Represents a collection of unordered points in 2D space. More...
#include <cloud.hpp>
Public Member Functions | |
| Cloud () | |
| Default constructor for the Cloud class. | |
| virtual | ~Cloud ()=default |
| Cloud (int npoints, uint seed, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) | |
| Constructs a new Cloud object with random positions and values. | |
| Cloud (const std::vector< Point > &points) | |
| Constructs a new Cloud object based on a list of existing points. | |
| Cloud (const std::vector< float > &x, const std::vector< float > &y, float default_value=0.f) | |
Constructs a new Cloud object from lists of x and y coordinates. | |
| Cloud (const std::vector< float > &x, const std::vector< float > &y, const std::vector< float > &v) | |
Constructs a new Cloud object from lists of x and y coordinates with assigned values. | |
| void | add_point (const Point &p) |
| Add a new point to the cloud. | |
| void | clear () |
| Clear all data from the cloud. | |
| bool | from_csv (const std::string &fname) |
| Loads point data from a CSV file into the Cloud object. | |
| glm::vec4 | get_bbox () const |
| Get the bounding box of the cloud. | |
| Point | get_center () const |
| Calculates the centroid of a set of points. | |
| std::vector< int > | get_convex_hull_point_indices () const |
| Computes the indices of the points that form the convex hull of a set of points. | |
| size_t | get_npoints () const |
| Get the number of points in the cloud. | |
| std::vector< float > | get_values () const |
| Get the values assigned to the points in the cloud. | |
| float | get_values_max () const |
| Get the maximum value among the points in the cloud. | |
| float | get_values_min () const |
| Get the minimum value among the points in the cloud. | |
| virtual std::vector< float > | get_x () const |
Get the x coordinates of the points in the cloud. | |
| virtual std::vector< float > | get_xy () const |
Get the concatenated x and y coordinates of the points in the cloud. | |
| virtual std::vector< float > | get_y () const |
Get the y coordinates of the points in the cloud. | |
| std::vector< float > | interpolate_values_from_array (const Array &array, glm::vec4 bbox) |
Interpolate values from an array at the points' (x, y) locations. | |
| void | print () |
| Print information about the cloud's points. | |
| void | randomize (uint seed, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Randomize the positions and values of the cloud points. | |
| void | rejection_filter_density (const Array &density_mask, uint seed, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Filter a point cloud using rejection sampling based on a density mask. | |
| void | remap_values (float vmin, float vmax) |
| Remap the values of the cloud points to a target range. | |
| void | remove_point (int point_idx) |
| Remove a point from the cloud. | |
| void | set_points (const std::vector< float > &x, const std::vector< float > &y) |
| Set points of the using x, y coordinates. | |
| void | set_values (const std::vector< float > &new_values) |
| Set new values for the cloud points. | |
| void | set_values (float new_value) |
| Set a single value for all cloud points. | |
| void | set_values_from_array (const Array &array, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Set the values of the cloud points using values from an underlying array. | |
| void | set_values_from_border_distance (const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Sets point values based on their distance to the bounding box border. | |
| void | set_values_from_chull_distance () |
| Set the values of the cloud points based on the distance to the convex hull of the cloud. | |
| void | set_values_from_min_distance () |
| Sets point values based on the distance to their nearest neighbor. | |
| void | shuffle (float dx, float dy, uint seed, float dv=0.f) |
| Randomly perturbs the positions and values of all points in the cloud. | |
| void | to_array (Array &array, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) const |
| Project the cloud points onto an array. | |
| Array | to_array_sdf (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec4 bbox, Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox_array={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) const |
| Generate an array filled with the signed distance function (SDF) to the cloud points. | |
| void | to_array_interp (Array &array, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, InterpolationMethod2D interpolation_method=InterpolationMethod2D::DELAUNAY, Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox_array={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) const |
| Interpolate the values of an array using the cloud points. | |
| void | to_csv (const std::string &fname) const |
| Export the cloud data to a CSV file. | |
| Graph | to_graph_delaunay () |
| Convert the cloud to a graph using Delaunay triangulation. | |
| void | to_png (const std::string &fname, int cmap, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, int depth=CV_8U, glm::ivec2 shape={512, 512}) |
| Saves the current data as a PNG image file. | |
Public Attributes | |
| std::vector< Point > | points = {} |
| Points of the cloud. | |
Detailed Description
Represents a collection of unordered points in 2D space.
The Cloud class provides functionality to manage and manipulate an unordered set of points in a 2D space. It supports various operations such as adding points, calculating the centroid, merging with other point clouds, and more. This class is useful for applications involving point cloud processing, geometric computations, and spatial analysis.
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ Cloud() [1/5]
|
inline |
Default constructor for the Cloud class.
Initializes an empty cloud with no points.
◆ ~Cloud()
|
virtualdefault |
◆ Cloud() [2/5]
Constructs a new Cloud object with random positions and values.
This constructor generates a cloud with a specified number of points, where the positions and values of the points are randomly generated within a given bounding box.
- Parameters
-
npoints Number of points to generate. seed Random seed used to generate the points. Using the same seed will produce the same set of points. bbox Bounding box within which the points will be generated. The bounding box is defined as {xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax}.
◆ Cloud() [3/5]
|
inline |
◆ Cloud() [4/5]
| hmap::Cloud::Cloud | ( | const std::vector< float > & | x, |
| const std::vector< float > & | y, | ||
| float | default_value = 0.f |
||
| ) |
Constructs a new Cloud object from lists of x and y coordinates.
This constructor allows the creation of a cloud by providing separate lists of x and y coordinates. Each point will have an associated value, which is set to a default value.
- Parameters
-
x A vector of xcoordinates for the points.y A vector of ycoordinates for the points.default_value The default value assigned to each point. Defaults to 0 if not specified.
◆ Cloud() [5/5]
| hmap::Cloud::Cloud | ( | const std::vector< float > & | x, |
| const std::vector< float > & | y, | ||
| const std::vector< float > & | v | ||
| ) |
Constructs a new Cloud object from lists of x and y coordinates with assigned values.
This constructor allows the creation of a cloud by providing separate lists of x and y coordinates, along with a list of values associated with each point.
- Parameters
-
x A vector of xcoordinates for the points.y A vector of ycoordinates for the points.v A vector of values associated with each point.
Member Function Documentation
◆ add_point()
| void hmap::Cloud::add_point | ( | const Point & | p | ) |
Add a new point to the cloud.
This method appends a new point to the list of points in the cloud.
- Parameters
-
p The point to be added to the cloud.
◆ clear()
| void hmap::Cloud::clear | ( | ) |
Clear all data from the cloud.
This method removes all points from the cloud, leaving it empty.
◆ from_csv()
| bool hmap::Cloud::from_csv | ( | const std::string & | fname | ) |
Loads point data from a CSV file into the Cloud object.
This function reads a CSV file where each line contains either 2D (X, Y) or 3D (X, Y, Z) point data. The function automatically detects the dimensionality of the points based on the number of values per line. The loaded points are stored in the points member of the Cloud object.
- Parameters
-
fname The path to the CSV file to be read.
- Returns
- true if the file was successfully read and the points were loaded, false otherwise.
- Note
- The CSV file must be well-formed, with each line containing either 2 or 3 comma-separated values. Lines with an unexpected number of values will cause the function to return false.
- Warning
- If the file cannot be opened or contains invalid data (e.g., non-numeric values), the function will log an error and return false.
◆ get_bbox()
| glm::vec4 hmap::Cloud::get_bbox | ( | ) | const |
Get the bounding box of the cloud.
This method calculates and returns the axis-aligned bounding box of the cloud. The bounding box is represented as a glm::vec4 containing the minimum and maximum coordinates in both the x and y dimensions.
- Returns
- glm::vec4 The bounding box of the cloud in the format
[xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax].
◆ get_center()
| Point hmap::Cloud::get_center | ( | ) | const |
Calculates the centroid of a set of points.
This function computes the center (or centroid) of a collection of points by averaging their coordinates. It sums up all the point coordinates and then divides the result by the total number of points to obtain the average position. The centroid represents the geometric center of the point cloud.
◆ get_convex_hull_point_indices()
| std::vector< int > hmap::Cloud::get_convex_hull_point_indices | ( | ) | const |
Computes the indices of the points that form the convex hull of a set of points.
This function calculates the convex hull of a set of points and returns the indices of these points in the order they appear on the convex hull. The convex hull is the smallest convex polygon that encloses all the given points.
- Returns
- std::vector<int> A vector containing the indices of the points that make up the convex hull, listed in order.
Example
Result

◆ get_npoints()
| size_t hmap::Cloud::get_npoints | ( | ) | const |
Get the number of points in the cloud.
This method returns the total number of points currently stored in the cloud.
- Returns
- size_t The number of points in the cloud.
◆ get_values()
| std::vector< float > hmap::Cloud::get_values | ( | ) | const |
Get the values assigned to the points in the cloud.
This method returns a vector containing the values associated with each point in the cloud.
- Returns
- std::vector<float> A vector containing the values of all points in the cloud.
◆ get_values_max()
| float hmap::Cloud::get_values_max | ( | ) | const |
Get the maximum value among the points in the cloud.
This method returns the maximum value associated with any point in the cloud.
- Returns
- float The maximum value among the points.
◆ get_values_min()
| float hmap::Cloud::get_values_min | ( | ) | const |
Get the minimum value among the points in the cloud.
This method returns the minimum value associated with any point in the cloud.
- Returns
- float The minimum value among the points.
◆ get_x()
|
virtual |
Get the x coordinates of the points in the cloud.
This method returns a vector containing the x coordinates of all points in the cloud.
- Returns
- std::vector<float> A vector containing the
xcoordinates of the points.
Reimplemented in hmap::Path.
◆ get_xy()
|
virtual |
Get the concatenated x and y coordinates of the points in the cloud.
This method returns a vector containing the x and y coordinates of all points in the cloud, arranged in the form [x0, y0, x1, y1, ...].
- Returns
- std::vector<float> A vector containing the concatenated
xandycoordinates of the points.
Reimplemented in hmap::Path.
◆ get_y()
|
virtual |
Get the y coordinates of the points in the cloud.
This method returns a vector containing the y coordinates of all points in the cloud.
- Returns
- std::vector<float> A vector containing the
ycoordinates of the points.
Reimplemented in hmap::Path.
◆ interpolate_values_from_array()
| std::vector< float > hmap::Cloud::interpolate_values_from_array | ( | const Array & | array, |
| glm::vec4 | bbox | ||
| ) |
Interpolate values from an array at the points' (x, y) locations.
This method computes interpolated values for each point in the cloud based on its (x, y) coordinates and an underlying array, using bilinear interpolation within the specified bounding box.
- Parameters
-
array The input array from which to interpolate values. bbox The bounding box of the array.
- Returns
- std::vector<float> A vector containing the interpolated values for each point.
◆ print()
| void hmap::Cloud::print | ( | ) |
Print information about the cloud's points.
This method prints data related to the cloud's points, including their coordinates and values.
◆ randomize()
Randomize the positions and values of the cloud points.
This method randomizes the positions and values of the points in the cloud using a given random seed. The new positions are generated within the specified bounding box.
- Parameters
-
seed Random seed number for generating positions and values. bbox Bounding box within which the points will be randomized.
◆ rejection_filter_density()
| void hmap::Cloud::rejection_filter_density | ( | const Array & | density_mask, |
| uint | seed, | ||
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Filter a point cloud using rejection sampling based on a density mask.
Each point in the input cloud is retained or discarded according to a spatially varying probability derived from the provided 2D density mask. The mask is mapped to the bounding box and evaluated as a continuous function over the domain.
For a point \(p=(x,y)\), the probability of acceptance is:
\[ P(\text{keep } p) = \rho(x,y) \in [0,1] \]
where \(\rho(x,y)\) is the normalized density mask value at the point's position.
- Parameters
-
density_mask 2D array defining the spatial density field over the bounding box. Values should lie in \([0,1]\). seed Random seed used for reproducible rejection sampling. bbox Bounding box (xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)defining the spatial extent of the density mask in world coordinates.
- Note
- Points outside the bounding box are implicitly mapped to extrapolated density values.
- The method preserves the relative density pattern defined by the mask, but reduces the overall number of points according to rejection probability.
◆ remap_values()
| void hmap::Cloud::remap_values | ( | float | vmin, |
| float | vmax | ||
| ) |
Remap the values of the cloud points to a target range.
This method scales the values associated with the cloud points so that they fall within a specified range [vmin, vmax].
- Parameters
-
vmin The lower bound of the target range. vmax The upper bound of the target range.
◆ remove_point()
| void hmap::Cloud::remove_point | ( | int | point_idx | ) |
Remove a point from the cloud.
This method removes a point from the cloud based on its index.
- Parameters
-
point_idx Index of the point to be removed.
◆ set_points()
| void hmap::Cloud::set_points | ( | const std::vector< float > & | x, |
| const std::vector< float > & | y | ||
| ) |
Set points of the using x, y coordinates.
◆ set_values() [1/2]
| void hmap::Cloud::set_values | ( | const std::vector< float > & | new_values | ) |
Set new values for the cloud points.
This method assigns new values to the cloud points based on a given vector of values. The size of the input vector must match the number of points in the cloud.
- Parameters
-
new_values A vector of new values to assign to the points.
◆ set_values() [2/2]
| void hmap::Cloud::set_values | ( | float | new_value | ) |
Set a single value for all cloud points.
This method assigns the same value to all points in the cloud.
- Parameters
-
new_value The value to assign to all points.
◆ set_values_from_array()
| void hmap::Cloud::set_values_from_array | ( | const Array & | array, |
| const glm::vec4 & | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Set the values of the cloud points using values from an underlying array.
This method assigns values to the cloud points by interpolating values from an input array. The positions of the cloud points are mapped to the array using the specified bounding box.
- Parameters
-
array The input array from which to derive the values. bbox The bounding box that defines the mapping from the cloud points' coordinates to the array's coordinates.
◆ set_values_from_border_distance()
Sets point values based on their distance to the bounding box border.
For each point in the cloud, this method computes the shortest distance to the edges of the given bounding box and stores it as the point's value.
The distance is calculated in 2D space, where:
- The x and y coordinates are extracted from the cloud.
- Points are merged into a 2D coordinate list.
- The distance to the nearest boundary of the bounding box is computed.
- Parameters
-
bbox Bounding box in the format {xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax}.
◆ set_values_from_chull_distance()
| void hmap::Cloud::set_values_from_chull_distance | ( | ) |
Set the values of the cloud points based on the distance to the convex hull of the cloud.
This method assigns values to the cloud points based on their distance to the convex hull of the cloud. The convex hull must be initialized using to_graph_delaunay() before this method is called to ensure the correct indices of the convex hull points are available.
◆ set_values_from_min_distance()
| void hmap::Cloud::set_values_from_min_distance | ( | ) |
Sets point values based on the distance to their nearest neighbor.
The computation process:
- Extracts the x and y coordinates from the cloud.
- Merges them into a 2D point list.
- Calculates the minimum distance to any other point using
ps::first_neighbor_distance_squared.
◆ shuffle()
Randomly perturbs the positions and values of all points in the cloud.
This function applies a random offset to the x, y, and v components of each point in the points container. The random offsets are uniformly distributed between -1 and 1, and scaled by the provided dx, dy, and dv factors for each respective component.
- Parameters
-
dx Scale factor for the random displacement along the X-axis. dy Scale factor for the random displacement along the Y-axis. seed Seed value for the pseudo-random number generator, ensuring reproducibility. dv Scale factor for the random displacement applied to the point's value component v.
◆ to_array()
Project the cloud points onto an array.
This method projects the cloud points' values onto a given array, mapping their positions within the specified bounding box. The resulting array will be populated with the values of the points at their corresponding positions.
- Parameters
-
array The input array where the cloud points' values will be projected. bbox The bounding box that defines the mapping from the cloud points' coordinates to the array's coordinates.
◆ to_array_sdf()
| Array hmap::Cloud::to_array_sdf | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec4 | bbox, | ||
| Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox_array = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) | const |
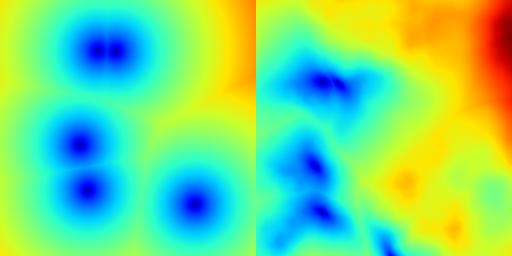
Generate an array filled with the signed distance function (SDF) to the cloud points.
This function returns an array where each value represents the signed distance to the nearest cloud point. The distance is positive outside the cloud and negative inside. The result can be domain-warped by applying optional noise arrays to the x and y coordinates.
- Parameters
-
shape The shape of the output array (width and height). bbox The bounding box that defines the cloud's coordinate system. p_noise_x Optional reference to a noise array applied to the x-coordinates for domain warping (not in pixels). p_noise_y Optional reference to a noise array applied to the y-coordinates for domain warping (not in pixels). bbox_array The bounding box of the destination array.
- Returns
- Array The resulting array filled with the signed distance function.
Example
Result
◆ to_array_interp()
| void hmap::Cloud::to_array_interp | ( | Array & | array, |
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, |
||
| InterpolationMethod2D | interpolation_method = InterpolationMethod2D::DELAUNAY, |
||
| Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox_array = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) | const |
Interpolate the values of an array using the cloud points.
This method populates an array with interpolated values based on the positions and values of the cloud points. The interpolation method can be specified, and optional noise arrays can be used for domain warping.
- Parameters
-
array The output array that will be populated with interpolated values. bbox The bounding box that defines the cloud's coordinate system. interpolation_method The method used for interpolation (e.g., nearest neighbor, bilinear). p_noise_x Optional reference to a noise array applied to the x-coordinates for domain warping (not in pixels). p_noise_y Optional reference to a noise array applied to the y-coordinates for domain warping (not in pixels). bbox_array The bounding box of the destination array.
Example
Result

◆ to_csv()
| void hmap::Cloud::to_csv | ( | const std::string & | fname | ) | const |
Export the cloud data to a CSV file.
This function saves the cloud points and their associated values to a CSV file.
- Parameters
-
fname The name of the output CSV file.
◆ to_graph_delaunay()
| Graph hmap::Cloud::to_graph_delaunay | ( | ) |
Convert the cloud to a graph using Delaunay triangulation.
This function generates a graph representation of the cloud using Delaunay triangulation. The resulting graph can be used for various geometric and topological analyses.
- Returns
- Graph The resulting graph from Delaunay triangulation.
◆ to_png()
| void hmap::Cloud::to_png | ( | const std::string & | fname, |
| int | cmap, | ||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, |
||
| int | depth = CV_8U, |
||
| glm::ivec2 | shape = {512, 512} |
||
| ) |
Saves the current data as a PNG image file.
This function exports the current data to a PNG file with specified parameters. The image is created using the provided colormap, bounding box, bit depth, and shape. The bounding box determines the area of the data to be included in the image, while the shape defines the dimensions of the output image.
- Parameters
-
fname The file name for the output PNG image. This should include the file extension (e.g., "output.png"). cmap An integer specifying the colormap to be used for rendering the data. This index refers to a predefined colormap. bbox A glm::vec4specifying the bounding box of the data to be included in the image. It is given as {xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax}. The default is {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}.depth An integer specifying the bit depth of the image. It should be a value defined by OpenCV (e.g., CV_8Ufor 8-bit unsigned). The default isCV_8U.shape A glm::ivec2specifying the dimensions of the output image. It is given as {width, height}. The default is {512, 512}.
Member Data Documentation
◆ points
| std::vector<Point> hmap::Cloud::points = {} |
Points of the cloud.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files: