [1/3]
Clamp array values lower than a given bound with a smooth transition.
This function smoothly clamps values in the input array that are below the specified lower bound vmin. The smoothing parameter k controls the degree of smoothness applied during the clamping process.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be clamped. vmin Lower bound for clamping. k Smoothing parameter in the range [0, 1] (default is 0.2f).
◆ clamp_min_smooth() [2/3]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ clamp_min_smooth() [3/3]
| float hmap::clamp_min_smooth | ( | float | x, |
| float | vmin, | ||
| float | k = 0.2f |
||
| ) |
Clamp a single value lower than a given bound with a smooth transition.
This function smoothly clamps a single value that is below the specified lower bound vmin. The smoothing parameter k controls the degree of smoothness applied during the clamping process.
- Parameters
-
x Input value to be clamped. vmin Lower bound for clamping. k Smoothing parameter in the range [0, 1] (default is 0.2f).
- Returns
- float The smoothly clamped value.
◆ clamp_max() [1/2]
| void hmap::clamp_max | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | vmax | ||
| ) |
◆ clamp_max() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ clamp_max_smooth() [1/2]
Clamp array values larger than a given bound with a smooth transition.
This function smoothly clamps values in the input array that are above the specified upper bound vmax. The smoothing parameter k controls the degree of smoothness applied during the clamping process.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be clamped. vmax Upper bound for clamping. k Smoothing parameter in the range [0, 1] (default is 0.2f).
◆ clamp_max_smooth() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ clamp_oblique_plane()
| void hmap::clamp_oblique_plane | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | vmax, | ||
| float | angle, | ||
| float | slope, | ||
| bool | use_max_operator = true, |
||
| float | k = 0.f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Clamps an array against an oblique plane.
Generates a sloped plane and clamps the input array either with a min or max operator, optionally using a smooth transition controlled by k.
- Parameters
-
array Array to be modified. vmax Offset applied to the generated plane. angle Plane angle in radians. slope_value Slope intensity of the plane. use_max_operator If true, apply a max-clamp; otherwise apply a min-clamp. k Smoothness factor (0 for hard clamp). center Center of the plane. bbox Bounding box used to generate the plane.
Example
Result

◆ clamp_smooth()
Clamp array values within a given interval with a smooth transition.
This function smoothly clamps values in the input array to be within a specified range. Values below vmin are smoothly transitioned to vmin, and values above vmax are smoothly transitioned to vmax. The smoothing parameter k controls the degree of smoothness applied during the clamping process.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be clamped. vmin Lower bound of the clamping range. vmax Upper bound of the clamping range. k Smoothing parameter in the range [0, 1] (default is 0.2f).
◆ maximum() [1/2]
Return the element-wise maximum of two arrays.
This function computes the element-wise maximum between two input arrays. Each element in the resulting array is the maximum of the corresponding elements from array1 and array2.
- Parameters
-
array1 First input array. array2 Second input array.
- Returns
- Array The element-wise maximum between
array1andarray2.
◆ maximum() [2/2]
Return the element-wise maximum of an array and a scalar value.
This overloaded function computes the element-wise maximum between an input array and a scalar value. Each element in the resulting array is the maximum of the corresponding element from the input array and the scalar value.
- Parameters
-
array1 Input array. value Scalar value to compare with each element of the array.
- Returns
- Array The element-wise maximum between
array1andvalue. This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ maximum_smooth() [1/2]
Return the polynomial cubic smooth element-wise maximum of two arrays.
This function computes the element-wise maximum of two input arrays with a smooth transition to avoid discontinuities that are present in the standard maximum function. The smoothness is controlled by the parameter k, which determines how smoothly the transition between the two arrays occurs.
The smooth transition is achieved using a polynomial cubic function, which provides a smooth blend between the two arrays. This approach helps in avoiding abrupt changes and can be useful in applications requiring smooth transitions.
- Parameters
-
array1 First array to be compared. array2 Second array to be compared. k Smoothing parameter in the range [0, 1]. Higher values result in smoother transitions between the arrays (default is 0.2).
- Returns
- Array Element-wise smooth maximum between the two input arrays.
Example
Result

- See also
minimum_smooth,minimum,maximum
◆ maximum_smooth() [2/2]
| float hmap::maximum_smooth | ( | const float | a, |
| const float | b, | ||
| float | k = 0.2 |
||
| ) |
Return the polynomial cubic smooth maximum of two scalar values.
This function computes the smooth maximum of two scalar values with a polynomial cubic smooth transition. The parameter k controls the degree of smoothness applied to the maximum calculation, ensuring a continuous and smooth blend between the two values.
The smooth transition helps in avoiding abrupt changes, making this function suitable for applications that require smooth variations.
- Parameters
-
a First scalar value. b Second scalar value. k Smoothing parameter in the range [0, 1]. Higher values result in smoother transitions between the values (default is 0.2).
- Returns
- float Smooth maximum value between the two input values.
Example
Result

- See also
minimum_smooth,minimum,maximumThis is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ minimum() [1/2]
Return the element-wise minimum of two arrays.
This function computes the element-wise minimum between two input arrays. Each element in the resulting array is the minimum of the corresponding elements from array1 and array2.
- Parameters
-
array1 First input array. array2 Second input array.
- Returns
- Array The element-wise minimum between
array1andarray2.
◆ minimum() [2/2]
Return the element-wise minimum of an array and a scalar value.
This overloaded function computes the element-wise minimum between an input array and a scalar value. Each element in the resulting array is the minimum of the corresponding element from the input array and the scalar value.
- Parameters
-
array1 Input array. value Scalar value to compare with each element of the array.
- Returns
- Array The element-wise minimum between
array1andvalue. This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ minimum_smooth() [1/2]
Return the polynomial cubic smooth element-wise minimum of two arrays.
This function computes a smooth element-wise minimum between two input arrays using a polynomial cubic smoothing function. The smoothing parameter k controls the blending between the arrays, reducing the discontinuity found in a standard minimum operation. For details on the smoothing technique, refer to Inigo Quilez's articles.
- Parameters
-
array1 First input array. array2 Second input array. k Smoothing parameter in the range [0, 1] that determines the degree of blending between the two arrays (default is 0.2).
- Returns
- Array The element-wise smooth minimum between
array1andarray2.
- See also
maximum_smooth,minimum,maximum
◆ minimum_smooth() [2/2]
| float hmap::minimum_smooth | ( | const float | a, |
| const float | b, | ||
| float | k | ||
| ) |
Return the polynomial cubic smooth minimum of two scalar values.
This overloaded function computes a smooth minimum between two scalar values using a polynomial cubic smoothing function. The smoothing parameter k controls the blending between the values, reducing discontinuity compared to a standard minimum operation.
- Parameters
-
a First scalar value. b Second scalar value. k Smoothing parameter in the range [0, 1] that determines the degree of blending between the two values (default is 0.2).
- Returns
- float The smooth minimum between
aandb. This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ remap() [1/2]
| void hmap::remap | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | vmin, | ||
| float | vmax, | ||
| float | from_min, | ||
| float | from_max | ||
| ) |
Remap array elements from a starting range to a target range.
This function maps the values in the input array from one specified range to another. By default, the function uses the minimum and maximum values of the input array as the starting range. The target range is specified by vmin and vmax.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be remapped. vmin The lower bound of the target range to remap to. vmax The upper bound of the target range to remap to. from_min The lower bound of the starting range to remap from. from_max The upper bound of the starting range to remap from.
Example
- See also
clamp
◆ remap() [2/2]
| void hmap::remap | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | vmin = 0, |
||
| float | vmax = 1 |
||
| ) |
Remap array elements from a starting range to a target range (default range).
This overloaded function remaps the values in the input array from the default starting range (the minimum and maximum values of the array) to a target range specified by vmin and vmax.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be remapped. vmin The lower bound of the target range to remap to (default is 0). vmax The upper bound of the target range to remap to (default is 1). This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ rescale()
Remap array elements from a starting range to a target range.
This function adjusts the values in the input array by scaling them and shifting them to fit within a new range. The scaling factor determines how much the values are stretched or compressed, and the reference value shifts the values to align with the target range.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be rescaled. scaling Amplitude scaling factor to adjust the range of array elements. vref Reference 'zero' value used to shift the values (default is 0.f).
◆ generate_network_alpha_model()
| Graph hmap::generate_network_alpha_model | ( | const std::vector< float > & | xc, |
| const std::vector< float > & | yc, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | size, | ||
| glm::vec4 | bbox, | ||
| const Array & | z, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | alpha = 0.7f, |
||
| int | n_dummy_nodes = 2500, |
||
| float | dz_weight = 1.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_weight = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Generate a large scale road network between "nodes" (or cities) using the alpha model.
Based on the paper of Molinero et al. [Molinero2020].
- Parameters
-
xc xlocations of the cities.yc ylocations of the cities.size City sizes (arbitrary unit). bbox Bounding box. z Heightmap. seed Random seed number. alpha "Alpha coefficient" of the model (cost difference between creating a new and using an old one). n_dummy_nodes Number of dummy nodes added for the tesselation. dz_weight Weight of the elevation difference in the cost function. p_weight Map defining the local value added to the cost function (can be used to add large penalizations to create "no go" zones).
- Returns
- Graph Road network, edge weights correspond to the road "size".
Example
Result

◆ sdf_2d_polyline()
| Array hmap::sdf_2d_polyline | ( | const Path & | path, |
| glm::ivec2 | shape, | ||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Computes the signed distance field (SDF) of a 2D polyline.
This function calculates the distance of each grid cell in the specified 2D array to the closest segment of a polyline. The polyline is represented by a Path object, and optional noise fields can be added to perturb the array coordinates.
- Parameters
-
path The polyline path represented as a Pathobject containing the nodes.shape The dimensions (width, height) of the output array grid. bbox The bounding box of the array grid in the format (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax). p_noise_x Pointer to an optional noise array for perturbing x-coordinates (can be nullptr). p_noise_y Pointer to an optional noise array for perturbing y-coordinates (can be nullptr).
- Returns
- Array The resulting signed distance field (SDF) as a 2D array.
Example
Result
◆ sdf_2d_polyline_bezier()
| Array hmap::sdf_2d_polyline_bezier | ( | const Path & | path, |
| glm::ivec2 | shape, | ||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr |
||
| ) |
See hmap::sdf_2d_polyline, with a Bezier approximation of the path.
◆ perturb_mask_contour()
| Array hmap::perturb_mask_contour | ( | const Array & | mask, |
| const Array & | noise, | ||
| float | max_displacement, | ||
| int | ir = 1 |
||
| ) |
Perturb the contour of a binary mask using a displacement field, while trying to preserve a single connected component without holes.
This function takes a binary mask and a noise map of the same size, computes the boundary of the mask, estimates a local outward normal for each boundary pixel, and displaces that pixel by an amount proportional to the noise value. The displacement is clamped to remain inside the image domain.
- Parameters
-
mask Input binary mask as an Array (0 = background, >0 = foreground). Must be at least 3×3 in size. noise Noise field providing signed displacement factors, typically in [-1, 1]. Must have the same dimensions as mask.max_displacement Maximum displacement magnitude in pixels applied along the estimated boundary normal for each pixel.
- Returns
- A new Array representing the perturbed binary mask, with values 0 (background) and 1 (foreground), guaranteed to be a single connectedcomponent without holes.
Example
Result

◆ scan_mask()
Mask adjustement using a 'scanning' method.
See https://www.shadertoy.com/view/stjSRR
- Parameters
-
array Input array. contrast Contrast. brightness Brightness.
- Returns
- Ouput array.
Example
Result
◆ select_angle()
Return angle selection for a given angle and a tolerance half-width on this value.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. angle Selected angle (degree). sigma Selected angle tolerance (degree). ir Prefilter radius.
- Returns
- Output array.
Example
Result
◆ select_blob_log()
Return blob detection using the Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) approach.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. ir Kernel radius.
- Returns
- Array Output array.
Example
Result

◆ select_cavities()
Return holes or bumps detection based on the mean curvature of the heightmap.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. ir Kernel radius. concave Select 'holes' if set to true, and select 'bumps' if set to false.
- Returns
- Array Output array.
Example
Result
◆ select_elevation_slope() [1/2]
- Parameters
-
array
- Returns
- Array
Example
Result
◆ select_elevation_slope() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ select_eq()
Return an array with elements equal to 1 where input elements are equal to value.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. value Criteria value.
- Returns
- Array Output array.
Example
Result




◆ select_gradient_angle()
Return an array weighted by the gap between the gradient angle and a given angle.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. angle Reference angle (degree).
- Returns
- Array Output array.
◆ select_gradient_binary()
Return an array filled with 1 where the gradient is larger than a given value and 0 elsewhere.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. talus_center Reference talus.
- Returns
- Array Output array.
◆ select_gradient_exp()
Return an array weighted (exponantial decay) by the gradient norm of the input array.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. talus_center Reference talus. talus_sigma Talus half-width.
- Returns
- Array Output array.
◆ select_gradient_inv()
Return an array weighted (square inverse) by the gradient norm of the input array.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. talus_center Reference talus. talus_sigma Talus half-width.
- Returns
- Array Output array.
◆ select_gt()
Return an array with elements equal to 1 where input elements are larger than value.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. value Criteria value.
- Returns
- Array Output array.
Example
Result





◆ select_interval()
Return an array with elements equal to 1 where input elements are within the bounds provided.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. value1 Lower bound. value2 Upper bound.
- Returns
- Array Output array.
Example
Result





◆ select_inward_outward_slope()
| Array hmap::select_inward_outward_slope | ( | const Array & | array, |
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return an array with positive values if the slope is pointing to the center (slope is inward), and negative values otherwise (slope is outward).
- Parameters
-
array Input array. center Reference center. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Output array.
Example
Result
◆ select_lt()
Return an array with elements equal to 1 where input elements are smaller than value.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. value Criteria value.
- Returns
- Array Output array.
Example
Result





◆ select_midrange() [1/2]
Selects the midrange values of the input array within a specified range.
- Parameters
-
array The input array from which the midrange values are selected. gain The gain factor to scale the selected midrange values. vmin The minimum value for range. vmax The maximum value for range.
- Returns
- An array containing the midrange values.
Example
Result
◆ select_midrange() [2/2]
Selects and scales the midrange values of the input array.
This function extracts the midrange portion of the input array and scales it by the specified gain.
- Parameters
-
array The input array from which the midrange values are selected. gain The gain factor to scale the selected midrange values.
- Returns
- An array containing the midrange values scaled by the gain.
Example
Result

◆ select_multiband3() [1/2]
| void hmap::select_multiband3 | ( | const Array & | array, |
| Array & | band_low, | ||
| Array & | band_mid, | ||
| Array & | band_high, | ||
| float | ratio1, | ||
| float | ratio2, | ||
| float | overlap, | ||
| float | vmin, | ||
| float | vmax | ||
| ) |
Splits the input array into three bands (low, mid, and high) based on given ratios and overlap.
This function processes the input array and divides it into three value bands: low, mid, and high. The bands are determined by the provided ratios and overlap. Optionally, a range (vmin, vmax) can be applied to the values in the array.
- Parameters
-
array The input array that contains the data to be split into bands. band_low The output array for the low-value band. band_mid The output array for the mid-value band. band_high The output array for the high-value band. ratio1 The ratio that defines the split between the low and mid bands. ratio2 The ratio that defines the split between the mid and high bands. overlap The amount of overlap between adjacent bands. vmin The minimum value for range filtering. Values below vmin will be clamped. (Optional, only in the first function) vmax The maximum value for range filtering. Values above vmax will be clamped. (Optional, only in the first function)
Example
Result
◆ select_multiband3() [2/2]
| void hmap::select_multiband3 | ( | const Array & | array, |
| Array & | band_low, | ||
| Array & | band_mid, | ||
| Array & | band_high, | ||
| float | ratio1, | ||
| float | ratio2, | ||
| float | overlap | ||
| ) |
Splits the input array into three bands (low, mid, and high) based on given ratios and overlap.
This function processes the input array and divides it into three value bands: low, mid, and high. The bands are determined by the provided ratios and overlap.
- Parameters
-
array The input array that contains the data to be split into bands. band_low The output array for the low-value band. band_mid The output array for the mid-value band. band_high The output array for the high-value band. ratio1 The ratio that defines the split between the low and mid bands. ratio2 The ratio that defines the split between the mid and high bands. overlap The amount of overlap between adjacent bands.
Example
Result

◆ select_pulse()
Return an array filled with non-zero values where the input is in the interval [value - sigma, value + sigma]. Output array values have a cubic pulse distribution within this interval.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. value Central value. sigma Pulse width.
- Returns
- Array Output array.
Example
Result
◆ select_rivers()
Return an array filled with a criterion based on the occurence of a river bed.
- Parameters
-
array Input array. talus_ref Reference talus used to localy define the flow-partition. clipping_ratio Flow accumulation clipping ratio.
- Returns
- Array Output array.
Example
Result
◆ select_transitions()
| Array hmap::select_transitions | ( | const Array & | array1, |
| const Array & | array2, | ||
| const Array & | array_blend | ||
| ) |
Return an array filled with 1 at the blending transition between two arrays, and 0 elsewhere.
- Parameters
-
array1 Input array 1. array2 Input array 2. array_blend Blending of array 1 and 2 to analyze.
- Returns
- Array Resulting array
Example
Result

◆ select_valley()
◆ hillshade()
Compute the shaded relief map (hillshading) from a heightmap.
This function calculates the shaded relief map of the input array based on the sun's azimuth (direction) and zenith (elevation) angles. The shading effect simulates the appearance of topographic features based on light direction.
- Parameters
-
z Input array representing the heightmap. azimuth Sun azimuth (direction) in degrees. zenith Sun zenith (elevation) in degrees. talus_ref Reference talus used to normalize gradient computations. It can be useful when working with true angles. Default is 1.f.
- Returns
- Array Resulting shaded relief map.
Example
Result

- See also
topographic_shading
◆ shadow_grid()
Compute the shadow intensity using a grid-based technique.
This function calculates the shadow intensity from the input array using a grid-based approach. The shadow talus parameter influences the calculation of shadow intensity.
- Parameters
-
z Input array representing the heightmap. shadow_talus Parameter affecting the shadow intensity computation.
- Returns
- Array Resulting shadow intensity map.
◆ shadow_heightmap()
| Array hmap::shadow_heightmap | ( | const Array & | z, |
| float | azimuth = 180.f, |
||
| float | zenith = 45.f, |
||
| float | distance = 0.2f |
||
| ) |
Compute crude shadows from a heightmap.
This function generates crude shadow effects from the input heightmap using the specified light azimuth, zenith, and distance. The method is based on the technique described in https://www.shadertoy.com/view/Xlsfzl.
- Parameters
-
z Input array representing the heightmap. azimuth Light azimuth (direction) in degrees. Default is 180.f. zenith Light zenith (elevation) in degrees. Default is 45.f. distance Light distance. Default is 0.2f.
- Returns
- Array Resulting crude shadow map.
◆ topographic_shading()
| Array hmap::topographic_shading | ( | const Array & | z, |
| float | azimuth, | ||
| float | zenith, | ||
| float | talus_ref = 1.f |
||
| ) |
Compute the topographic shadow intensity in the range [-1, 1].
This function calculates the topographic shadow intensity of the input array based on the sun's azimuth and zenith. The shadow intensity is normalized to fall within the range [-1, 1].
- Parameters
-
z Input array representing the heightmap. azimuth Sun azimuth (direction) in degrees. zenith Sun zenith (elevation) in degrees. talus_ref Reference talus used to normalize gradient computations. It can be useful when working with true angles. Default is 1.f.
- Returns
- Array Resulting topographic shadow intensity map.
Example
Result


- See also
hillshade
◆ find_path_dijkstra() [1/2]
| void hmap::find_path_dijkstra | ( | const Array & | z, |
| glm::ivec2 | ij_start, | ||
| glm::ivec2 | ij_end, | ||
| std::vector< int > & | i_path, | ||
| std::vector< int > & | j_path, | ||
| float | elevation_ratio = 0.1f, |
||
| float | distance_exponent = 2.f, |
||
| float | upward_penalization = 1.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_mask_nogo = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Finds the path with the lowest elevation and elevation difference between two points in a 2D array using Dijkstra's algorithm.
This function calculates the shortest path considering both elevation and elevation differences. It uses a cost function that balances between absolute elevation and elevation change. The path is determined by minimizing the combined cost function.
- See also
- [Dijkstra1971] and https://math.stackexchange.com/questions/3088292
- Warning
- The
elevation_ratioparameter must be less than 1 for the algorithm to converge properly.
- Parameters
-
ij_start Starting coordinates (i, j) for the pathfinding. ij_end Ending coordinates (i, j) for the pathfinding. i_path[out] Vector to store the resulting shortest path indices in the i direction. j_path[out] Vector to store the resulting shortest path indices in the j direction. elevation_ratio Balance factor between absolute elevation and elevation difference in the cost function. Should be in the range [0, 1[. distance_exponent Exponent used in the distance calculation between points. A higher exponent increases the cost of elevation gaps, encouraging the path to minimize elevation changes and reduce overall cumulative elevation gain. upward_penalization Penalize upstream slopes. p_mask_nogo Optional pointer to an array mask that defines areas to avoid during pathfinding.
Example
Result

◆ find_path_dijkstra() [2/2]
| void hmap::find_path_dijkstra | ( | const Array & | z, |
| glm::ivec2 | ij_start, | ||
| std::vector< glm::ivec2 > | ij_end_list, | ||
| std::vector< std::vector< int > > & | i_path_list, | ||
| std::vector< std::vector< int > > & | j_path_list, | ||
| float | elevation_ratio = 0.1f, |
||
| float | distance_exponent = 2.f, |
||
| float | upward_penalization = 1.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_mask_nogo = nullptr |
||
| ) |
◆ non_parametric_sampling()
| Array hmap::non_parametric_sampling | ( | const Array & | array, |
| glm::ivec2 | patch_shape, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | error_threshold = 0.1f |
||
| ) |
Synthesize a new heightmap based on an input array using a non-parametric sampling method.
This method generates a new heightmap by sampling patches from the input array non-parametrically. It is a slow process and is based on the technique described in [Efros1999].
- Parameters
-
array Input array from which patches are sampled. patch_shape Shape of the patches used for sampling. seed Random seed number for patch selection. error_threshold Threshold for patch selection based on error.
- Returns
- Array Resulting synthesized heightmap.
Example
Result

◆ quilting()
| Array hmap::quilting | ( | const std::vector< const Array * > & | p_arrays, |
| glm::ivec2 | patch_base_shape, | ||
| glm::ivec2 | tiling, | ||
| float | overlap, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| std::vector< Array * > | secondary_arrays = {}, |
||
| bool | patch_flip = true, |
||
| bool | patch_rotate = true, |
||
| bool | patch_transpose = true, |
||
| float | filter_width_ratio = 0.25f |
||
| ) |
Synthesize a new heightmap by stitching together small patches from input heightmaps.
This function creates a new heightmap by stitching patches from a set of input heightmaps. The stitching process allows for flipping, rotating, and transposing patches, and includes options for smoothing based on the overlap between patches. This technique is based on [Efros2001].
- Parameters
-
p_arrays Vector of pointers to input heightmaps. patch_base_shape Shape of the patches to be used. tiling Number of patches in each direction (x, y). overlap Overlap between patches, in the range ]0, 1[. seed Random seed number for patch placement. patch_flip Allow flipping of patches (up-down, left-right). patch_rotate Allow 90-degree rotation of patches (for square patches). patch_transpose Allow transposition of patches (for square patches). filter_width_ratio Ratio of filter width to overlap length for smoothing.
- Returns
- Array Resulting synthesized heightmap.
Example
Result
◆ quilting_blend()
| Array hmap::quilting_blend | ( | const std::vector< const Array * > & | p_arrays, |
| glm::ivec2 | patch_base_shape, | ||
| float | overlap, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| bool | patch_flip = true, |
||
| bool | patch_rotate = true, |
||
| bool | patch_transpose = true, |
||
| float | filter_width_ratio = 0.25f |
||
| ) |
Synthesize a new heightmap by stitching together small patches from a list of input heightmaps.
This function creates a new heightmap by stitching patches from a set of input heightmaps, similar to quilting, but the patches are blended together. The blending options include flipping, rotating, and transposing patches, with smoothing based on the overlap between patches.
- Parameters
-
p_arrays Vector of pointers to input heightmaps. patch_base_shape Shape of the patches to be used. overlap Overlap between patches, in the range ]0, 1[. seed Random seed number for patch placement. patch_flip Allow flipping of patches (up-down, left-right). patch_rotate Allow 90-degree rotation of patches (for square patches). patch_transpose Allow transposition of patches (for square patches). filter_width_ratio Ratio of filter width to overlap length for smoothing.
- Returns
- Array Resulting synthesized heightmap.
Example
Result





◆ quilting_expand()
| Array hmap::quilting_expand | ( | const Array & | array, |
| float | expansion_ratio, | ||
| glm::ivec2 | patch_base_shape, | ||
| float | overlap, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| std::vector< Array * > | secondary_arrays = {}, |
||
| bool | keep_input_shape = false, |
||
| bool | patch_flip = true, |
||
| bool | patch_rotate = true, |
||
| bool | patch_transpose = true, |
||
| float | filter_width_ratio = 0.25f |
||
| ) |
Synthesize a new heightmap by expanding the input heightmap and stitching patches.
This function generates a larger heightmap by expanding the input heightmap and stitching patches based on the given parameters. The expansion ratio determines the new size of the heightmap, and the function includes options for flipping, rotating, and transposing patches. The output can be either the same shape as the input or expanded based on the given ratio.
- Parameters
-
array Input heightmap to be expanded. expansion_ratio Ratio by which to expand the heightmap (e.g., 2 for doubling the size). patch_base_shape Shape of the patches to be used. overlap Overlap between patches, in the range ]0, 1[. seed Random seed number for patch placement. keep_input_shape If true, the output heightmap retains the input shape. patch_flip Allow flipping of patches (up-down, left-right). patch_rotate Allow 90-degree rotation of patches (for square patches). patch_transpose Allow transposition of patches (for square patches). filter_width_ratio Ratio of filter width to overlap length for smoothing.
- Returns
- Array Resulting synthesized heightmap.
Example
Result





◆ quilting_shuffle()
| Array hmap::quilting_shuffle | ( | const Array & | array, |
| glm::ivec2 | patch_base_shape, | ||
| float | overlap, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| std::vector< Array * > | secondary_arrays = {}, |
||
| bool | patch_flip = true, |
||
| bool | patch_rotate = true, |
||
| bool | patch_transpose = true, |
||
| float | filter_width_ratio = 0.25f |
||
| ) |
Synthesize a new heightmap by reshuffling patches of the input heightmap.
This function generates a new heightmap by reshuffling patches of the input heightmap, effectively creating a new pattern while keeping the same shape as the input heightmap. The function includes options for patch flipping, rotating, and transposing.
- Parameters
-
array Input heightmap to be reshuffled. patch_base_shape Shape of the patches to be used. overlap Overlap between patches, in the range ]0, 1[. seed Random seed number for patch placement. patch_flip Allow flipping of patches (up-down, left-right). patch_rotate Allow 90-degree rotation of patches (for square patches). patch_transpose Allow transposition of patches (for square patches). filter_width_ratio Ratio of filter width to overlap length for smoothing.
- Returns
- Array Resulting synthesized heightmap with reshuffled patches.
Example
Result





◆ flip_lr()
| void hmap::flip_lr | ( | Array & | array | ) |
Flip the array horizontally (left/right).
This function flips the input array along the vertical axis, resulting in a left-to-right mirror image of the original array.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be flipped horizontally.
Example
Result

◆ flip_ud()
| void hmap::flip_ud | ( | Array & | array | ) |
Flip the array vertically (up/down).
This function flips the input array along the horizontal axis, resulting in an up-to-down mirror image of the original array.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be flipped vertically.
Example
Result

◆ rot180()
| void hmap::rot180 | ( | Array & | array | ) |
Rotate the array by 180 degrees.
This function rotates the input array by 180 degrees in the counterclockwise direction. The dimensions of the array will be adjusted accordingly.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be rotated by 180 degrees.
◆ rot270()
| void hmap::rot270 | ( | Array & | array | ) |
Rotate the array by 270 degrees.
This function rotates the input array by 270 degrees in the counterclockwise direction. The dimensions of the array will be adjusted accordingly.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be rotated by 270 degrees.
◆ rot90()
| void hmap::rot90 | ( | Array & | array | ) |
Rotate the array by 90 degrees.
This function rotates the input array by 90 degrees in the counterclockwise direction. The dimensions of the array will be adjusted accordingly.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be rotated by 90 degrees.
Example
Result
◆ rotate()
| void hmap::rotate | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | angle, | ||
| bool | zoom_in = true, |
||
| bool | zero_padding = false |
||
| ) |
Rotate the array by a specified angle.
This function rotates the input array by a given angle in degrees. The rotation can be performed with optional zero-padding, which fills in the borders with zeros instead of using symmetric padding. This is particularly useful when the array contains zero values at its borders.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be rotated. angle Rotation angle in degrees. zero_padding If true, use zero-padding to fill the borders; otherwise, use symmetry (default is false).
Example
Result
◆ transpose()
Return the transposed array.
This function returns a new array that is the transpose of the input array. The transpose operation swaps the rows and columns of the array, effectively flipping the array over its diagonal.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be transposed.
- Returns
- Array The transposed array.
◆ translate()
| Array hmap::translate | ( | const Array & | array, |
| float | dx, | ||
| float | dy, | ||
| bool | periodic = false, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Translates a 2D array by a specified amount along the x and y axes.
This function shifts the contents of the input array by dx and dy units along the x and y axes, respectively. It supports both periodic boundary conditions, where the array wraps around, and non-periodic conditions, where the shifted areas are filled with zeros.
- Parameters
-
array The input 2D array to be translated. This array remains unmodified. dx The translation distance along the x-axis. Positive values shift the array to the right. dy The translation distance along the y-axis. Positive values shift the array downward. periodic If set to true, the translation is periodic, meaning that elements that move out of one side of the array reappear on the opposite side. Iffalse, the areas exposed by the translation are filled with zeros. The default isfalse.p_noise_x Optional pointer to a 2D array that contains x-direction noise to be added to the translation. If provided, the noise values are added to dxon a per-element basis.p_noise_y Optional pointer to a 2D array that contains y-direction noise to be added to the translation. If provided, the noise values are added to dyon a per-element basis.bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- A new 2D array that is the result of translating the input
arrayby the specifieddxanddyvalues.
Example
Result
◆ warp()
Apply a warping effect to the array.
This function applies a warping effect to the input array by translating its elements according to the specified x and y translation arrays. The warp effect distorts the array based on the displacement values provided by p_dx and p_dy.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be warped. p_dx Pointer to the array containing x-axis translation values. p_dy Pointer to the array containing y-axis translation values.
Example
Result
◆ warp_directional() [1/2]
| void hmap::warp_directional | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | angle, | ||
| float | amount = 0.02f, |
||
| int | ir = 4, |
||
| bool | reverse = false |
||
| ) |
Apply a warping effect following the downward local gradient direction (deflate/inflate effect).
This function applies a warping effect to the input array based on the downward local gradient direction, creating a deflate or inflate effect. The warp amount, pre-filtering radius, and displacement direction can be customized.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be warped. angle The angle to determine the gradient direction. amount Amount of displacement (default is 0.02f). ir Pre-filtering radius to smooth the input data (default is 4). reverse Reverse the displacement direction if set to true (default is false).
Example
Result
◆ warp_directional() [2/2]
| void hmap::warp_directional | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | angle, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | amount = 0.02f, |
||
| int | ir = 4, |
||
| bool | reverse = false |
||
| ) |
Apply a warping effect following the downward local gradient direction (deflate/inflate effect) with a mask.
This overloaded function applies a warping effect to the input array using a specified mask. The mask controls the regions where the warp effect is applied, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. The warp is based on the downward local gradient direction.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be warped. angle The angle to determine the gradient direction. p_mask Pointer to the mask array that filters the effect, expected in [0, 1]. amount Amount of displacement (default is 0.02f). ir Pre-filtering radius to smooth the input data (default is 4). reverse Reverse the displacement direction if set to true (default is false).
Example
Result

This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ warp_downslope() [1/2]
Apply a warping effect following the downward local gradient direction (deflate/inflate effect).
This function applies a warping effect to the input array based on the downward local gradient direction, simulating a deflate or inflate effect. The effect can be customized by adjusting the displacement amount, pre-filtering radius, and whether the displacement direction is reversed.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be warped. amount Amount of displacement (default is 0.02f). ir Pre-filtering radius to smooth the input data (default is 4). reverse Reverse the displacement direction if set to true (default is false).
Example
Result
◆ warp_downslope() [2/2]
| void hmap::warp_downslope | ( | Array & | array, |
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | amount = 0.02f, |
||
| int | ir = 4, |
||
| bool | reverse = false |
||
| ) |
Apply a warping effect following the downward local gradient direction (deflate/inflate effect) with a mask.
This overloaded function applies a warping effect to the input array based on the downward local gradient direction using a specified mask. The mask controls where the warp effect is applied, with values expected in the range [0, 1]. This function allows for additional customization of the warp effect.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be warped. p_mask Pointer to the mask array that filters the effect, expected in [0, 1]. amount Amount of displacement (default is 0.02f). ir Pre-filtering radius to smooth the input data (default is 4). reverse Reverse the displacement direction if set to true (default is false).
Example
Result

This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ zoom()
| Array hmap::zoom | ( | const Array & | array, |
| float | zoom_factor, | ||
| bool | periodic = false, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Applies a zoom effect to a 2D array with an adjustable center.
This function scales the input 2D array by a specified zoom factor, effectively resizing the array's contents. The zoom operation is centered around a specified point within the array, allowing for flexible zooming behavior. The function supports both periodic boundary conditions, where the array wraps around, and non-periodic conditions, where areas outside the original array bounds are filled with zeros.
- Parameters
-
array The input 2D array to be zoomed. This array remains unmodified. zoom_factor The factor by which to zoom the array. A value greater than 1 enlarges the contents, while a value between 0 and 1 reduces them. periodic If set to true, the zoom is periodic, meaning that elements moving out of the array bounds due to the zoom reappear on the opposite side. Iffalse, areas outside the original array bounds are filled with zeros. The default isfalse.center The center of the zoom operation, specified as a glm::vec2with coordinates in the range [0, 1], where {0.5f, 0.5f} represents the center of the array. The default center is {0.5f, 0.5f}.p_noise_x Optional pointer to a 2D array that contains x-direction noise to be added during the zoom operation. If provided, the noise values are applied to the x-coordinates of the zoomed array on a per-element basis. p_noise_y Optional pointer to a 2D array that contains y-direction noise to be added during the zoom operation. If provided, the noise values are applied to the y-coordinates of the zoomed array on a per-element basis. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- A new 2D array that is the result of applying the zoom effect to the input
arrayby the specifiedzoom_factorand centered at the specifiedcenter.
Example
Result
◆ to_string() [1/2]
|
inline |
◆ make_storage()
| std::unique_ptr< TileStorage > hmap::make_storage | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::ivec2 | tile_shape, | ||
| StorageMode | storage_mode | ||
| ) |
◆ to_string() [2/2]
|
inline |
◆ copy_data()
| void hmap::copy_data | ( | VirtualArray & | src, |
| VirtualArray & | dst, | ||
| const ComputeMode & | cm | ||
| ) |
◆ convert_texture_channels()
| VirtualTexture hmap::convert_texture_channels | ( | const VirtualTexture & | src, |
| int | dst_channels, | ||
| float | fill_value, | ||
| const ComputeMode & | cm | ||
| ) |
◆ for_each_tile()
| void hmap::for_each_tile | ( | VirtualTexture & | tex, |
| Func && | func, | ||
| const ComputeMode & | cm | ||
| ) |
◆ for_each_pixel()
| void hmap::for_each_pixel | ( | VirtualTexture & | tex, |
| Func && | func, | ||
| const ComputeMode & | cm | ||
| ) |
◆ operator*()
◆ operator/()
◆ operator+()
◆ operator-()
◆ convert_mat_to_array()
| void hmap::convert_mat_to_array | ( | const cv::Mat & | mat, |
| Array & | array, | ||
| bool | flip_j | ||
| ) |
◆ square_fill_md()
| void hmap::square_fill_md | ( | Array & | array, |
| Mat< int > & | is_done, | ||
| int | i1, | ||
| int | i2, | ||
| int | j1, | ||
| int | j2, | ||
| float | noise_scale, | ||
| std::mt19937 | gen, | ||
| std::uniform_real_distribution< float > | dis | ||
| ) |
◆ square_md()
| void hmap::square_md | ( | Array & | array, |
| Mat< int > & | is_done, | ||
| int | step, | ||
| float | noise_scale, | ||
| std::mt19937 | gen, | ||
| std::uniform_real_distribution< float > | dis | ||
| ) |
◆ helper_hash_u32()
|
inline |
◆ helper_hash_01()
|
inline |
◆ helper_tov3()
| std::vector< glm::vec3 > hmap::helper_tov3 | ( | const std::vector< std::vector< float > > & | colors | ) |
◆ helper_thermal_exchange()
| float hmap::helper_thermal_exchange | ( | float | self, |
| float | other, | ||
| float | dist, | ||
| float | talus | ||
| ) |
◆ helper_smooth_corners()
| void hmap::helper_smooth_corners | ( | Array & | cubemap, |
| int | noverlap, | ||
| int | ir, | ||
| glm::ivec4 | idx_front, | ||
| glm::ivec4 | idx_back | ||
| ) |
◆ helper_get_rtheta_stretch()
| void hmap::helper_get_rtheta_stretch | ( | int | i, |
| int | j, | ||
| int | ic, | ||
| int | jc, | ||
| int | nradius, | ||
| float & | radius, | ||
| float & | theta, | ||
| int | config | ||
| ) |
◆ helper_get_distance_polar()
| float hmap::helper_get_distance_polar | ( | float | r1, |
| float | theta1, | ||
| float | r2, | ||
| float | theta2 | ||
| ) |
◆ helper_smooth_triple_corner()
| void hmap::helper_smooth_triple_corner | ( | Array & | zfull, |
| int | ic, | ||
| int | jc, | ||
| int | noverlap, | ||
| int | ir, | ||
| int | config | ||
| ) |
◆ compute_splatmap()
| Tensor hmap::compute_splatmap | ( | const Array * | p_r, |
| const Array * | p_g, | ||
| const Array * | p_b, | ||
| const Array * | p_a | ||
| ) |
◆ helper_compute_tile_bounds()
| glm::ivec4 hmap::helper_compute_tile_bounds | ( | int | tile_x, |
| int | tile_y, | ||
| const glm::ivec2 & | tile_count, | ||
| const glm::ivec2 & | array_shape, | ||
| bool | overlapping_edges, | ||
| bool | reverse_tile_y_indexing | ||
| ) |
◆ recurve_bexp() [3/3]
◆ recurve_exp() [3/3]
◆ rescale_grid_from_unit_square_to_bbox()
| void hmap::rescale_grid_from_unit_square_to_bbox | ( | std::vector< float > & | x, |
| std::vector< float > & | y, | ||
| glm::vec4 | bbox | ||
| ) |
◆ helper_estimate_count()
| size_t hmap::helper_estimate_count | ( | const glm::vec4 & | bbox, |
| float | distance | ||
| ) |
◆ cmp_inf()
◆ compute_gradient()
| void hmap::compute_gradient | ( | const Array & | array, |
| Array & | dx, | ||
| Array & | dy, | ||
| float | x_coeff[3], | ||
| float | y_coeff[3], | ||
| float | normalize_factor | ||
| ) |
◆ compute_gradient_norm()
| Array hmap::compute_gradient_norm | ( | const Array & | array, |
| float | x_coeff[3], | ||
| float | y_coeff[3], | ||
| float | normalize_factor, | ||
| Array * | p_dx = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_dy = nullptr |
||
| ) |
◆ helper_find_up_downslope()
| void hmap::helper_find_up_downslope | ( | const Array & | z, |
| const glm::ivec2 & | ij, | ||
| glm::ivec2 & | ij_dw, | ||
| glm::ivec2 & | ij_up | ||
| ) |
◆ is_monotonic()
| bool hmap::is_monotonic | ( | const std::vector< float > & | data | ) |
◆ find_last_index_smaller_than()
| int hmap::find_last_index_smaller_than | ( | const std::vector< float > & | vec, |
| float | threshold | ||
| ) |
◆ hypot()
◆ helper_thinning()
| void hmap::helper_thinning | ( | Array & | in, |
| int | iter | ||
| ) |
◆ cmp_path()
| bool hmap::cmp_path | ( | std::pair< float, std::vector< int > > & | a, |
| std::pair< float, std::vector< int > > & | b | ||
| ) |
◆ helper_flip_rot_transpose()
| void hmap::helper_flip_rot_transpose | ( | Array & | array, |
| bool | do_flip_ud, | ||
| bool | do_flip_lr, | ||
| bool | do_rot90, | ||
| bool | do_transpose | ||
| ) |
◆ reindex_vector() [2/3]
| void hmap::reindex_vector | ( | std::vector< int > & | v, |
| std::vector< size_t > & | idx | ||
| ) |
◆ reindex_vector() [3/3]
| void hmap::reindex_vector | ( | std::vector< float > & | v, |
| std::vector< size_t > & | idx | ||
| ) |
◆ count_neighbors_to_fill()
| int hmap::count_neighbors_to_fill | ( | int | i, |
| int | j, | ||
| Mat< int > & | is_cell_done | ||
| ) |
◆ cmp_queue()
| bool hmap::cmp_queue | ( | std::pair< int, std::pair< int, int > > & | a, |
| std::pair< int, std::pair< int, int > > & | b | ||
| ) |