Functions | |
| Array | blend_gradients (const Array &array1, const Array &array2, int ir=4) |
| See hmap::blend_gradients. | |
| Array | blend_poisson_bf (const Array &array1, const Array &array2, const int iterations=500, const Array *p_mask=nullptr) |
| Blends two arrays using Poisson blending with a brute-force solver. | |
| Array | transfer (const Array &source, const Array &target, int ir, float amplitude, bool target_prefiltering=false) |
| See hmap::transfer. | |
| Array | accumulation_curvature (const Array &z, int ir) |
| See hmap::accumulation_curvature. | |
| Array | curvature_horizontal_cross_sectional (const Array &z, int ir) |
| See hmap::curvature_horizontal_cross_sectional. | |
| Array | curvature_horizontal_plan (const Array &z, int ir) |
| See hmap::curvature_horizontal_plan. | |
| Array | curvature_horizontal_tangential (const Array &z, int ir) |
| See hmap::curvature_horizontal_tangential. | |
| Array | curvature_ring (const Array &z, int ir) |
| See hmap::curvature_ring. | |
| Array | curvature_rotor (const Array &z, int ir) |
| See hmap::curvature_rotor. | |
| Array | curvature_vertical_longitudinal (const Array &z, int ir) |
| See hmap::curvature_vertical_longitudinal. | |
| Array | curvature_vertical_profile (const Array &z, int ir) |
| See hmap::curvature_vertical_profile. | |
| Array | level_set_curvature (const Array &array, int prefilter_ir) |
| See hmap::level_set_curvature. | |
| Array | shape_index (const Array &z, int ir) |
| See hmap::shape_index. | |
| Array | unsphericity (const Array &z, int ir) |
| See hmap::unsphericity. | |
| void | hydraulic_particle (Array &z, int nparticles, int seed, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_moisture_map=nullptr, Array *p_erosion_map=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, float c_capacity=10.f, float c_erosion=0.05f, float c_deposition=0.05f, float c_inertia=0.3f, float c_gravity=1.f, int radius=2, float drag_rate=0.001f, float evap_rate=0.001f, bool post_filtering=false) |
| See hmap::hydraulic_particle. | |
| void | hydraulic_particle (Array &z, Array *p_mask, int nparticles, int seed, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_moisture_map=nullptr, Array *p_erosion_map=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, float c_capacity=10.f, float c_erosion=0.05f, float c_deposition=0.05f, float c_inertia=0.3f, float c_gravity=1.f, int radius=2, float drag_rate=0.001f, float evap_rate=0.001f, bool post_filtering=false) |
| See hmap::hydraulic_particle. | |
| void | hydraulic_schott (Array &z, int iterations, const Array &talus, float c_erosion=1.f, float c_thermal=0.1f, float c_deposition=0.2f, float flow_acc_exponent=0.8f, float flow_acc_exponent_depo=0.8f, float flow_routing_exponent=1.3f, float thermal_weight=1.5f, float deposition_weight=2.5f, Array *p_flow=nullptr) |
| Simulates hydraulic erosion and deposition on a heightmap using the Schott method. | |
| void | hydraulic_schott (Array &z, int iterations, const Array &talus, Array *p_mask, float c_erosion=1.f, float c_thermal=0.1f, float c_deposition=0.2f, float flow_acc_exponent=0.8f, float flow_acc_exponent_depo=0.8f, float flow_routing_exponent=1.3f, float thermal_weight=1.5f, float deposition_weight=2.5f, Array *p_flow=nullptr) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | hydraulic_schott_erosion (Array &z, int iterations, float c_erosion=1.f, float flow_acc_exponent=0.8f, float flow_routing_exponent=1.3f, Array *p_flow=nullptr) |
| See hmap::hydraulic_schott. | |
| void | hydraulic_stream_log (Array &z, float c_erosion, float talus_ref, int deposition_ir=32, float deposition_scale_ratio=1.f, float gradient_power=0.8f, float gradient_scaling_ratio=1.f, int gradient_prefilter_ir=16, float saturation_ratio=1.f, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_moisture_map=nullptr, Array *p_erosion_map=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, Array *p_flow_map=nullptr) |
| See hmap::hydraulic_stream_log. | |
| void | hydraulic_stream_log (Array &z, float c_erosion, float talus_ref, Array *p_mask, int deposition_ir=32, float deposition_scale_ratio=1.f, float gradient_power=0.8f, float gradient_scaling_ratio=1.f, int gradient_prefilter_ir=16, float saturation_ratio=1.f, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_moisture_map=nullptr, Array *p_erosion_map=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr, Array *p_flow_map=nullptr) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | hydraulic_vpipes (Array &z, float water_height=1e-2f, bool maintain_water_volume=true, float evap_rate=0.1f, int iterations=50, float dt=0.5f, float k_capacity=0.5f, float k_erode=0.001f, float k_depose=0.01f, float k_discharge_exp=1.f, bool flux_diffusion=true, float flux_diffusion_strength=0.001f, Array *p_rain_map=nullptr, Array *p_water_depth=nullptr, Array *p_sediment=nullptr, Array *p_vel_u=nullptr, Array *p_vel_v=nullptr) |
| See hmap::hydraulic_vpipes. | |
| void | rifts (Array &z, const glm::vec2 &kw, float angle, float amplitude, uint seed, float elevation_noise_shift=0.f, float k_smooth_bottom=0.05f, float k_smooth_top=0.05f, float radial_spread_amp=0.2f, float elevation_noise_amp=0.1f, float clamp_vmin=0.f, float remap_vmin=0.f, bool apply_mask=true, bool reverse_mask=false, float mask_gamma=1.f, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_mask=nullptr, const glm::vec2 ¢er={0.5f, 0.5f}, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Applies a "rift" deformation effect to a heightmap array. | |
| void | strata (Array &z, float angle, float slope, float gamma, uint seed, bool linear_gamma=true, float kz=1.f, int octaves=4, float lacunarity=2.f, float gamma_noise_ratio=0.5f, float noise_amp=0.4f, const glm::vec2 &noise_kw={4.f, 4.f}, const glm::vec2 &ridge_noise_kw={4.f, 1.2f}, float ridge_angle_shift=45.f, float ridge_noise_amp=0.5f, float ridge_clamp_vmin=0.f, float ridge_remap_vmin=0.f, bool apply_elevation_mask=true, bool apply_ridge_mask=true, float mask_gamma=0.4f, const Array *p_mask=nullptr, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Applies stratification to a heightfield using directional noise and multiscale gamma transformations. | |
| void | thermal (Array &z, const Array &talus, int iterations=10, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| See hmap::thermal. | |
| void | thermal (Array &z, Array *p_mask, const Array &talus, int iterations=10, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| See hmap::thermal. | |
| void | thermal (Array &z, float talus, int iterations=10, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| See hmap::thermal. | |
| void | thermal_auto_bedrock (Array &z, const Array &talus, int iterations=10, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| See hmap::thermal_auto_bedrock. | |
| void | thermal_auto_bedrock (Array &z, Array *p_mask, const Array &talus, int iterations=10, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| See hmap::thermal_auto_bedrock. | |
| void | thermal_auto_bedrock (Array &z, float, int iterations=10, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| See hmap::thermal_auto_bedrock. | |
| void | thermal_olsen (Array &z, const Array &talus, int iterations) |
| See hmap::thermal_olsen. | |
| void | thermal_olsen (Array &z, Array *p_mask, const Array &talus, int iterations) |
| void | thermal_inflate (Array &z, const Array &talus, int iterations=10) |
| Apply thermal weathering erosion to give a scree like effect. | |
| void | thermal_inflate (Array &z, const Array *p_mask, const Array &talus, int iterations=10) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | thermal_rib (Array &z, int iterations, Array *p_bedrock=nullptr) |
| See hmap::thermal_rib. | |
| void | thermal_ridge (Array &z, const Array &talus, int iterations=10, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| Apply thermal weathering erosion to give a ridge like effect. | |
| void | thermal_ridge (Array &z, const Array *p_mask, const Array &talus, int iterations=10, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | thermal_scree (Array &z, const Array &talus, const Array &zmax, int iterations=10, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| Performs thermal scree erosion on a heightmap. | |
| void | thermal_scree (Array &z, const Array *p_mask, const Array &talus, const Array &zmax, int iterations=10, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | valley_fill (Array &z, const Array &talus, int iterations=100, float gamma=2.f, float ratio=0.8f, float zmin=0.f, float zmax=0.f, float elevation_max_ratio=1.f, bool preserve_elevation_range=true, const Array *p_noise=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| Fill valleys using thermal scree deposition and height-based blending. | |
| void | valley_fill (Array &z, const Array *p_mask, const Array &talus, int iterations=100, float gamma=2.f, float ratio=0.8f, float zmin=0.f, float zmax=0.f, float elevation_max_ratio=1.f, bool preserve_elevation_range=true, const Array *p_noise=nullptr, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| Array | watershed_ridge (const Array &z, float amplitude=0.5f, int ir=1, float edt_exponent=0.5f, FlowDirectionMethod fd_method=FlowDirectionMethod::FDM_D8, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr) |
| See hmap::watershed_ridge. | |
| Array | watershed_ridge (const Array &z, Array *p_mask, float amplitude=0.5f, int ir=1, float edt_exponent=0.5f, FlowDirectionMethod fd_method=FlowDirectionMethod::FDM_D8, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr) |
| See hmap::watershed_ridge. | |
| Array | local_median_deviation (const Array &array, int ir) |
| See hmap::local_median_deviation. | |
| Array | mean_local (const Array &array, int ir) |
| See hmap::mean_local. | |
| Array | relative_elevation (const Array &array, int ir) |
| See hmap::relative_elevation. | |
| Array | ruggedness (const Array &array, int ir) |
| See hmap::ruggedness. | |
| Array | rugosity (const Array &z, int ir, bool convex=true) |
| See hmap::rugosity. | |
| Array | std_local (const Array &array, int ir) |
| See hmap::std_local. | |
| Array | z_score (const Array &array, int ir) |
| See hmap::z_score. | |
| void | expand (Array &array, int ir, int iterations=1) |
| See hmap::expand. | |
| void | expand (Array &array, int ir, const Array *p_mask, int iterations=1) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | expand (Array &array, const Array &kernel, int iterations=1) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | expand (Array &array, const Array &kernel, const Array *p_mask, int iterations=1) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | gamma_correction_local (Array &array, float gamma, int ir, float k=0.1f) |
| See hmap::gamma_correction_local. | |
| void | gamma_correction_local (Array &array, float gamma, int ir, const Array *p_mask, float k=0.1f) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | laplace (Array &array, float sigma=0.2f, int iterations=3) |
| See hmap::laplace. | |
| void | laplace (Array &array, const Array *p_mask, float sigma=0.2f, int iterations=3) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| Array | maximum_local (const Array &array, int ir) |
| See hmap::maximum_local. | |
| Array | maximum_local_disk (const Array &array, int ir) |
| See hmap::maximum_local_disk. | |
| Array | mean_shift (const Array &array, int ir, float talus, int iterations=1, bool talus_weighted=true) |
| See hmap::mean_shift. | |
| Array | mean_shift (const Array &array, int ir, float talus, const Array *p_mask, int iterations=1, bool talus_weighted=true) |
| void | median_3x3 (Array &array) |
| See hmap::median_3x3. | |
| void | median_3x3 (Array &array, const Array *p_mask) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| Array | median_pseudo (const Array &array, int ir) |
| See hmap::median_pseudo. | |
| Array | minimum_local (const Array &array, int ir) |
| See hmap::minimum_local. | |
| Array | minimum_local_disk (const Array &array, int ir) |
| See hmap::minimum_local_disk. | |
| void | normal_displacement (Array &array, float amount=0.1f, int ir=0, bool reverse=false) |
| See hmap::normal_displacement. | |
| void | normal_displacement (Array &array, const Array *p_mask, float amount=0.1f, int ir=0, bool reverse=false) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | plateau (Array &array, const Array *p_mask, int ir, float factor) |
| See hmap::plateau. | |
| void | plateau (Array &array, int ir, float factor) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| Array | project_talus_along_direction (const Array &array, float talus, int direction=0) |
| Projects array values along a given direction using talus attenuation. | |
| Array | project_talus_along_direction (const Array &array, float talus, const Array *p_mask, int direction=0) |
| void | shrink (Array &array, int ir, int iterations=1) |
| See hmap::shrink. | |
| void | shrink (Array &array, int ir, const Array *p_mask, int iterations=1) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | shrink (Array &array, const Array &kernel, int iterations=1) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | shrink (Array &array, const Array &kernel, const Array *p_mask, int iterations=1) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | smooth_cpulse (Array &array, int ir) |
| See hmap::smooth_cpulse. | |
| void | smooth_cpulse (Array &array, int ir, const Array *p_mask) |
| See hmap::smooth_cpulse. | |
| void | smooth_cpulse_edge_removing (Array &array, float talus, float talus_width, int ir) |
| See hmap::smooth_cpulse_edge_removing. | |
| void | smooth_fill (Array &array, int ir, float k=0.1f, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| See hmap::smooth_fill. | |
| void | smooth_fill (Array &array, int ir, const Array *p_mask, float k=0.1f, Array *p_deposition_map=nullptr) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | smooth_fill_holes (Array &array, int ir) |
| See hmap::smooth_fill_holes. | |
| void | smooth_fill_holes (Array &array, int ir, const Array *p_mask) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| void | smooth_fill_smear_peaks (Array &array, int ir) |
| See hmap::smooth_fill_smear_peaks. | |
| void | smooth_fill_smear_peaks (Array &array, int ir, const Array *p_mask) |
| This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts. | |
| Array | gradient_norm (const Array &array) |
| See hmap::gradient_norm. | |
| Array | harmonic_interpolation (const Array &array, const Array &mask_fixed_values, int iterations_max=500) |
| See hmap::harmonic_interpolation. | |
| void | interpolate_array_bicubic (const Array &source, Array &target) |
| void | interpolate_array_bicubic (const Array &source, Array &target, const glm::vec4 &bbox_source, const glm::vec4 &bbox_target) |
| void | interpolate_array_bilinear (const Array &source, Array &target) |
| void | interpolate_array_bilinear (const Array &source, Array &target, const glm::vec4 &bbox_source, const glm::vec4 &bbox_target) |
| void | interpolate_array_lagrange (const Array &source, Array &target, int order) |
| void | interpolate_array_nearest (const Array &source, Array &target) |
| void | interpolate_array_nearest (const Array &source, Array &target, const glm::vec4 &bbox_source, const glm::vec4 &bbox_target) |
| Array | border (const Array &array, int ir, bool use_disk_kernel=true) |
| See hmap::border. | |
| Array | closing (const Array &array, int ir, bool use_disk_kernel=true) |
| See hmap::closing. | |
| Array | dilation (const Array &array, int ir, bool use_disk_kernel=true) |
| See hmap::dilation. | |
| Array | dilation_expand_border_only (const Array &array, int ir, bool use_disk_kernel=true) |
| See hmap::dilation_expand_border_only. | |
| Array | distance_transform_jfa (const Array &array, bool return_squared_distance=false) |
| Return the Euclidean distance transform. | |
| Array | erosion (const Array &array, int ir, bool use_disk_kernel=true) |
| See hmap::erosion. | |
| Array | morphological_black_hat (const Array &array, int ir, bool use_disk_kernel=true) |
| See hmap::morphological_black_hat. | |
| Array | morphological_gradient (const Array &array, int ir, bool use_disk_kernel=true) |
| See hmap::morphological_gradient. | |
| Array | morphological_top_hat (const Array &array, int ir, bool use_disk_kernel=true) |
| See hmap::morphological_top_hat. | |
| Array | opening (const Array &array, int ir, bool use_disk_kernel=true) |
| See hmap::opening. | |
| Array | relative_distance_from_skeleton (const Array &array, int ir_search, bool zero_at_borders=true, int ir_erosion=1, bool use_disk_kernel=true) |
| See hmap::relative_distance_from_skeleton. | |
| Array | signed_curvature_from_distance (const Array &array, int prefilter_ir=0) |
| See hmap::signed_curvature_from_distance. | |
| Array | signed_distance_transform (const Array &array, int prefilter_ir=0) |
| See hmap::signed_distance_transform. | |
| Array | skeleton (const Array &array, bool zero_at_borders=true) |
| See hmap::skeleton. | |
| void | helper_bind_optional_buffer (clwrapper::Run &run, const std::string &id, const Array *p_array) |
| bool | init_opencl () |
| Array | badlands (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, int octaves=8, float rugosity=0.2f, float angle=30.f, float k_smoothing=0.1f, float base_noise_amp=0.2f, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a synthetic "badlands" terrain heightmap. | |
| Array | basalt_field (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, float warp_kw=4.f, float large_scale_warp_amp=0.2f, float large_scale_gain=6.f, float large_scale_amp=0.2f, float medium_scale_kw_ratio=3.f, float medium_scale_warp_amp=1.f, float medium_scale_gain=7.f, float medium_scale_amp=0.08f, float small_scale_kw_ratio=10.f, float small_scale_amp=0.1f, float small_scale_overlay_amp=0.002f, float rugosity_kw_ratio=1.f, float rugosity_amp=1.f, bool flatten_activate=true, float flatten_kw_ratio=1.f, float flatten_amp=0.f, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a synthetic procedural terrain resembling basaltic landforms. | |
| Array | gabor_wave (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, const Array &angle, float angle_spread_ratio=1.f, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return an array filled with coherence Gabor noise. | |
| Array | gabor_wave (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, float angle=0.f, float angle_spread_ratio=1.f, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Array | gabor_wave_fbm (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, const Array &angle, float angle_spread_ratio=1.f, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return an array filled with coherence Gabor noise. | |
| Array | gabor_wave_fbm (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, float angle=0.f, float angle_spread_ratio=1.f, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Array | gavoronoise (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, const Array &angle, float amplitude=0.05f, float angle_spread_ratio=1.f, glm::vec2 kw_multiplier={4.f, 4.f}, float slope_strength=1.f, float branch_strength=2.f, float z_cut_min=0.2f, float z_cut_max=1.f, int octaves=8, float persistence=0.4f, float lacunarity=2.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a 2D array using the GavoroNoise algorithm, which is a procedural noise technique for terrain generation and other applications. | |
| Array | gavoronoise (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, float angle=0.f, float amplitude=0.05f, float angle_spread_ratio=1.f, glm::vec2 kw_multiplier={4.f, 4.f}, float slope_strength=1.f, float branch_strength=2.f, float z_cut_min=0.2f, float z_cut_max=1.f, int octaves=8, float persistence=0.4f, float lacunarity=2.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Array | gavoronoise (const Array &base, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, float amplitude=0.05f, glm::vec2 kw_multiplier={4.f, 4.f}, float slope_strength=1.f, float branch_strength=2.f, float z_cut_min=0.2f, float z_cut_max=1.f, int octaves=8, float persistence=0.4f, float lacunarity=2.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Array | hemisphere_field (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, float rmin=0.05f, float rmax=0.8f, float amplitude_random_ratio=1.f, float density=0.1f, glm::vec2 jitter={1.f, 1.f}, float shift=0.f, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_distance=nullptr, const Array *p_density_multiplier=nullptr, const Array *p_size_multiplier=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a scalar field representing the signed distance to randomly generated hemispheres. | |
| Array | hemisphere_field_fbm (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, float rmin=0.05f, float rmax=0.8f, float amplitude_random_ratio=1.f, float density=0.1f, glm::vec2 jitter={0.5f, 0.5f}, float shift=0.1f, int octaves=8, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_distance=nullptr, const Array *p_density_multiplier=nullptr, const Array *p_size_multiplier=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| See hmap::hemisphere_field. | |
| Array | island (const Array &land_mask, const Array *p_noise_r=nullptr, float apex_elevation=1.f, bool filter_distance=true, int filter_ir=32, float slope_min=0.1f, float slope_max=8.f, float slope_start=0.5f, float slope_end=1.f, float slope_noise_intensity=0.5f, float k_smooth=0.05f, float radial_noise_intensity=0.3f, float radial_profile_gain=2.f, float water_decay=0.05f, float water_depth=0.3f, float lee_angle=30.f, float lee_amp=0.f, float uplift_amp=0.f, Array *p_water_depth=nullptr, Array *p_inland_mask=nullptr) |
| Generates an island heightmap from a land mask using radial profiles, slope shaping, optional noise, and water attenuation. | |
| Array | island (const Array &land_mask, uint seed, float noise_amp=0.07f, glm::vec2 noise_kw={4.f, 4.f}, int noise_octaves=8, float noise_rugosity=0.7f, float noise_angle=45.f, float noise_k_smoothing=0.05f, float apex_elevation=1.f, bool filter_distance=true, int filter_ir=32, float slope_min=0.1f, float slope_max=8.f, float slope_start=0.5f, float slope_end=1.f, float slope_noise_intensity=0.5f, float k_smooth=0.05f, float radial_noise_intensity=0.3f, float radial_profile_gain=2.f, float water_decay=0.05f, float water_depth=0.3f, float lee_angle=30.f, float lee_amp=0.f, float uplift_amp=0.f, Array *p_water_depth=nullptr, Array *p_inland_mask=nullptr) |
| Generates an island heightmap from a land mask using internally generated FBM noise for radial perturbation and slope modulation. | |
| Array | mountain_cone (glm::ivec2 shape, uint seed, float scale=1.f, int octaves=8, float peak_kw=4.f, float rugosity=0.f, float angle=45.f, float k_smoothing=0.f, float gamma=0.5f, float cone_alpha=1.f, float ridge_amp=0.4f, float base_noise_amp=0.05f, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a procedural "mountain cone" heightmap using fractal noise and Voronoi patterns. | |
| Array | mountain_inselberg (glm::ivec2 shape, uint seed, float scale=1.f, int octaves=8, float rugosity=0.2f, float angle=45.f, float gamma=1.1f, bool round_shape=false, bool add_deposition=true, float bulk_amp=0.2f, float base_noise_amp=0.2f, float k_smoothing=0.1f, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a synthetic mountain-like inselberg (isolated hill) heightmap. | |
| Array | mountain_range_radial (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, float half_width=0.2f, float angle_spread_ratio=0.5f, float core_size_ratio=1.f, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_angle=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a heightmap representing a radial mountain range. | |
| Array | mountain_stump (glm::ivec2 shape, uint seed, float scale=1.f, int octaves=8, float peak_kw=6.f, float rugosity=0.f, float angle=45.f, float k_smoothing=0.f, float gamma=0.25f, bool add_deposition=true, float ridge_amp=0.75f, float base_noise_amp=0.1f, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a mountain-like heightmap with a flattened (stump-shaped) peak. | |
| Array | mountain_tibesti (glm::ivec2 shape, uint seed, float scale=1.f, int octaves=8, float peak_kw=20.f, float rugosity=0.f, float angle=30.f, float angle_spread_ratio=0.25f, float gamma=1.f, bool add_deposition=true, float bulk_amp=1.f, float base_noise_amp=0.1f, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a synthetic "Tibesti" mountain heightmap. | |
| Array | multisteps (glm::ivec2 shape, float angle, uint seed, glm::vec2 kw={2.f, 2.f}, float noise_amp=0.1f, float noise_rugosity=0.f, bool noise_inflate=true, float r=1.2f, int nsteps=8, float elevation_exponent=0.7f, float shape_gain=4.f, float scale=0.5f, float outer_slope=0.1f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const glm::vec2 ¢er={0.5f, 0.5f}, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| GPU-accelerated multi-step height generation with procedural noise. | |
| Array | noise (NoiseType noise_type, glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| See hmap::noise. | |
| Array | noise_fbm (NoiseType noise_type, glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_stretching=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| See hmap::noise_fbm. | |
| Array | plates (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, float talus, int direction=0, float mix_ratio=0.9f, float base_noise_amp=0.05f, float kw_multiplier=2.f, int octaves=8, float rugosity=0.f, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generate a tectonic plate–like heightfield using Voronoi FBM and directional talus projection. | |
| Array | polygon_field (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, float rmin=0.05f, float rmax=0.8f, float clamping_dist=0.1f, float clamping_k=0.1f, int n_vertices_min=3, int n_vertices_max=16, float density=0.5f, glm::vec2 jitter={0.5f, 0.5f}, float shift=0.1f, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_distance=nullptr, const Array *p_density_multiplier=nullptr, const Array *p_size_multiplier=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a scalar field representing the signed distance to randomly generated polygons. | |
| Array | polygon_field_fbm (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, float rmin=0.05f, float rmax=0.8f, float clamping_dist=0.1f, float clamping_k=0.1f, int n_vertices_min=3, int n_vertices_max=16, float density=0.1f, glm::vec2 jitter={0.5f, 0.5f}, float shift=0.1f, int octaves=8, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_distance=nullptr, const Array *p_density_multiplier=nullptr, const Array *p_size_multiplier=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a scalar field representing the signed distance to randomly generated polygons combined with fractal Brownian motion (fBm) noise modulation. | |
| Array | shattered_peak (glm::ivec2 shape, uint seed, float scale=1.f, int octaves=8, float peak_kw=4.f, float rugosity=0.f, float angle=30.f, float gamma=1.f, bool add_deposition=true, float bulk_amp=0.3f, float base_noise_amp=0.1f, float k_smoothing=0.f, glm::vec2 center={0.5f, 0.5f}, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a synthetic "shattered peak" terrain heightmap. | |
| Array | vorolines (glm::ivec2 shape, float density, uint seed, float k_smoothing=0.f, float exp_sigma=0.f, float alpha=0.f, float alpha_span=M_PI, VoronoiReturnType return_type=VoronoiReturnType::F1_SQUARED, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, glm::vec4 bbox_points={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a Voronoi-based pattern where cells are defined by proximity to random lines. | |
| Array | vorolines_fbm (glm::ivec2 shape, float density, uint seed, float k_smoothing=0.f, float exp_sigma=0.f, float alpha=0.f, float alpha_span=M_PI, VoronoiReturnType return_type=VoronoiReturnType::F1_SQUARED, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, glm::vec4 bbox_points={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a Voronoi-based pattern using distances to lines defined by random points and angles, with additional fractal Brownian motion (fBm) noise modulation. | |
| Array | voronoi (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, glm::vec2 jitter={0.5f, 0.5f}, float k_smoothing=0.f, float exp_sigma=0.f, VoronoiReturnType return_type=VoronoiReturnType::F1_SQUARED, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a Voronoi diagram in a 2D array with configurable properties. | |
| Array | voronoi_fbm (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, glm::vec2 jitter={0.5f, 0.5f}, float k_smoothing=0.f, float exp_sigma=0.f, VoronoiReturnType return_type=VoronoiReturnType::F1_SQUARED, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a Voronoi diagram in a 2D array with configurable properties. | |
| Array | voronoi_edge_distance (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, glm::vec2 jitter={0.5f, 0.5f}, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Computes the Voronoi edge distance. | |
| Array | voronoise (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, float u_param, float v_param, uint seed, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a 2D Voronoi noise array. | |
| Array | voronoise_fbm (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, float u_param, float v_param, uint seed, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return an array filled with coherence Voronoise. | |
| Array | vororand (glm::ivec2 shape, float density, float variability, uint seed, float k_smoothing=0.f, float exp_sigma=0.f, VoronoiReturnType return_type=VoronoiReturnType::F1_SQUARED, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, glm::vec4 bbox_points={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates a 2D Voronoi-based scalar field using OpenCL. | |
| Array | vororand (glm::ivec2 shape, const std::vector< float > &xp, const std::vector< float > &yp, float k_smoothing=0.f, float exp_sigma=0.f, VoronoiReturnType return_type=VoronoiReturnType::F1_SQUARED, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Array | wavelet_noise (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec2 kw, uint seed, float kw_multiplier=2.f, float vorticity=0.f, float density=1.f, int octaves=8, float weight=0.7f, float persistence=0.5f, float lacunarity=2.f, const Array *p_ctrl_param=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Generates 2D wavelet noise using an OpenCL kernel. | |
| Array | maximum_smooth (const Array &array1, const Array &array2, float k=0.2f) |
| See hmap::maximum_smooth. | |
| Array | minimum_smooth (const Array &array1, const Array &array2, float k=0.2f) |
| See hmap::minimum_smooth. | |
| Array | sdf_2d_polyline (const Path &path, glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr) |
| See hmap::sdf_2d_polyline. | |
| Array | sdf_2d_polyline_bezier (const Path &path, glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, const Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, const Array *p_noise_y=nullptr) |
| See hmap::sdf_2d_polyline_bezier. | |
| Array | select_cavities (const Array &array, int ir, bool concave=true) |
| See hmap::select_cavities. | |
| Array | select_soil_flow (const Array &z, int ir_gradient=1, float gradient_weight=1.f, float gradient_scaling_factor=0.f, float flow_weight=0.05f, float talus_ref=0.f, float clipping_ratio=50.f, float flow_gamma=1.f, float k_smooth=0.01f) |
| Computes a soil–flow selection map based on terrain gradient, river mask, and smoothing parameters. | |
| Array | select_soil_rocks (const Array &z, int ir_max=64, int ir_min=0, int steps=4, float smaller_scales_weight=1.f, ClampMode curvature_clamp_mode=ClampMode::POSITIVE_ONLY, float curvature_clamping=1.f) |
| Computes a multi-scale soil/rock selector using curvature analysis. | |
| Array | select_soil_weathered (const Array &z, int ir_curvature=0, int ir_gradient=4, ClampMode curvature_clamp_mode=ClampMode::POSITIVE_ONLY, float curvature_clamping=10.f, float curvature_weight=1.f, float gradient_weight=1.f, float gradient_scaling_factor=0.f) |
| Computes a soil weathering selection map based on curvature and gradient analysis. | |
| Array | select_soil_weathered (const Array &z, const Array &gradient_norm, int ir_curvature, ClampMode curvature_clamp_mode, float curvature_clamping, float curvature_weight, float gradient_weight, float gradient_scaling_factor) |
| Array | select_valley (const Array &z, int ir, bool ridge_select=false) |
| See hmap::select_valley. | |
| Array | advection_particle (const Array &z, const Array &advected_field, int iterations, int nparticles, uint seed, bool reverse=false, bool post_filter=true, float post_filter_sigma=0.125f, float advection_length=0.1f, float value_persistence=0.99f, float inertia=0.f, const Array *p_advection_mask=nullptr, const Array *p_mask=nullptr) |
| Performs particle-based advection on a scalar field. | |
| Array | advection_particle (const Array &z, const Array &advected_field, int nparticles, uint seed, bool reverse=false, bool post_filter=true, float post_filter_sigma=0.125f, float advection_length=0.1f, float value_persistence=0.99f, float inertia=0.f, const Array *p_advection_mask=nullptr, const Array *p_mask=nullptr) |
| Array | advection_particle (const Array &dx, const Array &dy, const Array &advected_field, int nparticles, uint seed, bool reverse=false, bool post_filter=true, float post_filter_sigma=0.125f, float advection_length=0.1f, float value_persistence=0.99f, float inertia=0.f, const Array *p_advection_mask=nullptr, const Array *p_mask=nullptr) |
| Array | advection_warp (const Array &z, const Array &advected_field, float advection_length=0.1f, float value_persistence=0.9f, const Array *p_mask=nullptr) |
| Performs 2D field advection based on the gradient of a heightmap using a warp-based technic (simplified approach). | |
| Array | advection_warp (const Array &z, const Array &advected_field, const Array &dx, const Array &dy, float advection_length=0.1f, float value_persistence=0.9f, const Array *p_mask=nullptr) |
| void | rotate (Array &array, float angle, bool zoom_in=true) |
| See hmap::rotate. | |
| void | warp (Array &array, const Array *p_dx, const Array *p_dy) |
| See hmap::warp. | |
| glm::vec4 | helper_transform_bbox (const glm::vec4 &bbox_source, const glm::vec4 &bbox_target) |
| float | helper_radial_profile (float r, float slope_start, float slope_end, float apex_elevation, float k_smooth, float radial_gain) |
| float | helper_apply_leeward (float h, float r, float hs, float slope_max, float k_smooth, float lee_amp, float alpha, float lee_alpha) |
| float | helper_apply_uplift (float h, float r, float slope_max, float uplift_amp, float k_smooth) |
| void | helper_bind_optional_buffers (clwrapper::Run &run, const Array *p_noise_x, const Array *p_noise_y) |
Function Documentation
◆ blend_gradients()
◆ blend_poisson_bf()
| Array hmap::gpu::blend_poisson_bf | ( | const Array & | array1, |
| const Array & | array2, | ||
| const int | iterations = 500, |
||
| const Array * | p_mask = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Blends two arrays using Poisson blending with a brute-force solver.
This function performs Poisson blending between array1 and array2 over a specified number of iterations. Optionally, a mask can be provided to control the blending regions.
- Parameters
-
array1 The first input array. array2 The second input array. iterations The number of iterations for the blending process (default: 500). p_mask Optional pointer to an array defining the blending mask. If null, blending is applied globally.
- Returns
- The blended array resulting from the Poisson blending operation.
Example
Result
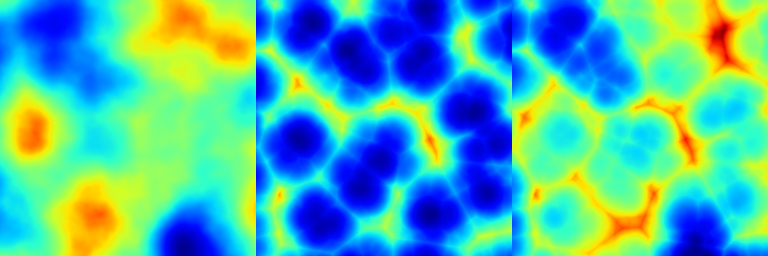
◆ transfer()
| Array hmap::gpu::transfer | ( | const Array & | source, |
| const Array & | target, | ||
| int | ir, | ||
| float | amplitude, | ||
| bool | target_prefiltering = false |
||
| ) |
See hmap::transfer.
◆ accumulation_curvature()
◆ curvature_horizontal_cross_sectional()
◆ curvature_horizontal_plan()
◆ curvature_horizontal_tangential()
◆ curvature_ring()
See hmap::curvature_ring.
◆ curvature_rotor()
◆ curvature_vertical_longitudinal()
◆ curvature_vertical_profile()
◆ level_set_curvature()
◆ shape_index()
See hmap::shape_index.
◆ unsphericity()
See hmap::unsphericity.
◆ hydraulic_particle() [1/2]
| void hmap::gpu::hydraulic_particle | ( | Array & | z, |
| int | nparticles, | ||
| int | seed, | ||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_moisture_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_erosion_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| float | c_capacity = 10.f, |
||
| float | c_erosion = 0.05f, |
||
| float | c_deposition = 0.05f, |
||
| float | c_inertia = 0.3f, |
||
| float | c_gravity = 1.f, |
||
| int | radius = 2, |
||
| float | drag_rate = 0.001f, |
||
| float | evap_rate = 0.001f, |
||
| bool | post_filtering = false |
||
| ) |
◆ hydraulic_particle() [2/2]
| void hmap::gpu::hydraulic_particle | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| int | nparticles, | ||
| int | seed, | ||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_moisture_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_erosion_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| float | c_capacity = 10.f, |
||
| float | c_erosion = 0.05f, |
||
| float | c_deposition = 0.05f, |
||
| float | c_inertia = 0.3f, |
||
| float | c_gravity = 1.f, |
||
| int | radius = 2, |
||
| float | drag_rate = 0.001f, |
||
| float | evap_rate = 0.001f, |
||
| bool | post_filtering = false |
||
| ) |
◆ hydraulic_schott() [1/2]
| void hmap::gpu::hydraulic_schott | ( | Array & | z, |
| int | iterations, | ||
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| float | c_erosion = 1.f, |
||
| float | c_thermal = 0.1f, |
||
| float | c_deposition = 0.2f, |
||
| float | flow_acc_exponent = 0.8f, |
||
| float | flow_acc_exponent_depo = 0.8f, |
||
| float | flow_routing_exponent = 1.3f, |
||
| float | thermal_weight = 1.5f, |
||
| float | deposition_weight = 2.5f, |
||
| Array * | p_flow = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Simulates hydraulic erosion and deposition on a heightmap using the Schott method.
This function performs hydraulic erosion on the given heightmap z over a specified number of iterations. It includes parameters for controlling erosion, deposition, and flow routing. Optional flow accumulation can also be computed and stored in the p_flow array.
- Parameters
-
[in,out] z The heightmap array to be modified. Heights are updated in-place. [in] iterations The number of iterations for the hydraulic erosion process. [in] talus An array defining the slope threshold for erosion. [in] c_erosion Erosion coefficient (default: 1.0f). [in] c_thermal Thermal erosion coefficient (default: 0.1f). [in] c_deposition Deposition coefficient (default: 0.2f). [in] flow_acc_exponent Exponent controlling the influence of flow accumulation on erosion (default: 0.8f). [in] flow_acc_exponent_depo Exponent controlling the influence of flow accumulation on deposition (default: 0.8f). [in] flow_routing_exponent Exponent controlling flow routing behavior (default: 1.3f). [in] thermal_weight Weight of thermal erosion effects (default: 1.5f). [in] deposition_weight Weight of deposition effects (default: 2.5f). [out] p_flow Optional pointer to an array for storing flow accumulation data. If null, flow data is not returned (default: nullptr).
- Note
- Taken from https://hal.science/hal-04565030v1/document
- Only available if OpenCL is enabled.
Example
Result
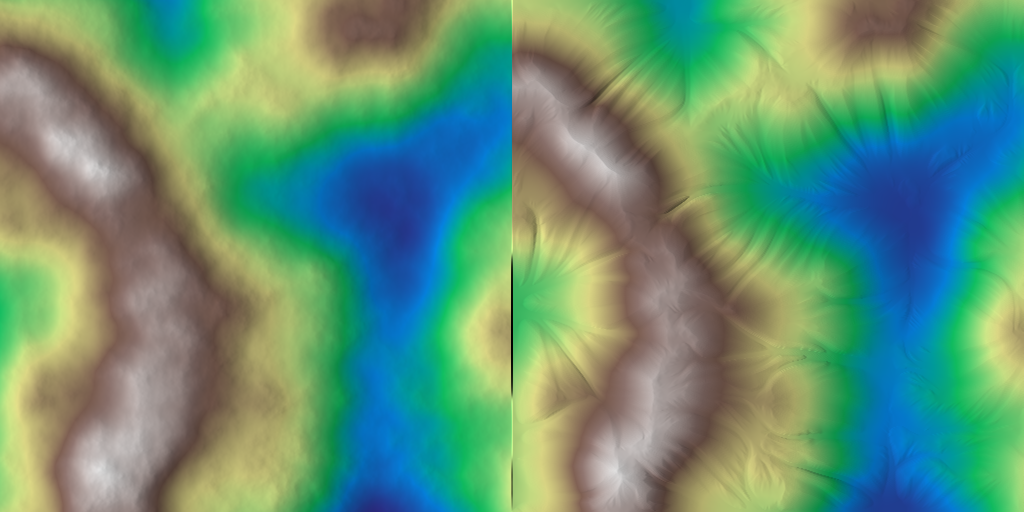
◆ hydraulic_schott() [2/2]
| void hmap::gpu::hydraulic_schott | ( | Array & | z, |
| int | iterations, | ||
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | c_erosion = 1.f, |
||
| float | c_thermal = 0.1f, |
||
| float | c_deposition = 0.2f, |
||
| float | flow_acc_exponent = 0.8f, |
||
| float | flow_acc_exponent_depo = 0.8f, |
||
| float | flow_routing_exponent = 1.3f, |
||
| float | thermal_weight = 1.5f, |
||
| float | deposition_weight = 2.5f, |
||
| Array * | p_flow = nullptr |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ hydraulic_schott_erosion()
| void hmap::gpu::hydraulic_schott_erosion | ( | Array & | z, |
| int | iterations, | ||
| float | c_erosion = 1.f, |
||
| float | flow_acc_exponent = 0.8f, |
||
| float | flow_routing_exponent = 1.3f, |
||
| Array * | p_flow = nullptr |
||
| ) |
See hmap::hydraulic_schott.
◆ hydraulic_stream_log() [1/2]
| void hmap::gpu::hydraulic_stream_log | ( | Array & | z, |
| float | c_erosion, | ||
| float | talus_ref, | ||
| int | deposition_ir = 32, |
||
| float | deposition_scale_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| float | gradient_power = 0.8f, |
||
| float | gradient_scaling_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| int | gradient_prefilter_ir = 16, |
||
| float | saturation_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_moisture_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_erosion_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_flow_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
◆ hydraulic_stream_log() [2/2]
| void hmap::gpu::hydraulic_stream_log | ( | Array & | z, |
| float | c_erosion, | ||
| float | talus_ref, | ||
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| int | deposition_ir = 32, |
||
| float | deposition_scale_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| float | gradient_power = 0.8f, |
||
| float | gradient_scaling_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| int | gradient_prefilter_ir = 16, |
||
| float | saturation_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_moisture_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_erosion_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_flow_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ hydraulic_vpipes()
| void hmap::gpu::hydraulic_vpipes | ( | Array & | z, |
| float | water_height = 1e-2f, |
||
| bool | maintain_water_volume = true, |
||
| float | evap_rate = 0.1f, |
||
| int | iterations = 50, |
||
| float | dt = 0.5f, |
||
| float | k_capacity = 0.5f, |
||
| float | k_erode = 0.001f, |
||
| float | k_depose = 0.01f, |
||
| float | k_discharge_exp = 1.f, |
||
| bool | flux_diffusion = true, |
||
| float | flux_diffusion_strength = 0.001f, |
||
| Array * | p_rain_map = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_water_depth = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_sediment = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_vel_u = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_vel_v = nullptr |
||
| ) |
◆ rifts()
| void hmap::gpu::rifts | ( | Array & | z, |
| const glm::vec2 & | kw, | ||
| float | angle, | ||
| float | amplitude, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | elevation_noise_shift = 0.f, |
||
| float | k_smooth_bottom = 0.05f, |
||
| float | k_smooth_top = 0.05f, |
||
| float | radial_spread_amp = 0.2f, |
||
| float | elevation_noise_amp = 0.1f, |
||
| float | clamp_vmin = 0.f, |
||
| float | remap_vmin = 0.f, |
||
| bool | apply_mask = true, |
||
| bool | reverse_mask = false, |
||
| float | mask_gamma = 1.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_mask = nullptr, |
||
| const glm::vec2 & | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Applies a "rift" deformation effect to a heightmap array.
This function modifies the given heightmap by introducing linear or radial "rift-like" noise patterns. The deformation can be controlled by several parameters such as direction, amplitude, noise shifts, and optional external noise arrays. Optionally, the effect can be masked using a power-based blending function.
- Parameters
-
z Reference to the heightmap array to be modified in-place. kw Frequency vector (kx, ky) scaling the deformation in X and Y directions. angle Orientation of the rift in degrees (0° = horizontal, 90° = vertical). amplitude Strength of the rift deformation applied to the heightmap. seed Random seed used for deterministic noise generation. elevation_noise_shift Vertical offset applied to the base noise to shift elevation influence. k_smooth_bottom Lower smoothing factor for Voronoi-based noise computation. k_smooth_top Upper smoothing factor for Voronoi-based noise computation. radial_spread_amp Amplitude controlling radial spreading away from the rift axis. elevation_noise_amp Amplitude scaling the influence of the heightmap's initial values as noise input. clamp_vmin Minimum clamp value for the Voronoi noise before remapping. remap_vmin Minimum remap value for scaling noise output. apply_mask If true, applies a power-based blending mask instead of a direct overwrite. mask_gamma Gamma exponent used when applying the mask to control blending. p_noise_x Optional pointer to an external noise array for X-offset perturbation (nullptr if unused). p_noise_y Optional pointer to an external noise array for Y-offset perturbation (nullptr if unused). center 2D vector specifying the central point around which the rift effect is computed. bbox Bounding box (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax) defining the spatial domain of the heightmap.
Example
Result
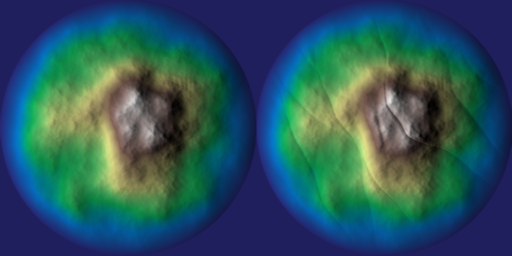
◆ strata()
| void hmap::gpu::strata | ( | Array & | z, |
| float | angle, | ||
| float | slope, | ||
| float | gamma, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| bool | linear_gamma = true, |
||
| float | kz = 1.f, |
||
| int | octaves = 4, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| float | gamma_noise_ratio = 0.5f, |
||
| float | noise_amp = 0.4f, |
||
| const glm::vec2 & | noise_kw = {4.f, 4.f}, |
||
| const glm::vec2 & | ridge_noise_kw = {4.f, 1.2f}, |
||
| float | ridge_angle_shift = 45.f, |
||
| float | ridge_noise_amp = 0.5f, |
||
| float | ridge_clamp_vmin = 0.f, |
||
| float | ridge_remap_vmin = 0.f, |
||
| bool | apply_elevation_mask = true, |
||
| bool | apply_ridge_mask = true, |
||
| float | mask_gamma = 0.4f, |
||
| const Array * | p_mask = nullptr, |
||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Applies stratification to a heightfield using directional noise and multiscale gamma transformations.
This function modifies the input heightfield z by simulating geological strata patterns. It combines directional shifts, fractal noise, and ridge-based perturbations to produce layered structures in the data. The MUST BE NORMALIZED in [0, 1].
- Parameters
-
z Reference to the heightfield array to modify, MUST BE NORMALIZED in [0, 1]. angle Horizontal orientation of the strata in degrees. slope Vertical slope of the strata. gamma Gamma exponent for the non-linear remapping (e.g., 0.5 for smoothing, 1.5 for sharpening). seed Seed for deterministic noise generation. linear_gamma If true, applies sharp linear gamma mapping; if false, uses smooth gamma mapping. kz Base scaling factor for the stratification frequency. octaves Number of iterative stratification passes (multiscale detail). lacunarity Frequency multiplier applied at each octave for fractal scaling. gamma_noise_ratio Ratio controlling how noise influences gamma variation (0 = no noise, 1 = full influence). noise_amp Amplitude of the base Perlin noise used to modulate the strata. noise_kw Frequency vector for the base Perlin noise along X and Y axes. ridge_noise_kw Frequency vector for the Voronoi ridge noise (x = main frequency, y = directional frequency). ridge_angle_shift Additional angular shift (in degrees) for the ridge direction, relative to angle.ridge_noise_amp Amplitude of the ridge noise modulation. ridge_clamp_vmin Minimum clamp value for ridge noise response. ridge_remap_vmin Minimum remap value for ridge modulation (used for reverse remapping). apply_mask If true, applied an elevation mask on the effect. mask_gamma Gamma applied to the mask used for blending original and stratified values for the elevation mask. p_mask Optional filter mask, expected in the range [0, 1]. bbox Bounding box of the domain as {xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax}.
- Note
- Setting
linear_gammatofalseproduces smoother transitions, whiletruecreates sharper layer boundaries. - Increasing
octavesadds multiscale detail but also increases computational cost.
- Setting
Example
Result
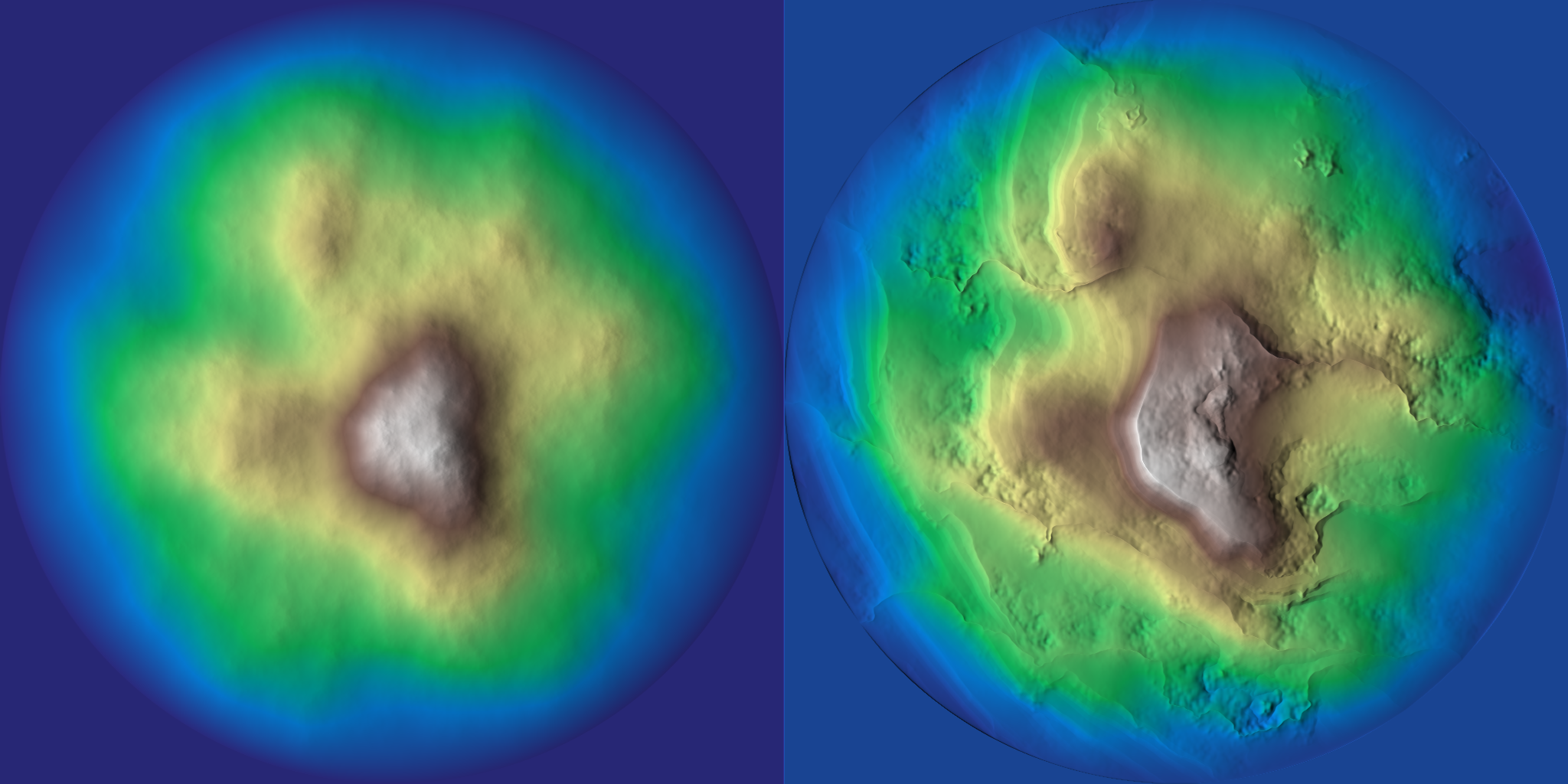
◆ thermal() [1/3]
| void hmap::gpu::thermal | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
See hmap::thermal.
◆ thermal() [2/3]
| void hmap::gpu::thermal | ( | Array & | z, |
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
See hmap::thermal.
◆ thermal() [3/3]
| void hmap::gpu::thermal | ( | Array & | z, |
| float | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| Array * | p_bedrock = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
See hmap::thermal.
◆ thermal_auto_bedrock() [1/3]
◆ thermal_auto_bedrock() [2/3]
◆ thermal_auto_bedrock() [3/3]
◆ thermal_olsen() [1/2]
See hmap::thermal_olsen.
◆ thermal_olsen() [2/2]
◆ thermal_inflate() [1/2]
Apply thermal weathering erosion to give a scree like effect.
- Note
- Only available if OpenCL is enabled.
- Parameters
-
z Input array. talus Talus limit. p_deposition_map [out] Reference to the deposition map, provided as an output field. iterations Number of iterations.
Example
Result
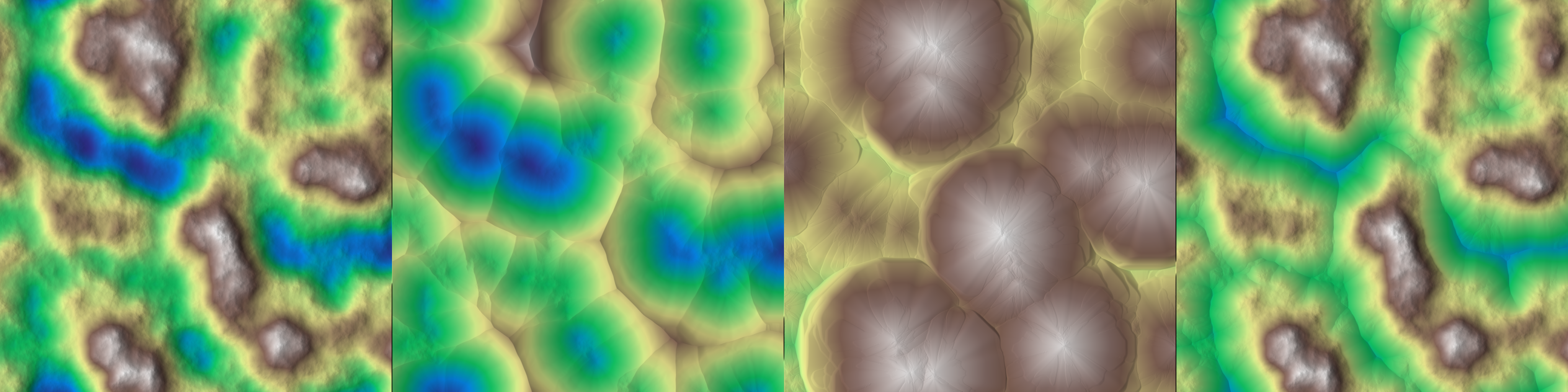
◆ thermal_inflate() [2/2]
| void hmap::gpu::thermal_inflate | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 10 |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ thermal_rib()
See hmap::thermal_rib.
◆ thermal_ridge() [1/2]
| void hmap::gpu::thermal_ridge | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Apply thermal weathering erosion to give a ridge like effect.
- Note
- Based on https://www.fractal-landscapes.co.uk/maths.html
- Only available if OpenCL is enabled.
- Parameters
-
z Input array. talus Talus limit. p_deposition_map [out] Reference to the deposition map, provided as an output field. iterations Number of iterations.
Example
Result

◆ thermal_ridge() [2/2]
| void hmap::gpu::thermal_ridge | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ thermal_scree() [1/2]
| void hmap::gpu::thermal_scree | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| const Array & | zmax, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Performs thermal scree erosion on a heightmap.
This function applies a thermal erosion process that redistributes material from steeper slopes to flatter areas, simulating talus formation. The process iterates a given number of times to achieve a more stable terrain profile.
- Parameters
-
[out] z The heightmap to be modified in-place by the erosion process. [in] talus The threshold slope angles that determine where material is moved. [in] zmax The maximum allowed elevation for erosion effects. [in] iterations The number of erosion iterations to apply (default: 10). [out] p_deposition_map Optional pointer to an array that stores the deposited material per cell.
◆ thermal_scree() [2/2]
| void hmap::gpu::thermal_scree | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| const Array & | zmax, | ||
| int | iterations = 10, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ valley_fill() [1/2]
| void hmap::gpu::valley_fill | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 100, |
||
| float | gamma = 2.f, |
||
| float | ratio = 0.8f, |
||
| float | zmin = 0.f, |
||
| float | zmax = 0.f, |
||
| float | elevation_max_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| bool | preserve_elevation_range = true, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Fill valleys using thermal scree deposition and height-based blending.
Applies an erosion-based fill to valleys, then blends the result with the original heightmap using a gamma-shaped mask derived from elevation.
- Parameters
-
z Heightmap to modify in place. talus Talus angle map controlling scree deposition. iterations Number of erosion iterations. gamma Gamma applied to the height-based mixing mask. ratio Blend ratio controlling valley influence. zmin Minimum height for normalization (auto if zmax <= zmin). zmax Maximum height for normalization (auto if zmax <= zmin).
Example
Result
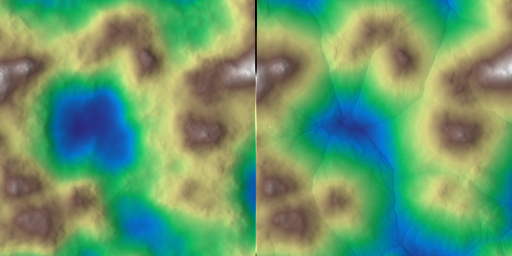
◆ valley_fill() [2/2]
| void hmap::gpu::valley_fill | ( | Array & | z, |
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| const Array & | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 100, |
||
| float | gamma = 2.f, |
||
| float | ratio = 0.8f, |
||
| float | zmin = 0.f, |
||
| float | zmax = 0.f, |
||
| float | elevation_max_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| bool | preserve_elevation_range = true, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
◆ watershed_ridge() [1/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::watershed_ridge | ( | const Array & | z, |
| float | amplitude = 0.5f, |
||
| int | ir = 1, |
||
| float | edt_exponent = 0.5f, |
||
| FlowDirectionMethod | fd_method = FlowDirectionMethod::FDM_D8, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr |
||
| ) |
◆ watershed_ridge() [2/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::watershed_ridge | ( | const Array & | z, |
| Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | amplitude = 0.5f, |
||
| int | ir = 1, |
||
| float | edt_exponent = 0.5f, |
||
| FlowDirectionMethod | fd_method = FlowDirectionMethod::FDM_D8, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr |
||
| ) |
◆ local_median_deviation()
◆ mean_local()
See hmap::mean_local.
◆ relative_elevation()
◆ ruggedness()
See hmap::ruggedness.
◆ rugosity()
See hmap::rugosity.
◆ std_local()
See hmap::std_local.
◆ z_score()
See hmap::z_score.
◆ expand() [1/4]
| void hmap::gpu::expand | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| int | iterations = 1 |
||
| ) |
See hmap::expand.
◆ expand() [2/4]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ expand() [3/4]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ expand() [4/4]
| void hmap::gpu::expand | ( | Array & | array, |
| const Array & | kernel, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| int | iterations = 1 |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ gamma_correction_local() [1/2]
◆ gamma_correction_local() [2/2]
| void hmap::gpu::gamma_correction_local | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | gamma, | ||
| int | ir, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | k = 0.1f |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ laplace() [1/2]
See hmap::laplace.
◆ laplace() [2/2]
| void hmap::gpu::laplace | ( | Array & | array, |
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | sigma = 0.2f, |
||
| int | iterations = 3 |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ maximum_local()
See hmap::maximum_local.
◆ maximum_local_disk()
◆ mean_shift() [1/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::mean_shift | ( | const Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| float | talus, | ||
| int | iterations = 1, |
||
| bool | talus_weighted = true |
||
| ) |
See hmap::mean_shift.
◆ mean_shift() [2/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::mean_shift | ( | const Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| float | talus, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| int | iterations = 1, |
||
| bool | talus_weighted = true |
||
| ) |
◆ median_3x3() [1/2]
| void hmap::gpu::median_3x3 | ( | Array & | array | ) |
See hmap::median_3x3.
◆ median_3x3() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ median_pseudo()
See hmap::median_pseudo.
◆ minimum_local()
See hmap::minimum_local.
◆ minimum_local_disk()
◆ normal_displacement() [1/2]
◆ normal_displacement() [2/2]
| void hmap::gpu::normal_displacement | ( | Array & | array, |
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | amount = 0.1f, |
||
| int | ir = 0, |
||
| bool | reverse = false |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ plateau() [1/2]
See hmap::plateau.
◆ plateau() [2/2]
| void hmap::gpu::plateau | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| float | factor | ||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ project_talus_along_direction() [1/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::project_talus_along_direction | ( | const Array & | array, |
| float | talus, | ||
| int | direction = 0 |
||
| ) |
Projects array values along a given direction using talus attenuation.
Applies a directional propagation (D8 convention) where values decay with distance according to a talus coefficient. The computation is performed on the GPU using an OpenCL kernel.
- Parameters
-
array Input 2D array. talus Talus coefficient controlling distance-based attenuation. direction Propagation direction (D8 convention, range [0–7]).
- Returns
- A new Array containing the projected values.
- Note
- The array is temporarily shifted to non-negative values to ensure correctness of OpenCL atomic operations on floats.
Example
Result
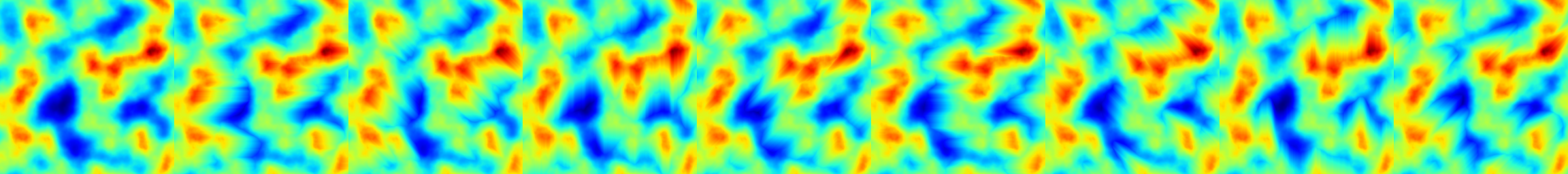
◆ project_talus_along_direction() [2/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::project_talus_along_direction | ( | const Array & | array, |
| float | talus, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| int | direction = 0 |
||
| ) |
◆ shrink() [1/4]
| void hmap::gpu::shrink | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| int | iterations = 1 |
||
| ) |
See hmap::shrink.
◆ shrink() [2/4]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ shrink() [3/4]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ shrink() [4/4]
| void hmap::gpu::shrink | ( | Array & | array, |
| const Array & | kernel, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| int | iterations = 1 |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ smooth_cpulse() [1/2]
| void hmap::gpu::smooth_cpulse | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir | ||
| ) |
See hmap::smooth_cpulse.
◆ smooth_cpulse() [2/2]
See hmap::smooth_cpulse.
◆ smooth_cpulse_edge_removing()
| void hmap::gpu::smooth_cpulse_edge_removing | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | talus, | ||
| float | talus_width, | ||
| int | ir | ||
| ) |
◆ smooth_fill() [1/2]
| void hmap::gpu::smooth_fill | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| float | k = 0.1f, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
See hmap::smooth_fill.
◆ smooth_fill() [2/2]
| void hmap::gpu::smooth_fill | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir, | ||
| const Array * | p_mask, | ||
| float | k = 0.1f, |
||
| Array * | p_deposition_map = nullptr |
||
| ) |
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ smooth_fill_holes() [1/2]
| void hmap::gpu::smooth_fill_holes | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir | ||
| ) |
◆ smooth_fill_holes() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ smooth_fill_smear_peaks() [1/2]
| void hmap::gpu::smooth_fill_smear_peaks | ( | Array & | array, |
| int | ir | ||
| ) |
◆ smooth_fill_smear_peaks() [2/2]
This is an overloaded member function, provided for convenience. It differs from the above function only in what argument(s) it accepts.
◆ gradient_norm()
See hmap::gradient_norm.
◆ harmonic_interpolation()
◆ interpolate_array_bicubic() [1/2]
◆ interpolate_array_bicubic() [2/2]
| void hmap::gpu::interpolate_array_bicubic | ( | const Array & | source, |
| Array & | target, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox_source, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox_target | ||
| ) |
◆ interpolate_array_bilinear() [1/2]
◆ interpolate_array_bilinear() [2/2]
| void hmap::gpu::interpolate_array_bilinear | ( | const Array & | source, |
| Array & | target, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox_source, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox_target | ||
| ) |
◆ interpolate_array_lagrange()
◆ interpolate_array_nearest() [1/2]
◆ interpolate_array_nearest() [2/2]
| void hmap::gpu::interpolate_array_nearest | ( | const Array & | source, |
| Array & | target, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox_source, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox_target | ||
| ) |
◆ border()
See hmap::border.
◆ closing()
See hmap::closing.
◆ dilation()
See hmap::dilation.
◆ dilation_expand_border_only()
◆ distance_transform_jfa()
| Array hmap::gpu::distance_transform_jfa | ( | const Array & | array, |
| bool | return_squared_distance = false |
||
| ) |
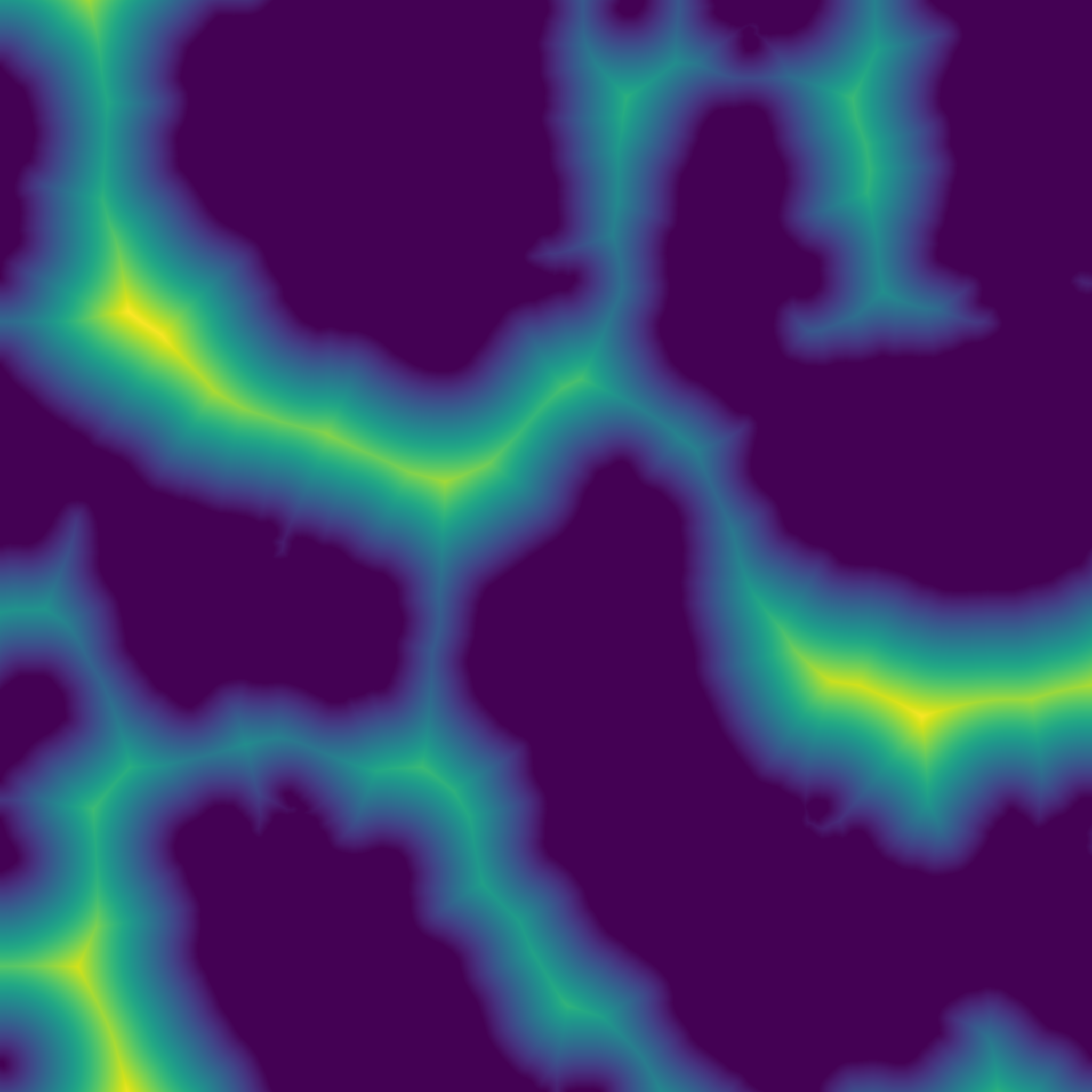
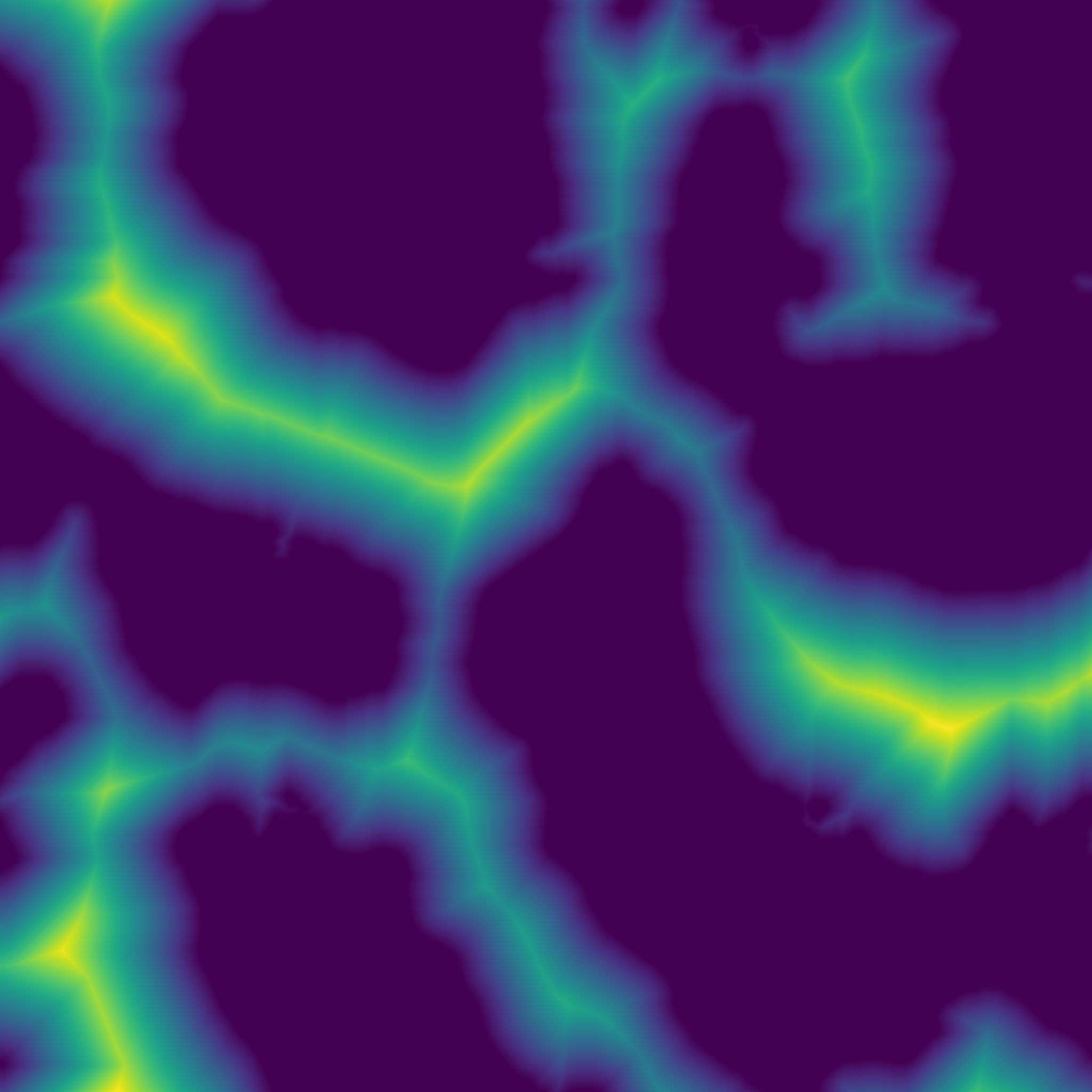
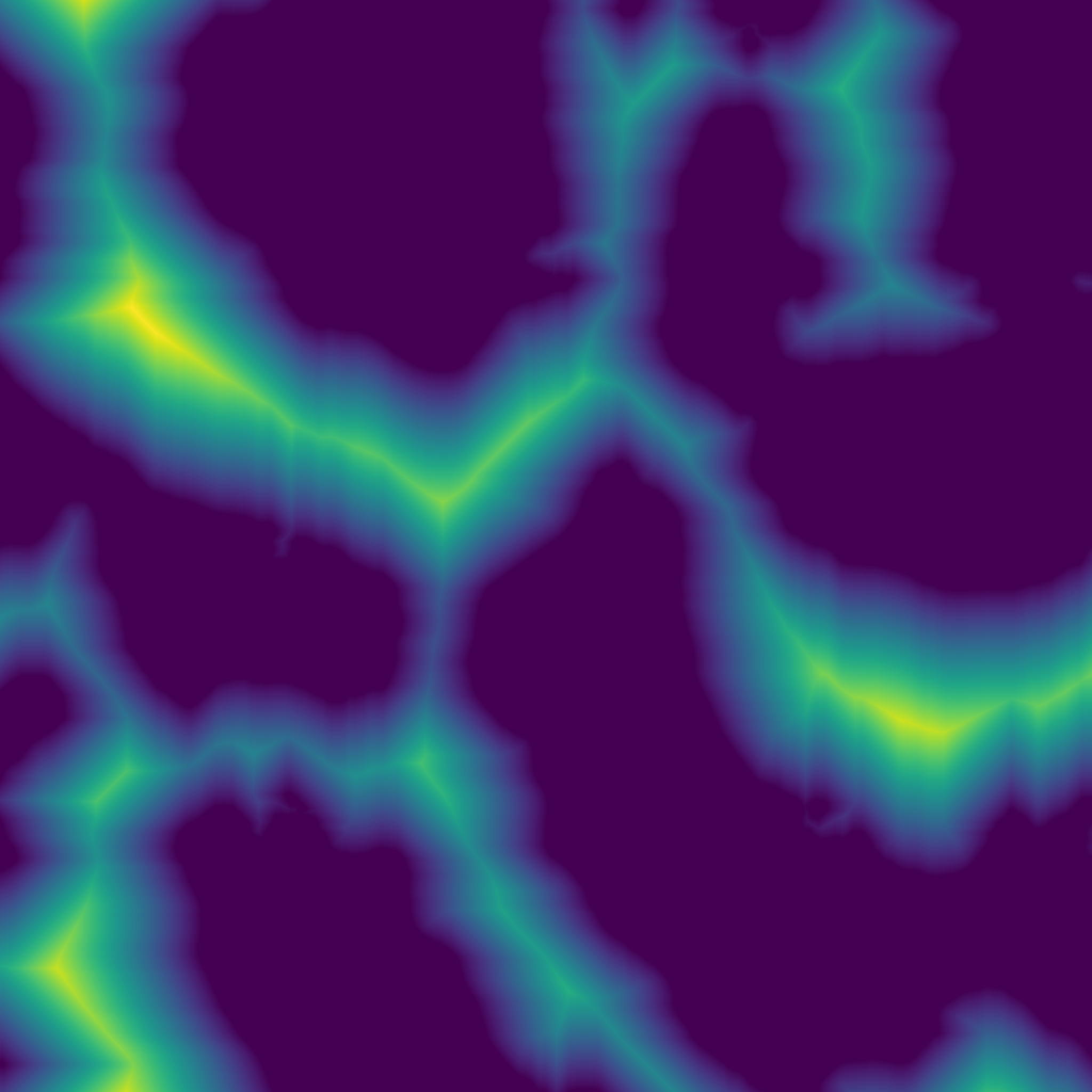
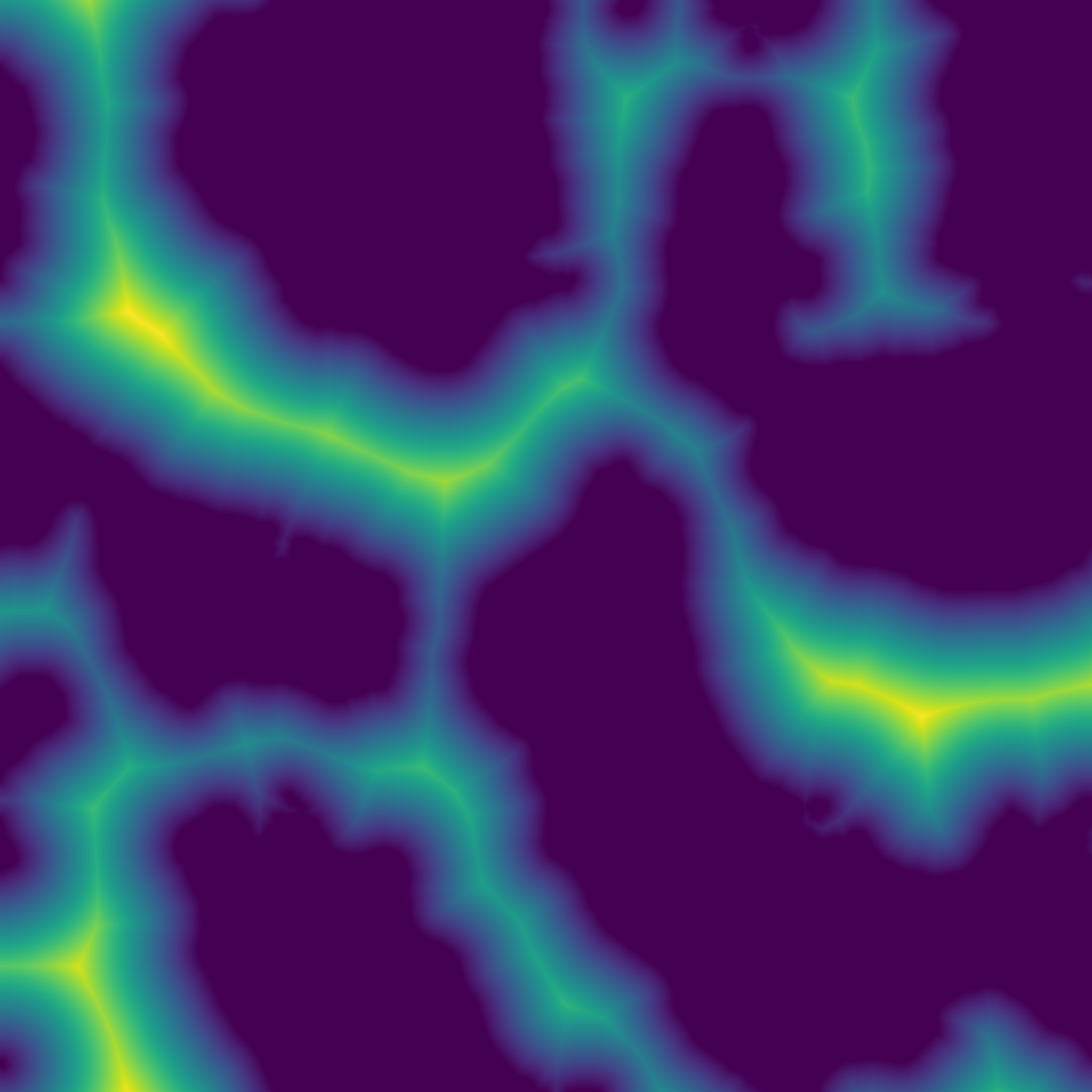
Return the Euclidean distance transform.
(Almost) exact transform based on the jump flooding algorithm.
- Parameters
-
array Input array to be transformed, will be converted into binary: 1 wherever input is greater than 0, 0 elsewhere. return_squared_distance Whether the distance returned is squared or not.
- Returns
- Array Reference to the output array.
Example
Result
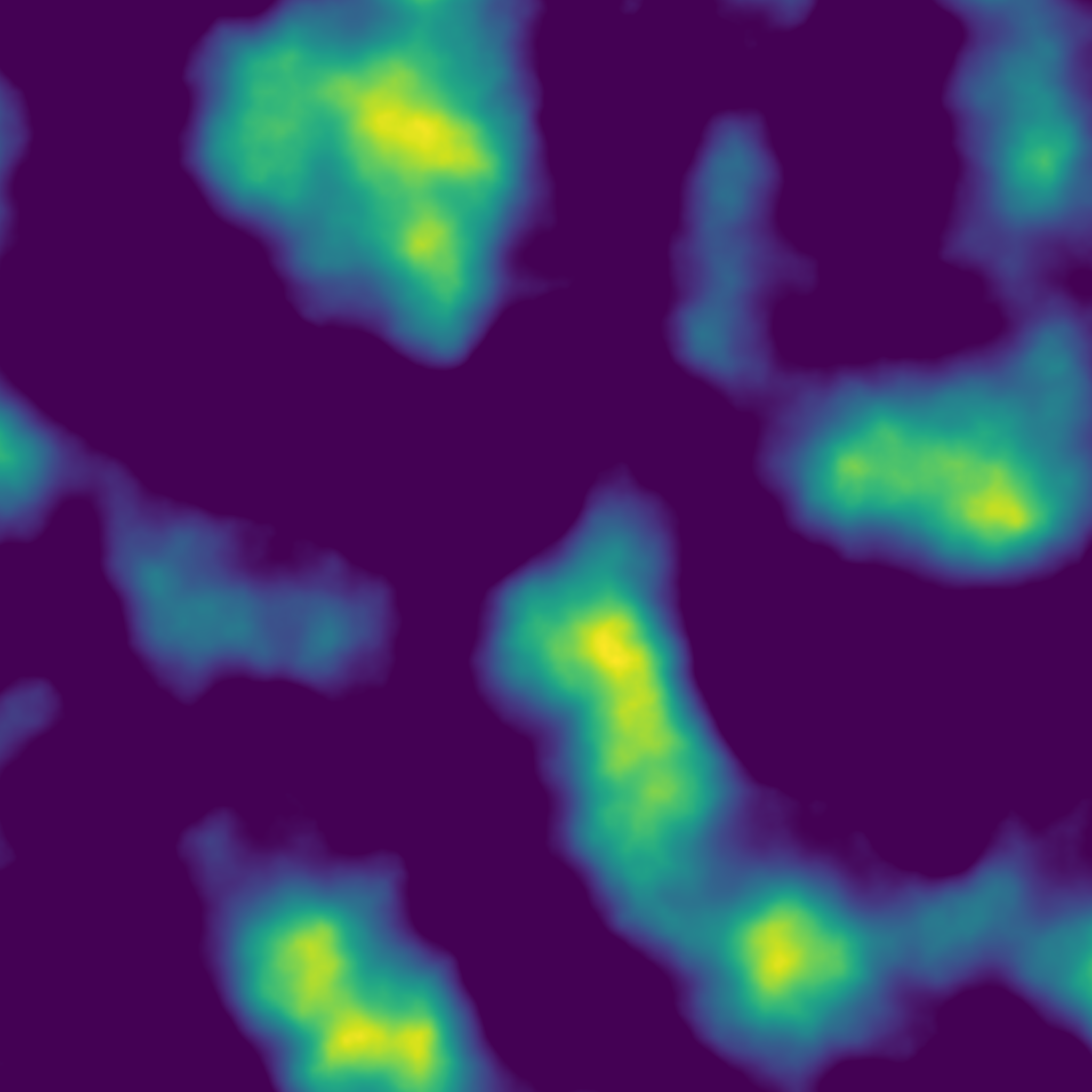
◆ erosion()
See hmap::erosion.
◆ morphological_black_hat()
◆ morphological_gradient()
◆ morphological_top_hat()
◆ opening()
See hmap::opening.
◆ relative_distance_from_skeleton()
◆ signed_curvature_from_distance()
◆ signed_distance_transform()
◆ skeleton()
See hmap::skeleton.
◆ helper_bind_optional_buffer()
| void hmap::gpu::helper_bind_optional_buffer | ( | clwrapper::Run & | run, |
| const std::string & | id, | ||
| const Array * | p_array | ||
| ) |
◆ init_opencl()
| bool hmap::gpu::init_opencl | ( | ) |
◆ badlands()
| Array hmap::gpu::badlands | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | rugosity = 0.2f, |
||
| float | angle = 30.f, |
||
| float | k_smoothing = 0.1f, |
||
| float | base_noise_amp = 0.2f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a synthetic "badlands" terrain heightmap.
This function procedurally creates a 2D elevation field resembling badlands (highly eroded terrain with sharp ridges and valleys). It combines fractal noise (FBM) with a Voronoi-based primitive, displaced along a specified orientation.
- Parameters
-
shape Output array shape (resolution in x and y). kw Frequency vector controlling the scale of the features. seed Random seed used for noise and Voronoi generation. rugosity Controls roughness of the fractal noise (higher = more irregular). angle Orientation angle (degrees) of terrain displacements. k_smoothing Voronoi smoothing parameter (controls ridge sharpness). base_noise_amp Amplitude of the base displacement noise. p_noise_x Optional pointer to external displacement noise field (X-axis). p_noise_y Optional pointer to external displacement noise field (Y-axis). bbox Bounding box of the generation domain in normalized coordinates.
- Returns
- Array containing the generated badlands heightmap.
Example
Result
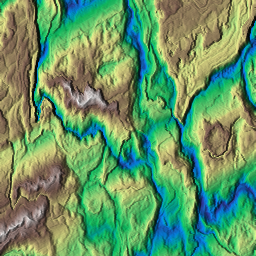
◆ basalt_field()
| Array hmap::gpu::basalt_field | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | warp_kw = 4.f, |
||
| float | large_scale_warp_amp = 0.2f, |
||
| float | large_scale_gain = 6.f, |
||
| float | large_scale_amp = 0.2f, |
||
| float | medium_scale_kw_ratio = 3.f, |
||
| float | medium_scale_warp_amp = 1.f, |
||
| float | medium_scale_gain = 7.f, |
||
| float | medium_scale_amp = 0.08f, |
||
| float | small_scale_kw_ratio = 10.f, |
||
| float | small_scale_amp = 0.1f, |
||
| float | small_scale_overlay_amp = 0.002f, |
||
| float | rugosity_kw_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| float | rugosity_amp = 1.f, |
||
| bool | flatten_activate = true, |
||
| float | flatten_kw_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| float | flatten_amp = 0.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a synthetic procedural terrain resembling basaltic landforms.
This function creates a multi-scale procedural field combining large, medium, and small-scale Voronoi-based patterns, noise warping, and optional flattening, simulating the morphology of fractured basalt or volcanic terrains. The terrain is constructed using a combination of Voronoi diagrams (via voronoi_fbm) and fractal noise (noise_fbm), layered with frequency-domain manipulations and amplitude/gain controls at each scale.
The final output is a heightmap represented as an Array, normalized and composed of:
- Large-scale cellular patterns with smoothed Voronoi edge distances.
- Medium and small-scale structures introducing finer surface variation.
- Optional rugosity (fine detail) and flattening to simulate erosion or flow effects.
- Parameters
-
shape Output resolution (width x height) of the field. kw Base wave numbers (frequency) for the terrain features. seed Initial seed used for deterministic random generation. warp_kw Frequency of the warping noise that displaces Voronoi positions. large_scale_warp_amp Amplitude of displacement for large-scale Voronoi warping. large_scale_gain Gain adjustment applied to the large-scale features. large_scale_amp Final amplitude of the large-scale height contribution. medium_scale_kw_ratio Scaling factor for the frequency of the medium-scale patterns. medium_scale_warp_amp Amplitude of warping for the medium-scale displacement. medium_scale_gain Gain control for medium-scale modulation. medium_scale_amp Amplitude of the medium-scale heightmap. small_scale_kw_ratio Frequency ratio for small-scale details. small_scale_amp Amplitude of small-scale pattern contribution. small_scale_overlay_amp Additional overlay strength for repeating the small-scale pattern. rugosity_kw_ratio Frequency ratio for high-frequency noise applied as fine roughness. rugosity_amp Strength of the rugosity (high-frequency modulation). flatten_activate Enables or disables the final flattening operation. flatten_kw_ratio Frequency scaling of the flattening noise field. flatten_amp Amplitude control of the flattening operation. p_noise_x Optional pointer to a noise field used to displace grid coordinates in X. p_noise_y Optional pointer to a noise field used to displace grid coordinates in Y. bbox The 2D bounding box ({xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax}) over which the terrain is generated.
- Returns
- A procedurally generated
Arrayrepresenting the synthetic basalt-like terrain field.
- Note
- This function relies on OpenCL-based kernels via the
gpu::namespace. - The returned field is normalized in amplitude but may require rescaling to match specific physical units.
- Adjusting
seed,warp_kw, and the gain/amplitude values can produce a wide variety of terrain features.
- This function relies on OpenCL-based kernels via the
Example
Result
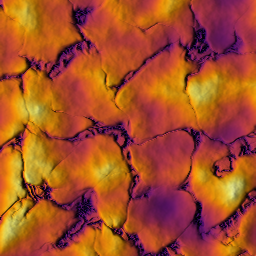
◆ gabor_wave() [1/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::gabor_wave | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| const Array & | angle, | ||
| float | angle_spread_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return an array filled with coherence Gabor noise.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. kw Noise wavenumbers {kx, ky} for each directions. seed Random seed number. angle Base orientation angle for the Gabor wavelets (in radians). Defaults to 0. angle_spread_ratio Ratio that controls the spread of wave orientations around the base angle. Defaults to 1. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array Fractal noise.
- Note
- Taken from https://www.shadertoy.com/view/clGyWm
- Only available if OpenCL is enabled.
Example
Result
◆ gabor_wave() [2/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::gabor_wave | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | angle = 0.f, |
||
| float | angle_spread_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
◆ gabor_wave_fbm() [1/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::gabor_wave_fbm | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| const Array & | angle, | ||
| float | angle_spread_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return an array filled with coherence Gabor noise.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. kw Noise wavenumbers {kx, ky} for each directions. seed Random seed number. angle Base orientation angle for the Gabor wavelets (in radians). Defaults to 0. angle_spread_ratio Ratio that controls the spread of wave orientations around the base angle. Defaults to 1. octaves Number of octaves. weigth Octave weighting. persistence Octave persistence. lacunarity Defines the wavenumber ratio between each octaves. p_ctrl_param Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the weight parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array Fractal noise.
- Note
- Taken from https://www.shadertoy.com/view/clGyWm
- Only available if OpenCL is enabled.
Example
Result

◆ gabor_wave_fbm() [2/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::gabor_wave_fbm | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | angle = 0.f, |
||
| float | angle_spread_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
◆ gavoronoise() [1/3]
| Array hmap::gpu::gavoronoise | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| const Array & | angle, | ||
| float | amplitude = 0.05f, |
||
| float | angle_spread_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | kw_multiplier = {4.f, 4.f}, |
||
| float | slope_strength = 1.f, |
||
| float | branch_strength = 2.f, |
||
| float | z_cut_min = 0.2f, |
||
| float | z_cut_max = 1.f, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.4f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a 2D array using the GavoroNoise algorithm, which is a procedural noise technique for terrain generation and other applications.
- Parameters
-
shape Dimensions of the output array. kw Wave number vector controlling the noise frequency. seed Seed value for random number generation. amplitude Amplitude of the noise. kw_multiplier Multiplier for wave numbers in the noise function. slope_strength Strength of slope-based directional erosion in the noise. branch_strength Strength of branch-like structures in the generated noise. z_cut_min Minimum cutoff for Z-value in the noise. z_cut_max Maximum cutoff for Z-value in the noise. octaves Number of octaves for fractal Brownian motion (fBm). persistence Amplitude scaling factor between noise octaves. lacunarity Frequency scaling factor between noise octaves. p_ctrl_param Optional array for control parameters, can modify the Z cutoff dynamically. p_noise_x Optional array for X-axis noise perturbation. p_noise_y Optional array for Y-axis noise perturbation. bbox Bounding box for mapping grid coordinates to world space.
- Returns
- A 2D array containing the generated GavoroNoise values.
- Note
- Taken from https://www.shadertoy.com/view/MtGcWh
- Only available if OpenCL is enabled.
This function leverages an OpenCL kernel to compute the GavoroNoise values on the GPU, allowing for efficient large-scale generation. The kernel applies a combination of fractal Brownian motion (fBm), directional erosion, and other procedural techniques to generate intricate noise patterns.
The optional p_ctrl_param, p_noise_x, and p_noise_y buffers provide additional flexibility for dynamically adjusting noise parameters and perturbations.
Example
Result
◆ gavoronoise() [2/3]
| Array hmap::gpu::gavoronoise | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | angle = 0.f, |
||
| float | amplitude = 0.05f, |
||
| float | angle_spread_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | kw_multiplier = {4.f, 4.f}, |
||
| float | slope_strength = 1.f, |
||
| float | branch_strength = 2.f, |
||
| float | z_cut_min = 0.2f, |
||
| float | z_cut_max = 1.f, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.4f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
◆ gavoronoise() [3/3]
| Array hmap::gpu::gavoronoise | ( | const Array & | base, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | amplitude = 0.05f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | kw_multiplier = {4.f, 4.f}, |
||
| float | slope_strength = 1.f, |
||
| float | branch_strength = 2.f, |
||
| float | z_cut_min = 0.2f, |
||
| float | z_cut_max = 1.f, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.4f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
◆ hemisphere_field()
| Array hmap::gpu::hemisphere_field | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | rmin = 0.05f, |
||
| float | rmax = 0.8f, |
||
| float | amplitude_random_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| float | density = 0.1f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | jitter = {1.f, 1.f}, |
||
| float | shift = 0.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_distance = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_density_multiplier = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_size_multiplier = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a scalar field representing the signed distance to randomly generated hemispheres.
- Parameters
-
shape Resolution of the output field (width, height). kw Scaling factor for field coordinates (world units per pixel). seed Random seed generation. rmin Minimum sphere radius (relative to bbox size). rmax Maximum sphere radius (relative to bbox size). density Fraction of pixels covered by polygons (approximate). jitter Random displacement factor applied to sphere vertices. shift Random position shift applied to sphere center. p_noise_x Optional displacement noise field in the X direction (nullptr to disable). p_noise_y Optional displacement noise field in the Y direction (nullptr to disable). bbox Bounding box in normalized coordinates {xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax}.
- Returns
- Array 2D array containing the signed distance field.
Example
Result

◆ hemisphere_field_fbm()
| Array hmap::gpu::hemisphere_field_fbm | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | rmin = 0.05f, |
||
| float | rmax = 0.8f, |
||
| float | amplitude_random_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| float | density = 0.1f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | jitter = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| float | shift = 0.1f, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_distance = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_density_multiplier = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_size_multiplier = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
See hmap::hemisphere_field.
◆ island() [1/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::island | ( | const Array & | land_mask, |
| const Array * | p_noise_r = nullptr, |
||
| float | apex_elevation = 1.f, |
||
| bool | filter_distance = true, |
||
| int | filter_ir = 32, |
||
| float | slope_min = 0.1f, |
||
| float | slope_max = 8.f, |
||
| float | slope_start = 0.5f, |
||
| float | slope_end = 1.f, |
||
| float | slope_noise_intensity = 0.5f, |
||
| float | k_smooth = 0.05f, |
||
| float | radial_noise_intensity = 0.3f, |
||
| float | radial_profile_gain = 2.f, |
||
| float | water_decay = 0.05f, |
||
| float | water_depth = 0.3f, |
||
| float | lee_angle = 30.f, |
||
| float | lee_amp = 0.f, |
||
| float | uplift_amp = 0.f, |
||
| Array * | p_water_depth = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_inland_mask = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Generates an island heightmap from a land mask using radial profiles, slope shaping, optional noise, and water attenuation.
Applies elevation shaping inside the land mask using distance-based profiles, slope controls, optional radial and slope noise, and water-depth modeling.
- Parameters
-
land_mask Binary mask defining the island shape. p_noise_r Optional radial noise field (same size as mask). apex_elevation Maximum elevation at island center. filter_distance Enable smoothing of the distance transform. filter_ir Radius of the distance filter. slope_min Minimum slope. slope_max Maximum slope. slope_start Start of slope ramp (0–1). slope_end End of slope ramp (0–1). slope_noise_intensity Intensity of slope noise modulation. k_smooth Smoothing factor for the final profile. radial_noise_intensity Intensity of radial displacement noise. radial_profile_gain Exponent for radial falloff. water_decay Transition sharpness to water level. water_depth Water depth below the shoreline. lee_angle Angle for lee-side (wind shadow) erosion. lee_amp Amplitude of lee-side erosion. uplift_amp Amplitude of uplift (orographic) effect. p_water_depth Optional output: per-pixel water depth. p_inland_mask Optional output: mask of inland pixels.
- Returns
- Heightmap array representing the generated island.
Example
Result
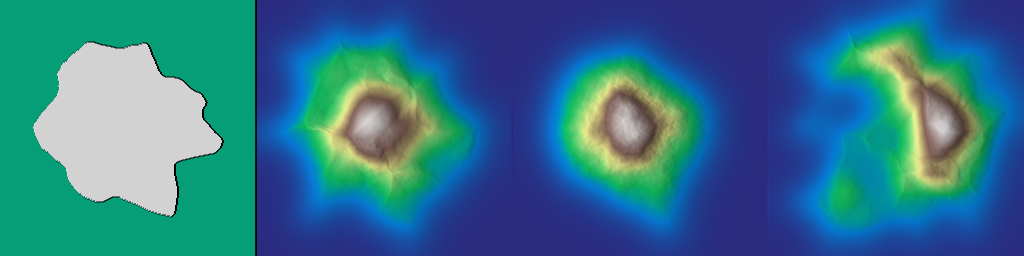
◆ island() [2/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::island | ( | const Array & | land_mask, |
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | noise_amp = 0.07f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | noise_kw = {4.f, 4.f}, |
||
| int | noise_octaves = 8, |
||
| float | noise_rugosity = 0.7f, |
||
| float | noise_angle = 45.f, |
||
| float | noise_k_smoothing = 0.05f, |
||
| float | apex_elevation = 1.f, |
||
| bool | filter_distance = true, |
||
| int | filter_ir = 32, |
||
| float | slope_min = 0.1f, |
||
| float | slope_max = 8.f, |
||
| float | slope_start = 0.5f, |
||
| float | slope_end = 1.f, |
||
| float | slope_noise_intensity = 0.5f, |
||
| float | k_smooth = 0.05f, |
||
| float | radial_noise_intensity = 0.3f, |
||
| float | radial_profile_gain = 2.f, |
||
| float | water_decay = 0.05f, |
||
| float | water_depth = 0.3f, |
||
| float | lee_angle = 30.f, |
||
| float | lee_amp = 0.f, |
||
| float | uplift_amp = 0.f, |
||
| Array * | p_water_depth = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_inland_mask = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Generates an island heightmap from a land mask using internally generated FBM noise for radial perturbation and slope modulation.
Same as the other overload but creates a noise field procedurally from a seed, including frequency, octaves, orientation, and smoothing controls.
- Parameters
-
land_mask Binary mask defining the island shape. seed Noise seed. noise_amp Amplitude of generated noise. noise_kw Noise frequencies (x, y). noise_octaves Number of FBM octaves. noise_rugosity Persistence-like roughness control. noise_angle Rotation of the noise field (radians). noise_k_smoothing Smoothing applied to the noise field. apex_elevation Maximum elevation at island center. filter_distance Enable smoothing of the distance transform. filter_ir Radius of distance filter. slope_min Minimum slope. slope_max Maximum slope. slope_start Start of slope ramp (0–1). slope_end End of slope ramp (0–1). slope_noise_intensity Intensity of slope noise modulation. k_smooth Smoothing factor for final profile. radial_noise_intensity Intensity of radial displacement noise. radial_profile_gain Exponent for radial falloff. water_decay Transition sharpness to water level. water_depth Water depth below the shoreline. lee_angle Angle for lee-side erosion. lee_amp Amplitude for lee-side erosion. uplift_amp Amplitude of uplift (orographic) effect. p_water_depth Optional output: per-pixel water depth. p_inland_mask Optional output: mask of inland pixels.
- Returns
- Heightmap array representing the generated island.
Example
Result

◆ mountain_cone()
| Array hmap::gpu::mountain_cone | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | scale = 1.f, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | peak_kw = 4.f, |
||
| float | rugosity = 0.f, |
||
| float | angle = 45.f, |
||
| float | k_smoothing = 0.f, |
||
| float | gamma = 0.5f, |
||
| float | cone_alpha = 1.f, |
||
| float | ridge_amp = 0.4f, |
||
| float | base_noise_amp = 0.05f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a procedural "mountain cone" heightmap using fractal noise and Voronoi patterns.
This function synthesizes a terrain-like array shaped as a cone with noise-based ridges and surface roughness. The generation combines a cone-shaped envelope (cone_sigmoid), a fractal base noise (gpu::noise_fbm), and a Voronoi ridge structure (voronoi_fbm), producing a mountain with controlled smoothness, angular distortion, and noise-based displacements.
- Parameters
-
shape The output array dimensions (width, height). seed The random seed for noise generation. scale Global scaling factor for the mountain size. octaves Number of fractal noise octaves for both FBM and Voronoi. peak_kw Controls the base frequency (inverse wavelength) of the peak noise. rugosity Controls the amplitude decay across octaves (higher = rougher surface). angle Direction (in degrees) for the displacement noise distortion. k_smoothing Smoothing factor applied in Voronoi blending. gamma Gamma correction exponent applied at the end. cone_alpha Controls the cone envelope steepness (higher = sharper peak). ridge_amp Controls the amplitude of ridge enhancement in the Voronoi term. base_noise_amp Amplitude multiplier for the displacement noise. center The 2D position (in normalized coordinates) of the mountain cone center. p_noise_x Optional pointer to an external X displacement noise field (can be nullptr). p_noise_y Optional pointer to an external Y displacement noise field (can be nullptr). bbox The bounding box (min_x, min_y, max_x, max_y) defining the spatial extent of the map.
- Returns
- An Array representing the final terrain heightmap in normalized [0, 1] range.
Example
Result
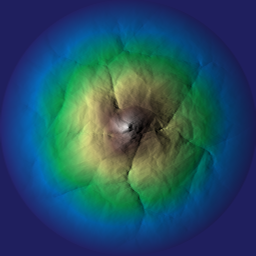
◆ mountain_inselberg()
| Array hmap::gpu::mountain_inselberg | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | scale = 1.f, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | rugosity = 0.2f, |
||
| float | angle = 45.f, |
||
| float | gamma = 1.1f, |
||
| bool | round_shape = false, |
||
| bool | add_deposition = true, |
||
| float | bulk_amp = 0.2f, |
||
| float | base_noise_amp = 0.2f, |
||
| float | k_smoothing = 0.1f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a synthetic mountain-like inselberg (isolated hill) heightmap.
This function procedurally creates a 2D elevation field resembling an inselberg, using a combination of fractal noise (FBM), Gaussian pulses, and Voronoi-based structures. It allows control over scale, shape, orientation, rugosity, and optional geological-like effects such as bulk uplift and deposition smoothing.
- Parameters
-
shape Output array shape (resolution in x and y). seed Random seed used for noise and Voronoi generation. scale Global scaling factor for the inselberg width and structure. rugosity Controls roughness of the fractal noise (higher = more irregular). angle Orientation angle (degrees) for directional displacements. gamma Gamma correction factor applied to the final heightmap. round_shape If true, generates a symmetric round shape; if false, adds directional displacement. add_deposition If true, applies a smoothing fill step simulating sediment deposition. bulk_amp Amplitude of bulk uplift applied to the base pulse (0 = none, >0 = raises and normalizes the feature). base_noise_amp Amplitude of the base displacement noise. k_smoothing Voronoi smoothing parameter (controls ridge sharpness). center Center of the inselberg in normalized coordinates. p_noise_x Optional pointer to external displacement noise field (X-axis). p_noise_y Optional pointer to external displacement noise field (Y-axis). bbox Bounding box of the generation domain in normalized coordinates.
- Returns
- Array containing the generated inselberg heightmap.
Example
Result**
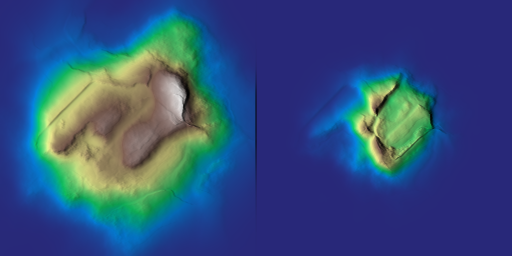
◆ mountain_range_radial()
| Array hmap::gpu::mountain_range_radial | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | half_width = 0.2f, |
||
| float | angle_spread_ratio = 0.5f, |
||
| float | core_size_ratio = 1.f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_angle = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a heightmap representing a radial mountain range.
This function creates a heightmap that simulates a mountain range emanating radially from a specified center. The mountain range is influenced by various noise parameters and control attributes.
- Parameters
-
shape The dimensions of the output heightmap as a 2D vector. kw The wave numbers (frequency components) as a 2D vector. seed The seed for random noise generation. half_width The half-width of the radial mountain range, controlling its spread. Default is 0.2f. angle_spread_ratio The ratio controlling the angular spread of the mountain range. Default is 0.5f. center The center point of the radial mountain range as normalized coordinates within [0, 1]. Default is {0.5f, 0.5f}. octaves The number of octaves for fractal noise generation. Default is 8. weight The initial weight for noise contribution. Default is 0.7f. persistence The amplitude scaling factor for subsequent noise octaves. Default is 0.5f. lacunarity The frequency scaling factor for subsequent noise octaves. Default is 2.0f. p_ctrl_param Optional pointer to an array of control parameters influencing the terrain generation. p_noise_x Optional pointer to a precomputed noise array for the X-axis. p_noise_y Optional pointer to a precomputed noise array for the Y-axis. p_angle Optional pointer to an array to output the angle. bbox The bounding box of the output heightmap in normalized coordinates [xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax]. Default is {0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f}.
- Returns
- Array The generated heightmap representing the radial mountain range.
- Note
- Only available if OpenCL is enabled.
Example
Result
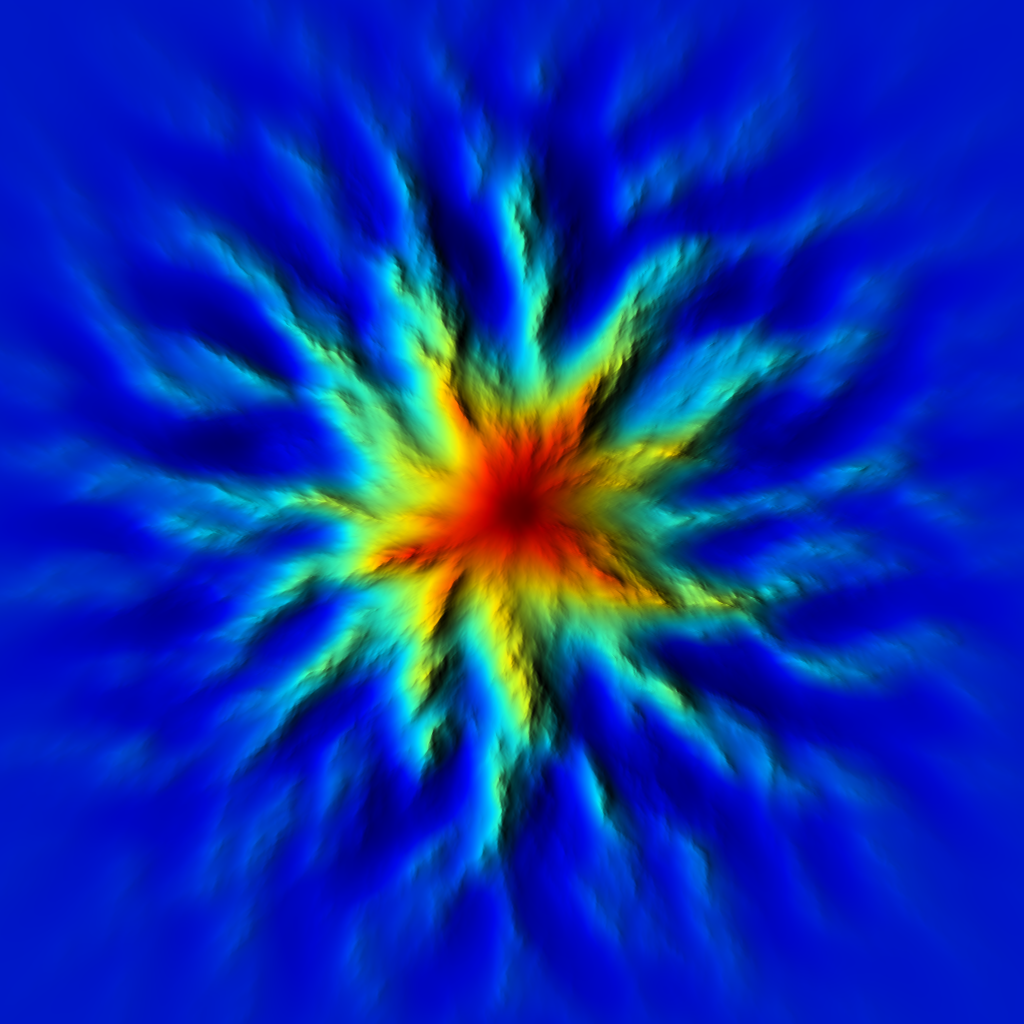
◆ mountain_stump()
| Array hmap::gpu::mountain_stump | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | scale = 1.f, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | peak_kw = 6.f, |
||
| float | rugosity = 0.f, |
||
| float | angle = 45.f, |
||
| float | k_smoothing = 0.f, |
||
| float | gamma = 0.25f, |
||
| bool | add_deposition = true, |
||
| float | ridge_amp = 0.75f, |
||
| float | base_noise_amp = 0.1f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a mountain-like heightmap with a flattened (stump-shaped) peak.
This function procedurally creates a terrain resembling a broad mountain with a smooth, truncated summit. The result combines layered fractal noise (FBM), Gaussian shaping, and Voronoi-based ridge formation to produce natural-looking geomorphological features. The shape can be modulated by directional displacement noise, smoothed using deposition simulation, and refined through gamma and smoothing parameters.
- Parameters
-
shape Dimensions of the output heightmap (width, height). seed Random seed for noise generation. scale Global scale factor controlling the size of features. octaves Number of noise octaves used in FBM generation. peak_kw Base spatial frequency of the main ridge/peak structure. rugosity Controls the roughness of base noise displacements. angle Orientation angle (in degrees) of the main ridge direction. k_smoothing Smoothing coefficient applied to the Voronoi FBM ridges. gamma Gamma correction applied to the ridge intensity. add_deposition If true, applies an additional smoothing pass to simulate sediment deposition. ridge_amp Amplitude scaling factor for ridge prominence. base_noise_amp Amplitude scaling factor for base displacement noise. center Normalized coordinates of the mountain’s center (default domain: [0, 1]²). p_noise_x Optional pointer to horizontal displacement noise (nullptr for none). p_noise_y Optional pointer to vertical displacement noise (nullptr for none). bbox Bounding box of the generated region (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax).
- Returns
- A 2D Array containing the generated mountain stump heightmap.
Example
Result
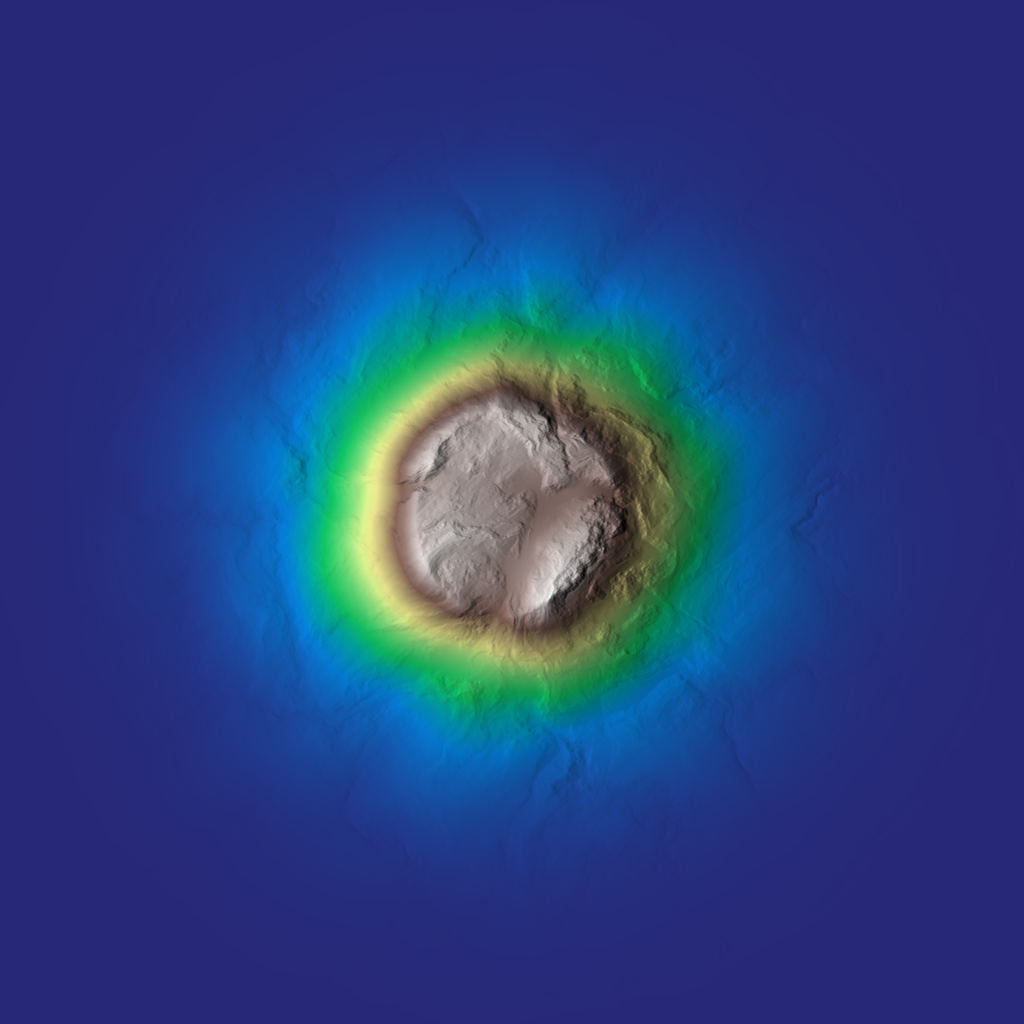
◆ mountain_tibesti()
| Array hmap::gpu::mountain_tibesti | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | scale = 1.f, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | peak_kw = 20.f, |
||
| float | rugosity = 0.f, |
||
| float | angle = 30.f, |
||
| float | angle_spread_ratio = 0.25f, |
||
| float | gamma = 1.f, |
||
| bool | add_deposition = true, |
||
| float | bulk_amp = 1.f, |
||
| float | base_noise_amp = 0.1f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a synthetic "Tibesti" mountain heightmap.
This function procedurally creates a 2D elevation field inspired by the Tibesti mountains, a desert volcanic range. The terrain is built by combining Gabor wavelets, fractal simplex noise, and a Gaussian envelope, producing sharp volcanic peaks modulated by erosion-like patterns.
- Parameters
-
shape Output array shape (resolution in x and y). seed Random seed used for noise and wavelet generation. scale Global scaling factor controlling the overall mountain size. octaves Number of octaves used in the fractal noise and Gabor FBM. peak_kw Base frequency of the peak features (scaled internally by scale).rugosity Controls roughness of the fractal noise (higher = more irregular). angle Orientation angle (degrees) for Gabor waves. angle_spread_ratio Spread ratio of the Gabor wave orientation (controls anisotropy). gamma Gamma correction factor applied to auxiliary noise fields. add_deposition If true, applies a smoothing fill step simulating sediment deposition. bulk_amp Amplitude of bulk uplift applied to the peaks (affects normalization with noise weighting). base_noise_amp Amplitude of the base displacement noise. center Center of the mountain in normalized coordinates. p_noise_x Optional pointer to external displacement noise field (X-axis). p_noise_y Optional pointer to external displacement noise field (Y-axis). bbox Bounding box of the generation domain in normalized coordinates.
- Returns
- Array containing the generated Tibesti mountain heightmap.
Example
Result
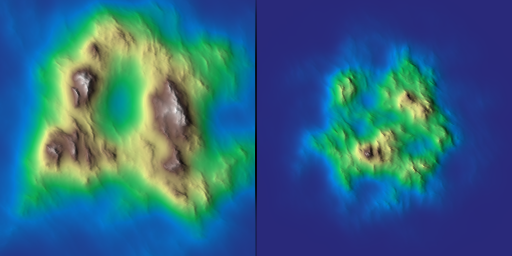
◆ multisteps()
| Array hmap::gpu::multisteps | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | angle, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| glm::vec2 | kw = {2.f, 2.f}, |
||
| float | noise_amp = 0.1f, |
||
| float | noise_rugosity = 0.f, |
||
| bool | noise_inflate = true, |
||
| float | r = 1.2f, |
||
| int | nsteps = 8, |
||
| float | elevation_exponent = 0.7f, |
||
| float | shape_gain = 4.f, |
||
| float | scale = 0.5f, |
||
| float | outer_slope = 0.1f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const glm::vec2 & | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
GPU-accelerated multi-step height generation with procedural noise.
Builds the same multi-step profile as the CPU version but injects a Voronoi-FBM noise field to modulate the step positions. Noise can be inflated or deflated and is projected onto the step axis before being passed to the CPU multisteps() implementation.
- Parameters
-
shape Output array resolution. angle Rotation angle in degrees. seed Noise seed. kw Base wave numbers for noise. noise_amp Amplitude of injected noise. noise_rugosity Roughness of the FBM noise. noise_inflate Whether to invert noise direction. r Geometric ratio between steps. nsteps Number of steps. elevation_exponent Exponent shaping step heights. shape_gain Gain used to reshape intra-step transitions. scale Scale of the step axis. outer_slope Slope outside the [0,1] axis interval. p_ctrl_param Optional control parameter array. center Center of the step axis. bbox Bounding box of the domain.
- Returns
- Generated Array.
Example
Result
◆ noise()
| Array hmap::gpu::noise | ( | NoiseType | noise_type, |
| glm::ivec2 | shape, | ||
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
See hmap::noise.
◆ noise_fbm()
| Array hmap::gpu::noise_fbm | ( | NoiseType | noise_type, |
| glm::ivec2 | shape, | ||
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_stretching = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
See hmap::noise_fbm.
◆ plates()
| Array hmap::gpu::plates | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | talus, | ||
| int | direction = 0, |
||
| float | mix_ratio = 0.9f, |
||
| float | base_noise_amp = 0.05f, |
||
| float | kw_multiplier = 2.f, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | rugosity = 0.f, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generate a tectonic plate–like heightfield using Voronoi FBM and directional talus projection.
Combines Voronoi edge-distance FBM with a base noise displacement, then applies a talus projection along a given direction and blends the result with the original field.
- Parameters
-
shape Grid resolution. kw Base wavelength/frequency. seed Random seed. talus Talus strength for directional projection. direction Projection direction. mix_ratio Blend factor between raw Voronoi and projected plates. base_noise_amp Amplitude of the displacement noise. kw_multiplier Frequency multiplier for base noise. rugosity Noise roughness. bbox Bounding box for noise evaluation.
- Returns
- Generated plate heightfield.
Example
Result
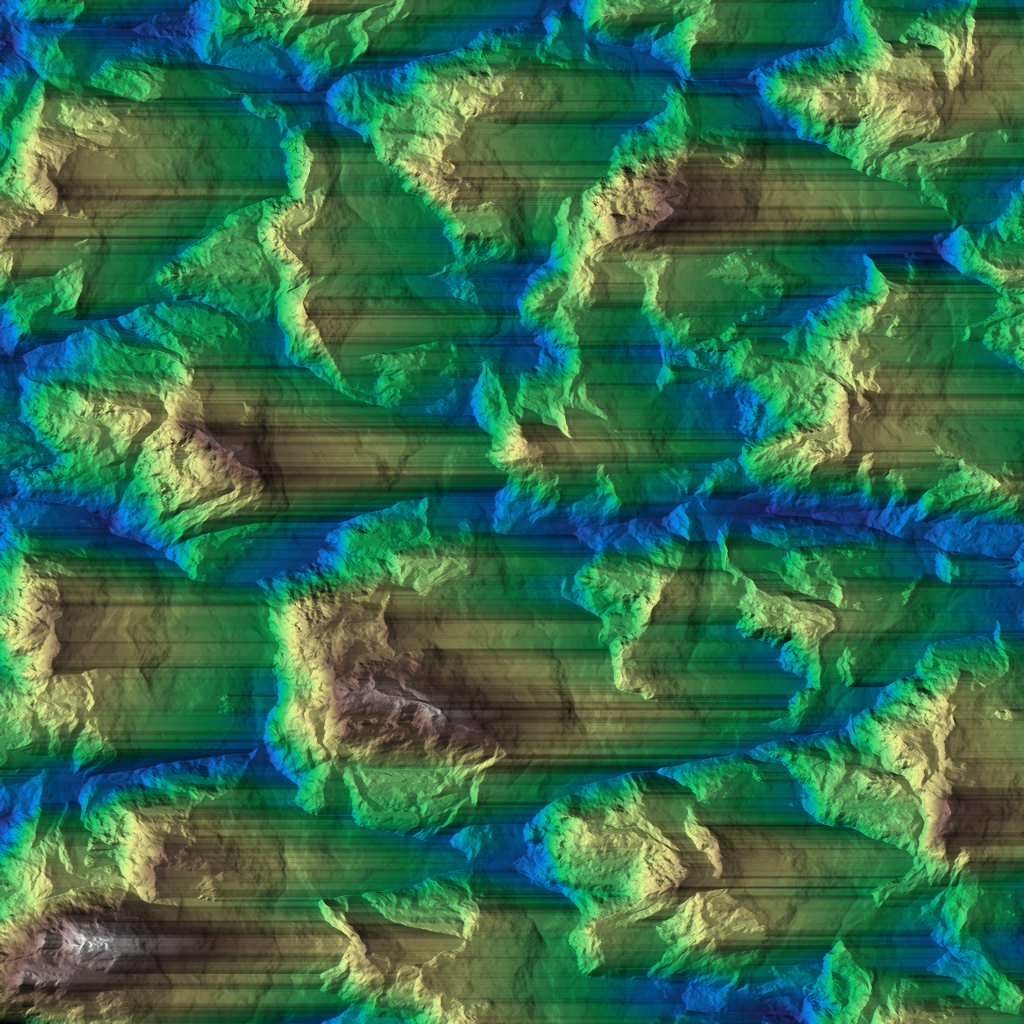
◆ polygon_field()
| Array hmap::gpu::polygon_field | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | rmin = 0.05f, |
||
| float | rmax = 0.8f, |
||
| float | clamping_dist = 0.1f, |
||
| float | clamping_k = 0.1f, |
||
| int | n_vertices_min = 3, |
||
| int | n_vertices_max = 16, |
||
| float | density = 0.5f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | jitter = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| float | shift = 0.1f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_distance = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_density_multiplier = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_size_multiplier = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a scalar field representing the signed distance to randomly generated polygons.
This function procedurally generates a field where each pixel stores the signed distance to the nearest polygon, using a smooth signed distance function (SDF) with optional clamping. The polygons are generated randomly within the specified bounding box, with configurable vertex counts, sizes, jitter, and density. Optionally, displacement noise fields can be applied to polygon positions.
- Parameters
-
shape Resolution of the output field (width, height). kw Scaling factor for field coordinates (world units per pixel). seed Random seed for polygon generation. rmin Minimum polygon radius (relative to bbox size). rmax Maximum polygon radius (relative to bbox size). clamping_dist Distance threshold for clamping the SDF value (used to soften edges). clamping_k Smoothness parameter for clamping. n_vertices_min Minimum number of vertices per polygon. n_vertices_max Maximum number of vertices per polygon. density Fraction of pixels covered by polygons (approximate). jitter Random displacement factor applied to polygon vertices. shift Random position shift applied to polygon center. p_noise_x Optional displacement noise field in the X direction (nullptr to disable). p_noise_y Optional displacement noise field in the Y direction (nullptr to disable). bbox Bounding box in normalized coordinates {xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax}.
- Returns
- Array 2D array containing the signed distance field.
- Note
- Polygons are randomly generated per call and are not guaranteed to be convex.
- The sign of the SDF is negative inside polygons and positive outside.
Example
Result

◆ polygon_field_fbm()
| Array hmap::gpu::polygon_field_fbm | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | rmin = 0.05f, |
||
| float | rmax = 0.8f, |
||
| float | clamping_dist = 0.1f, |
||
| float | clamping_k = 0.1f, |
||
| int | n_vertices_min = 3, |
||
| int | n_vertices_max = 16, |
||
| float | density = 0.1f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | jitter = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| float | shift = 0.1f, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_distance = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_density_multiplier = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_size_multiplier = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a scalar field representing the signed distance to randomly generated polygons combined with fractal Brownian motion (fBm) noise modulation.
Similar to polygon_field(), but the generated SDF is modulated by an fBm noise function to create more natural, irregular shapes. The fBm parameters allow control over the noise persistence, lacunarity, and number of octaves.
- Parameters
-
shape Resolution of the output field (width, height). kw Scaling factor for field coordinates (world units per pixel). seed Random seed for polygon generation and fBm noise. rmin Minimum polygon radius (relative to bbox size). rmax Maximum polygon radius (relative to bbox size). clamping_dist Distance threshold for clamping the SDF value (used to soften edges). clamping_k Smoothness parameter for clamping. n_vertices_min Minimum number of vertices per polygon. n_vertices_max Maximum number of vertices per polygon. density Fraction of pixels covered by polygons (approximate). jitter Random displacement factor applied to polygon vertices. shift Random position shift applied to polygon center. octaves Number of fBm octaves. persistence Amplitude decay per octave in fBm. lacunarity Frequency multiplier per octave in fBm. p_noise_x Optional displacement noise field in the X direction (nullptr to disable). p_noise_y Optional displacement noise field in the Y direction (nullptr to disable). bbox Bounding box in normalized coordinates {xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax}.
- Returns
- Array 2D array containing the signed distance field modulated by fBm.
- Note
- The sign of the SDF is negative inside polygons and positive outside.
Example
Result

◆ shattered_peak()
| Array hmap::gpu::shattered_peak | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | scale = 1.f, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | peak_kw = 4.f, |
||
| float | rugosity = 0.f, |
||
| float | angle = 30.f, |
||
| float | gamma = 1.f, |
||
| bool | add_deposition = true, |
||
| float | bulk_amp = 0.3f, |
||
| float | base_noise_amp = 0.1f, |
||
| float | k_smoothing = 0.f, |
||
| glm::vec2 | center = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a synthetic "shattered peak" terrain heightmap.
This function procedurally creates a 2D elevation field resembling a sharp, fractured mountain peak. It combines a Gaussian pulse envelope, fractal noise displacements, and Voronoi-based primitives with edge-distance shaping. The result is a rugged peak structure with broken ridges and steep slopes.
- Parameters
-
shape Output array shape (resolution in x and y). seed Random seed used for noise and Voronoi generation. scale Global scaling factor controlling the overall peak size. peak_kw Base frequency of the peak features (scaled internally by scale).rugosity Controls roughness of the fractal noise (higher = more irregular). angle Orientation angle (degrees) for directional displacements. gamma Gamma correction factor applied to the final heightmap. add_deposition If true, applies a smoothing fill step simulating sediment deposition. bulk_amp Amplitude of bulk uplift applied to the peak (internally overridden to 0.5f for normalization). base_noise_amp Amplitude of the base displacement noise. k_smoothing Voronoi smoothing parameter (controls ridge sharpness). center Center of the peak in normalized coordinates. p_noise_x Optional pointer to external displacement noise field (X-axis). p_noise_y Optional pointer to external displacement noise field (Y-axis). bbox Bounding box of the generation domain in normalized coordinates.
- Returns
- Array containing the generated shattered peak heightmap.
Example
Result
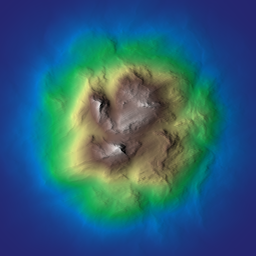
◆ vorolines()
| Array hmap::gpu::vorolines | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | density, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | k_smoothing = 0.f, |
||
| float | exp_sigma = 0.f, |
||
| float | alpha = 0.f, |
||
| float | alpha_span = M_PI, |
||
| VoronoiReturnType | return_type = VoronoiReturnType::F1_SQUARED, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox_points = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a Voronoi-based pattern where cells are defined by proximity to random lines.
This function generates an OpenCL-accelerated Voronoi-like pattern based on the distance from each pixel to a set of randomly oriented lines. Each line is defined by a random point and a direction sampled from a uniform distribution around a given angle.
- Parameters
-
shape The resolution of the resulting 2D array (width, height). density Number of base points per unit area used to define lines. seed Seed for the random number generator used to generate base points and directions. k_smoothing Kernel smoothing factor; controls how sharp or soft the distance fields are. exp_sigma Exponential smoothing parameter applied to the computed distance field. alpha Base angle (in radians) used to orient the generated lines. alpha_span Maximum angular deviation from alpha; controls line orientation variability.return_type Type of Voronoi output to return (e.g., F1, F2, edge distance, smoothed field, etc.). p_noise_x Optional pointer to an input noise field applied to the X coordinates (can be nullptr). p_noise_y Optional pointer to an input noise field applied to the Y coordinates (can be nullptr). bbox Bounding box in normalized coordinates (min_x, max_x, min_y, max_y) of the final array. bbox_points Bounding box within which random base points are sampled.
- Returns
- A 2D array (of type Array) containing the computed distance field based on line proximity.
- Note
- Each line is defined from a point (x, y) to a direction offset using angle
theta = alpha + rand * alpha_span. - The OpenCL kernel "vorolines" must be defined and compiled beforehand.
Example
Result
◆ vorolines_fbm()
| Array hmap::gpu::vorolines_fbm | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | density, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | k_smoothing = 0.f, |
||
| float | exp_sigma = 0.f, |
||
| float | alpha = 0.f, |
||
| float | alpha_span = M_PI, |
||
| VoronoiReturnType | return_type = VoronoiReturnType::F1_SQUARED, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox_points = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a Voronoi-based pattern using distances to lines defined by random points and angles, with additional fractal Brownian motion (fBm) noise modulation.
This function extends the standard vorolines generation by introducing fBm-based warping of the coordinate space, resulting in more organic and fractal-like structures. It creates a Voronoi distance field based on proximity to oriented line segments and distorts the result using multi-octave procedural noise.
- Parameters
-
shape Output resolution of the 2D array (width, height). density Number of base points per unit area used to define lines. seed Seed value for the random number generator. k_smoothing Kernel smoothing coefficient to soften distance values (e.g., for blending). exp_sigma Sigma value for optional exponential smoothing on the final field. alpha Base orientation angle (in radians) of lines generated from random points. alpha_span Maximum angle deviation from alpha, determining directional randomness of lines.return_type Type of output to return (e.g., F1, F2, distance to edge, smoothed version). octaves Number of noise octaves used in the fBm modulation. weight Weight of each octave's contribution to the total noise. persistence Amplitude decay factor for each successive octave (commonly 0.5–0.8). lacunarity Frequency multiplier for each successive octave (commonly 2.0). p_noise_x Optional pointer to an external noise field applied to X coordinates (can be nullptr). p_noise_y Optional pointer to an external noise field applied to Y coordinates (can be nullptr). bbox Bounding box for the final image domain (min_x, max_x, min_y, max_y). bbox_points Bounding box from which the initial set of points are sampled.
- Returns
- A 2D
Arrayrepresenting the Voronoi-fBm field, distorted by noise and influenced by distance to random lines.
- Note
- This version uses internally computed fBm noise unless external fields (
p_noise_x,p_noise_y) are provided. - This function requires an OpenCL kernel named "vorolines_fbm" to be compiled and accessible.
Example
Result


◆ voronoi()
| Array hmap::gpu::voronoi | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| glm::vec2 | jitter = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| float | k_smoothing = 0.f, |
||
| float | exp_sigma = 0.f, |
||
| VoronoiReturnType | return_type = VoronoiReturnType::F1_SQUARED, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a Voronoi diagram in a 2D array with configurable properties.
- Parameters
-
shape The dimensions of the output array as a 2D vector of integers. kw The frequency scale factors for the Voronoi cells, given as a 2D vector of floats. seed A seed value for random number generation, ensuring reproducibility. jitter (Optional) The amount of random variation in the positions of Voronoi cell sites, given as a 2D vector of floats. Defaults to {0.5f, 0.5f}. return_type (Optional) The type of value to compute for the Voronoi diagram. Defaults to VoronoiReturnType::F1_SQUARED.p_ctrl_param (Optional) A pointer to an Arrayused to control the Voronoi computation. Used here as a multiplier for the jitter. If nullptr, no control is applied.p_noise_x (Optional) A pointer to an Arrayproviding additional noise in the x-direction for cell positions. If nullptr, no x-noise is applied.p_noise_y (Optional) A pointer to an Arrayproviding additional noise in the y-direction for cell positions. If nullptr, no y-noise is applied.bbox (Optional) The bounding box for the Voronoi computation, given as a 4D vector of floats representing {min_x, max_x, min_y, max_y}. Defaults to {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
- Returns
- A 2D array representing the generated Voronoi diagram.
- Note
- Only available if OpenCL is enabled.
Example
Result

◆ voronoi_fbm()
| Array hmap::gpu::voronoi_fbm | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| glm::vec2 | jitter = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| float | k_smoothing = 0.f, |
||
| float | exp_sigma = 0.f, |
||
| VoronoiReturnType | return_type = VoronoiReturnType::F1_SQUARED, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a Voronoi diagram in a 2D array with configurable properties.
- Parameters
-
shape The dimensions of the output array as a 2D vector of integers. kw The frequency scale factors for the base Voronoi cells, given as a 2D vector of floats. seed A seed value for random number generation, ensuring reproducibility. jitter (Optional) The amount of random variation in the positions of Voronoi cell sites, given as a 2D vector of floats. Defaults to {0.5f, 0.5f}. return_type (Optional) The type of value to compute for the Voronoi diagram. Defaults to VoronoiReturnType::F1_SQUARED.octaves (Optional) The number of layers (octaves) in the fractal Brownian motion. Defaults to 8. weight (Optional) The initial weight of the base layer in the FBM computation. Defaults to 0.7f. persistence (Optional) The persistence factor that controls the amplitude reduction between octaves. Defaults to 0.5f. lacunarity (Optional) The lacunarity factor that controls the frequency increase between octaves. Defaults to 2.f. p_ctrl_param (Optional) A pointer to an Arrayused to control the Voronoi computation. If nullptr, no control is applied.p_noise_x (Optional) A pointer to an Arrayproviding additional noise in the x-direction for cell positions. If nullptr, no x-noise is applied.p_noise_y (Optional) A pointer to an Arrayproviding additional noise in the y-direction for cell positions. If nullptr, no y-noise is applied.bbox (Optional) The bounding box for the Voronoi computation, given as a 4D vector of floats representing {min_x, max_x, min_y, max_y}. Defaults to {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.
- Returns
- A 2D array representing the generated Voronoi diagram.
- Note
- Only available if OpenCL is enabled.
Example
Result

◆ voronoi_edge_distance()
| Array hmap::gpu::voronoi_edge_distance | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| glm::vec2 | jitter = {0.5f, 0.5f}, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Computes the Voronoi edge distance.
- Parameters
-
shape The shape of the grid as a 2D vector (width, height). kw The weights for the Voronoi kernel as a 2D vector. seed The random seed used for generating Voronoi points. jitter Optional parameter for controlling jitter in Voronoi point placement (default is {0.5f, 0.5f}). p_ctrl_param Optional pointer to an Array specifying control parameters for Voronoi grid jitter (default is nullptr). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. bbox The bounding box for the Voronoi diagram as {x_min, x_max, y_min, y_max} (default is {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}).
- Note
- Taken from https://www.shadertoy.com/view/llG3zy
- Only available if OpenCL is enabled.
- The resulting Array has the same dimensions as the input shape.
◆ voronoise()
| Array hmap::gpu::voronoise | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| float | u_param, | ||
| float | v_param, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a 2D Voronoi noise array.
This function computes a Voronoi noise pattern based on the input parameters and returns it as a 2D array. The noise is calculated in the OpenCL kernel noise_voronoise, which uses a combination of hashing and smoothstep functions to generate a weighted Voronoi noise field.
- Note
- Taken from https://www.shadertoy.com/view/Xd23Dh
- Only available if OpenCL is enabled.
- Parameters
-
shape The dimensions of the 2D output array as a vector (width and height). kw Wave numbers for scaling the noise pattern, represented as a 2D vector. u_param A control parameter for the noise, adjusting the contribution of random offsets. v_param A control parameter for the noise, affecting the smoothness of the pattern. p_ctrl_param Optional pointer to an Array specifying control parameters for Voronoi grid jitter (default is nullptr). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. seed A seed value for random number generation, ensuring reproducibility.
- Returns
- An
Arrayobject containing the generated 2D Voronoi noise values.
Example
Result
◆ voronoise_fbm()
| Array hmap::gpu::voronoise_fbm | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| float | u_param, | ||
| float | v_param, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return an array filled with coherence Voronoise.
- Parameters
-
shape Array shape. kw Noise wavenumbers {kx, ky} for each directions. seed Random seed number. octaves Number of octaves. weigth Octave weighting. persistence Octave persistence. lacunarity Defines the wavenumber ratio between each octaves. p_ctrl_param Reference to the control parameter array (acts as a multiplier for the weight parameter). p_noise_x,p_noise_y Reference to the input noise arrays. bbox Domain bounding box.
- Returns
- Array Fractal noise.
- Note
- Taken from https://www.shadertoy.com/view/clGyWm
- Only available if OpenCL is enabled.
Example
Result

◆ vororand() [1/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::vororand | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| float | density, | ||
| float | variability, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | k_smoothing = 0.f, |
||
| float | exp_sigma = 0.f, |
||
| VoronoiReturnType | return_type = VoronoiReturnType::F1_SQUARED, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox_points = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates a 2D Voronoi-based scalar field using OpenCL.
This function computes a Voronoi diagram or derived metric (such as F1, F2, or edge distances) on a grid of given shape. A set of random points is generated within an extended bounding box, based on the desired density and variability, to reduce edge artifacts. Optionally, per-pixel displacement can be applied through noise fields.
The result is stored in an Array object representing a 2D scalar field.
- Parameters
-
shape Dimensions of the output array (width x height). density Number of random points per unit area for Voronoi diagram. variability Amount of randomness added to the point generation bounding box. seed Seed for random number generation used in point sampling. k_smoothing Smoothing factor used in soft minimum/maximum Voronoi distance computations. exp_sigma Standard deviation used in exponential falloff for edge distance computation. return_type Type of Voronoi computation to perform (e.g., F1, F2, F2-F1, edge distance). p_noise_x Optional pointer to a noise field applied to X coordinates of grid points. p_noise_y Optional pointer to a noise field applied to Y coordinates of grid points. bbox Bounding box of the domain in which the field is computed: {xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax}. bbox_points Bounding box for point generation, usually larger than bboxto avoid edge effects.
- Returns
- An
Arrayobject containing the computed scalar field.
- Note
- The kernel
"vororand"must be compiled and available in the OpenCL context. - If
p_noise_xorp_noise_yare provided, they must match the shape of the output array. - The generated point cloud will be larger than
bboxto reduce border artifacts.
- The kernel
Example
Result
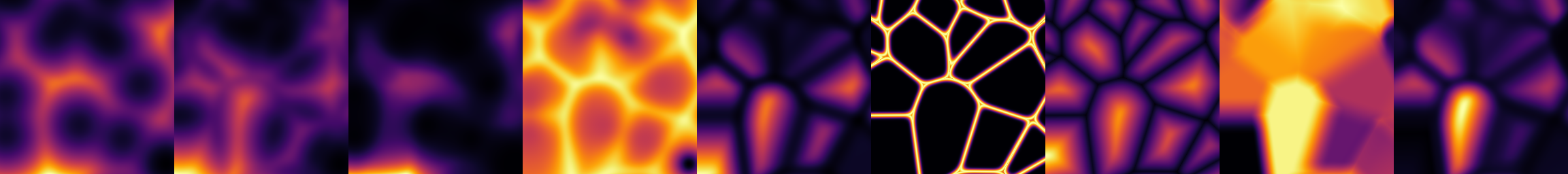
◆ vororand() [2/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::vororand | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| const std::vector< float > & | xp, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | yp, | ||
| float | k_smoothing = 0.f, |
||
| float | exp_sigma = 0.f, |
||
| VoronoiReturnType | return_type = VoronoiReturnType::F1_SQUARED, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
◆ wavelet_noise()
| Array hmap::gpu::wavelet_noise | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec2 | kw, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | kw_multiplier = 2.f, |
||
| float | vorticity = 0.f, |
||
| float | density = 1.f, |
||
| int | octaves = 8, |
||
| float | weight = 0.7f, |
||
| float | persistence = 0.5f, |
||
| float | lacunarity = 2.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_ctrl_param = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Generates 2D wavelet noise using an OpenCL kernel.
This function creates a 2D noise field of the given shape using multi-octave wavelet turbulence. The noise is computed on the GPU via the "wavelet_noise" OpenCL kernel. Various parameters control the frequency evolution, amplitude decay, vorticity injection, and optional modulation using additional input arrays.
- Parameters
-
shape Resolution of the output noise array (width, height). kw Base wave number (frequency) in each axis. Controls the initial spatial frequency of the wavelet field. seed Integer seed used by the random hashing functions inside the kernel. kw_multiplier Multiplier applied to the wave number per octave (similar to gain). Higher values increase frequency growth across octaves. vorticity Amount of rotational distortion injected into the noise. When > 0, the kernel applies additional angular perturbations to produce turbulent flow-like patterns. density Global scaling factor controlling the overall contrast or amplitude of the generated noise. octaves Number of wavelet noise layers combined. Higher octaves yield more detail but increase computational cost. weight Weight applied to the base octave, used as a global intensity multiplier before persistence attenuation is applied. persistence Amplitude decay factor per octave. Values in (0,1) produce the classic fractal noise falloff; higher values retain more high-frequency detail. lacunarity Frequency multiplier per octave. Controls how rapidly frequency increases at each octave, with typical values in the range [1.5, 3.0]. p_ctrl_param Optional pointer to a control-parameter array. When provided, values inside this array modulate the generated noise spatially. Pass nullptr to disable this feature. p_noise_x Optional pointer to an auxiliary noise array used to perturb sampling positions horizontally. Pass nullptr to disable. p_noise_y Optional pointer to an auxiliary noise array used to perturb sampling positions vertically. Pass nullptr to disable. bbox Bounding-box mapping (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax). Converts pixel-space indices into world-space coordinates for spatially consistent noise.
- Returns
- Array A 2D floating-point array containing the generated wavelet noise.
Example
Result
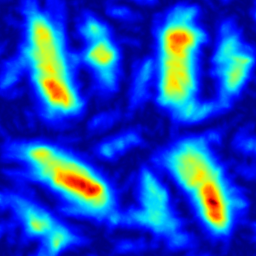
◆ maximum_smooth()
See hmap::maximum_smooth.
◆ minimum_smooth()
See hmap::minimum_smooth.
◆ sdf_2d_polyline()
◆ sdf_2d_polyline_bezier()
◆ select_cavities()
◆ select_soil_flow()
| Array hmap::gpu::select_soil_flow | ( | const Array & | z, |
| int | ir_gradient = 1, |
||
| float | gradient_weight = 1.f, |
||
| float | gradient_scaling_factor = 0.f, |
||
| float | flow_weight = 0.05f, |
||
| float | talus_ref = 0.f, |
||
| float | clipping_ratio = 50.f, |
||
| float | flow_gamma = 1.f, |
||
| float | k_smooth = 0.01f |
||
| ) |
Computes a soil–flow selection map based on terrain gradient, river mask, and smoothing parameters.
- Parameters
-
z Input heightmap. ir_gradient Radius used for the morphological gradient. gradient_weight Weight applied to the gradient magnitude. gradient_scaling_factor Scaling factor applied to the gradient; defaults to z.shape.x if <= 0. talus_ref Reference talus value for river extraction; defaults to 1.f / z.shape.x if <= 0. clipping_ratio Clipping ratio used in the river selection step. flow_gamma Gamma correction exponent applied to the river mask; 1.0 disables correction. k_smooth Smoothing parameter for the maximum blending.
- Returns
- A 2D Array representing the final soil-flow selection mask.
Example
Result
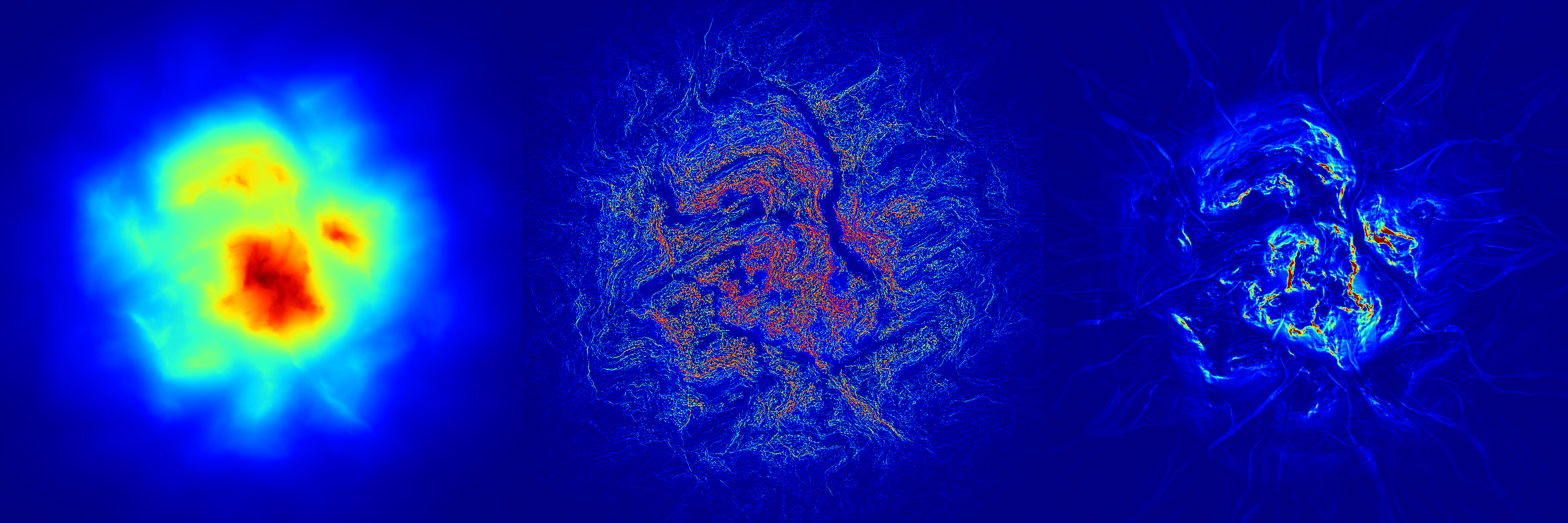
◆ select_soil_rocks()
| Array hmap::gpu::select_soil_rocks | ( | const Array & | z, |
| int | ir_max = 64, |
||
| int | ir_min = 0, |
||
| int | steps = 4, |
||
| float | smaller_scales_weight = 1.f, |
||
| ClampMode | curvature_clamp_mode = ClampMode::POSITIVE_ONLY, |
||
| float | curvature_clamping = 1.f |
||
| ) |
Computes a multi-scale soil/rock selector using curvature analysis.
Applies progressively increasing smoothing radii in logarithmic steps (handling ir_min = 0), computes the mean curvature at each scale, clamps it, and accumulates the maximum response across all scales.
- Parameters
-
z Input heightmap or scalar field. ir_max Maximum smoothing radius (log-scale upper bound). ir_min Minimum smoothing radius (0 allowed; replaced by 1 for log scale). steps Number of logarithmic scales to evaluate. smaller_scales_weight Weight factor applied when descending scales. curvature_clamp_mode Mode used to clamp curvature values. curvature_clamping Curvature clamp threshold.
- Returns
- An Array representing soil/rock selection values across scales.
Example
Result
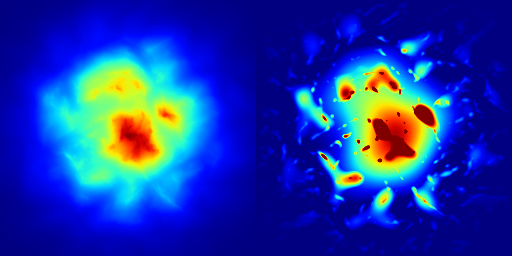
◆ select_soil_weathered() [1/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::select_soil_weathered | ( | const Array & | z, |
| int | ir_curvature = 0, |
||
| int | ir_gradient = 4, |
||
| ClampMode | curvature_clamp_mode = ClampMode::POSITIVE_ONLY, |
||
| float | curvature_clamping = 10.f, |
||
| float | curvature_weight = 1.f, |
||
| float | gradient_weight = 1.f, |
||
| float | gradient_scaling_factor = 0.f |
||
| ) |
Computes a soil weathering selection map based on curvature and gradient analysis.
This function generates a combined array representing the degree of soil weathering using two main components:
- Curvature contribution: derived from smoothed height variations.
- Gradient contribution: derived from local slope magnitudes.
- Parameters
-
z Input heightmap or scalar field. ir_curvature Radius (in pixels or samples) for curvature smoothing. If zero, curvature smoothing is skipped. ir_gradient Radius (in pixels or samples) for gradient computation. curvature_clamp_mode Clamping mode applied to curvature values (see ClampMode). curvature_clamping Maximum absolute value used for curvature clamping. curvature_weight Weight applied to the curvature component in the final mix. gradient_weight Weight applied to the gradient component in the final mix. gradient_scaling_factor Empirical scaling factor for both curvature and gradient terms. If non-positive, defaults to z.shape.x.
Example
Result

◆ select_soil_weathered() [2/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::select_soil_weathered | ( | const Array & | z, |
| const Array & | gradient_norm, | ||
| int | ir_curvature, | ||
| ClampMode | curvature_clamp_mode, | ||
| float | curvature_clamping, | ||
| float | curvature_weight, | ||
| float | gradient_weight, | ||
| float | gradient_scaling_factor | ||
| ) |
◆ select_valley()
See hmap::select_valley.
◆ advection_particle() [1/3]
| Array hmap::gpu::advection_particle | ( | const Array & | z, |
| const Array & | advected_field, | ||
| int | iterations, | ||
| int | nparticles, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| bool | reverse = false, |
||
| bool | post_filter = true, |
||
| float | post_filter_sigma = 0.125f, |
||
| float | advection_length = 0.1f, |
||
| float | value_persistence = 0.99f, |
||
| float | inertia = 0.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_advection_mask = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_mask = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Performs particle-based advection on a scalar field.
This function advects particles through a velocity field (or gradient field) derived from the input array z. Each particle carries a value from the advected_field and evolves over a number of iterations according to advection parameters such as inertia and persistence. Optionally, advection and masking fields can be applied to control which areas are affected.
- Parameters
-
z Input scalar field defining the base flow or gradient field used for particle advection. advected_field The scalar field whose values are transported along particle trajectories. iterations Number of advection iterations to perform per particle. nparticles Number of particles to simulate during advection. seed Random seed used for initializing particle positions and stochastic behavior. reverse If true, reverses the advection direction (useful for backtracing or inverse advection). post_filter If true, applies a smoothing or filtering operation after advection to reduce artifacts. advection_length Maximum advection step length per iteration (controls particle displacement scale). value_persistence Controls how much of a particle’s advected value is preserved between iterations (1.0 means full preservation, lower values introduce decay). inertia Controls how much a particle’s previous velocity affects its next step (simulates momentum). p_advection_mask Optional mask array controlling where advection occurs (nullptr to disable). p_mask Optional general mask restricting where output values are written (nullptr to disable).
- Returns
- An Array representing the advected version of
advected_fieldafter applying particle advection.
Example
Result
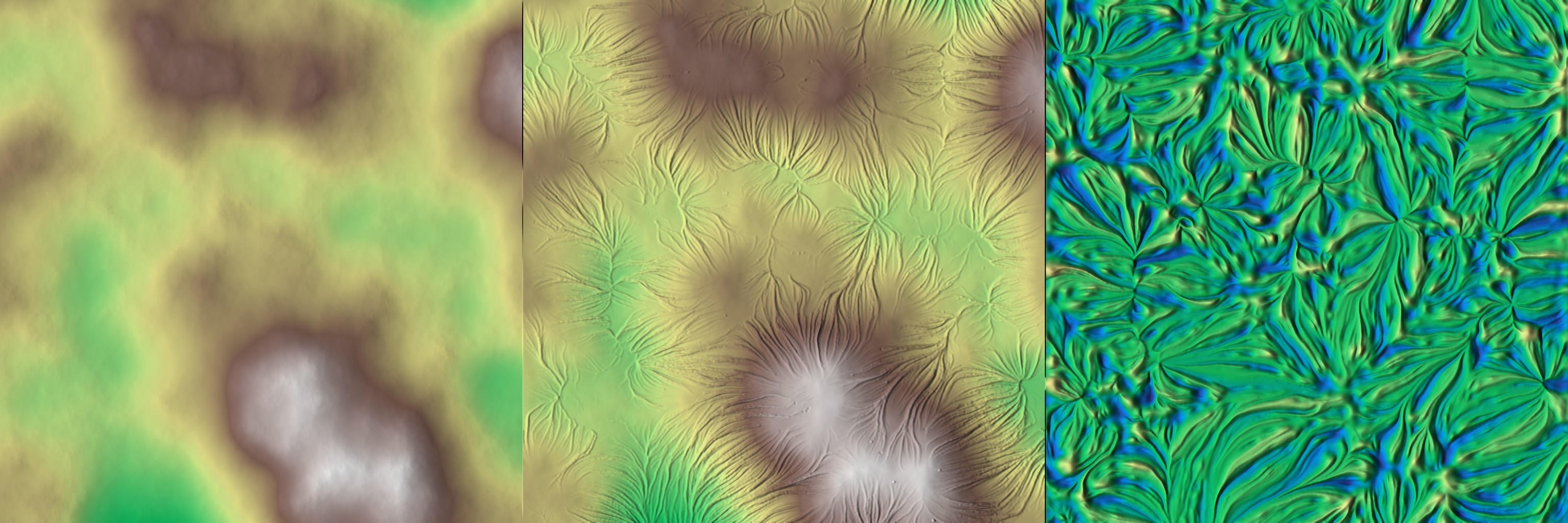

◆ advection_particle() [2/3]
| Array hmap::gpu::advection_particle | ( | const Array & | z, |
| const Array & | advected_field, | ||
| int | nparticles, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| bool | reverse = false, |
||
| bool | post_filter = true, |
||
| float | post_filter_sigma = 0.125f, |
||
| float | advection_length = 0.1f, |
||
| float | value_persistence = 0.99f, |
||
| float | inertia = 0.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_advection_mask = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_mask = nullptr |
||
| ) |
◆ advection_particle() [3/3]
| Array hmap::gpu::advection_particle | ( | const Array & | dx, |
| const Array & | dy, | ||
| const Array & | advected_field, | ||
| int | nparticles, | ||
| uint | seed, | ||
| bool | reverse = false, |
||
| bool | post_filter = true, |
||
| float | post_filter_sigma = 0.125f, |
||
| float | advection_length = 0.1f, |
||
| float | value_persistence = 0.99f, |
||
| float | inertia = 0.f, |
||
| const Array * | p_advection_mask = nullptr, |
||
| const Array * | p_mask = nullptr |
||
| ) |
◆ advection_warp() [1/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::advection_warp | ( | const Array & | z, |
| const Array & | advected_field, | ||
| float | advection_length = 0.1f, |
||
| float | value_persistence = 0.9f, |
||
| const Array * | p_mask = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Performs 2D field advection based on the gradient of a heightmap using a warp-based technic (simplified approach).
This function computes the X and Y gradients of the given heightmap z and uses them as flow directions to advect the input advected_field. The result is a new field where values have been displaced according to the gradient direction and the specified advection parameters.
- Parameters
-
z The heightmap (or scalar field) used to compute advection directions. advected_field The field to be advected along the gradient of z.advection_length The step length used for advection; larger values produce stronger displacement. value_persistence The persistence factor applied to the advected values, typically in the range [0, 1]; controls how much of the original value is preserved. p_mask Optional pointer to a mask array; if provided, advection is applied only where the mask is nonzero.
- Returns
- A new Array representing the advected version of
advected_field.
Example
Result
◆ advection_warp() [2/2]
| Array hmap::gpu::advection_warp | ( | const Array & | z, |
| const Array & | advected_field, | ||
| const Array & | dx, | ||
| const Array & | dy, | ||
| float | advection_length = 0.1f, |
||
| float | value_persistence = 0.9f, |
||
| const Array * | p_mask = nullptr |
||
| ) |
◆ rotate()
| void hmap::gpu::rotate | ( | Array & | array, |
| float | angle, | ||
| bool | zoom_in = true |
||
| ) |
See hmap::rotate.
◆ warp()
See hmap::warp.
◆ helper_transform_bbox()
| glm::vec4 hmap::gpu::helper_transform_bbox | ( | const glm::vec4 & | bbox_source, |
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox_target | ||
| ) |
◆ helper_radial_profile()
|
inline |
◆ helper_apply_leeward()
|
inline |
◆ helper_apply_uplift()
|
inline |