Represents an ordered set of points in 2D, forming a polyline (open or closed). More...
#include <path.hpp>
Public Member Functions | |
| Path (bool closed=false) | |
Construct a new Path object with default properties. Initializes an empty path with the closed property set to false. | |
| Path (int npoints, uint seed, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, bool closed=false) | |
| Construct a new Path object with random positions and values. Initializes a path with a specified number of points, random values, and the option to be open or closed. | |
| Path (std::vector< Point > points, bool closed=false) | |
| Construct a new Path object based on a list of points. Initializes a path with the specified points and an option to be open or closed. | |
| Path (std::vector< float > x, std::vector< float > y, bool closed=false) | |
Construct a new Path object based on x and y coordinates. Initializes a path with the specified x and y coordinates and an option to be open or closed. | |
| Path (std::vector< float > x, std::vector< float > y, std::vector< float > v, bool closed=false) | |
Construct a new Path object based on x, y coordinates, and values. Initializes a path with the specified x and y coordinates, associated values, and an option to be open or closed. | |
| void | bezier (float curvature_ratio=0.3f, int edge_divisions=10) |
| Smooth the path using Bezier curves. | |
| void | bezier_round (float curvature_ratio=0.3f, int edge_divisions=10) |
| Smooth the path using Bezier curves (alternative method). | |
| void | bspline (int edge_divisions=10) |
| Smooth the path using B-Spline curves. | |
| void | catmullrom (int edge_divisions=10) |
| Smooth the path using Catmull-Rom curves. | |
| void | clear () |
| Clear the path data. | |
| void | decasteljau (int edge_divisions=10) |
| Smooth the path using De Casteljau curves. | |
| void | decimate_cfit (int n_points_target=3) |
| Simplifies the current path using a curvature preserving algorithm. | |
| void | decimate_vw (int n_points_target=3) |
| Simplifies the current path using the Visvalingam-Whyatt algorithm. | |
| void | dijkstra (Array &array, glm::vec4 bbox, float elevation_ratio=0.f, float distance_exponent=0.5f, float upward_penalization=1.f, Array *p_mask_nogo=nullptr) |
| Divide the path by adding points based on the lowest elevation difference between each pair of edge endpoints. | |
| void | divide () |
| Divide the path by adding a point between each pair of consecutive points. | |
| void | fractalize (int iterations, uint seed, float sigma=0.3f, int orientation=0, float persistence=1.f, Array *p_control_field=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Applies fractalization to the path by adding points and randomly displacing their positions. | |
| std::vector< float > | get_arc_length () |
| Get the arc length of the path. | |
| std::vector< float > | get_cumulative_distance () |
| Get the cumulative distance of the path. | |
| std::vector< float > | get_values () const |
| Get the values assigned to the points on the path. | |
| std::vector< float > | get_x () const |
Get the x coordinates of the points on the path. | |
| std::vector< float > | get_xy () const |
| Get the coordinates of the points as a single vector. | |
| std::vector< float > | get_y () const |
Get the y coordinates of the points on the path. | |
| void | enforce_monotonic_values (bool decreasing=true) |
| Enforces monotonicity on the values of the points in the path. | |
| void | meanderize (float ratio, float noise_ratio=0.1f, uint seed=1, int iterations=1, int edge_divisions=10) |
| Add "meanders" to the path. | |
| void | reorder_nns (int start_index=0) |
| Reorder points using a nearest neighbor search. | |
| void | resample (float delta) |
| Resample the path to achieve an approximately constant distance between points. | |
| void | resample_uniform () |
| Resample the path to achieve fairly uniform distance between consecutive points. | |
| void | reverse () |
| Reverse the order of points in the path. | |
| float | sdf_angle_closed (float x, float y) |
| Return the angle of the closest edge to the point (x, y), assuming a closed path. | |
| float | sdf_angle_open (float x, float y) |
| Return the angle of the closest edge to the point (x, y), assuming an open path. | |
| float | sdf_closed (float x, float y) |
| Return the signed distance function value at (x, y), assuming a closed path. | |
| float | sdf_elevation_closed (float x, float y, float slope) |
Return the elevation value at (x, y) away from the path based on a downslope slope, assuming a closed path. | |
| float | sdf_elevation_open (float x, float y, float slope) |
Return the elevation value at (x, y) away from the path based on a downslope slope, assuming an open path. | |
| float | sdf_open (float x, float y) |
| Return the value of the signed distance function at (x, y), assuming an open path. | |
| void | smooth (int navg=1, float averaging_intensity=1.f, float inertia=0.f) |
| Applies a smoothing operation to the path points using a moving average filter. | |
| void | subsample (int step) |
| Subsample the path by keeping only every n-th point. | |
| void | to_array (Array &array, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, bool filled=false) const |
| Project path points to an array. | |
| Array | to_array_sdf (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec4 bbox, Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox_array={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Return an array filled with the signed distance function to the path. | |
| void | to_png (std::string fname, glm::ivec2 shape={512, 512}) |
| Export path as PNG image file. | |
 Public Member Functions inherited from hmap::Cloud Public Member Functions inherited from hmap::Cloud | |
| Cloud () | |
| Default constructor for the Cloud class. | |
| virtual | ~Cloud ()=default |
| Cloud (int npoints, uint seed, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) | |
| Constructs a new Cloud object with random positions and values. | |
| Cloud (const std::vector< Point > &points) | |
| Constructs a new Cloud object based on a list of existing points. | |
| Cloud (const std::vector< float > &x, const std::vector< float > &y, float default_value=0.f) | |
Constructs a new Cloud object from lists of x and y coordinates. | |
| Cloud (const std::vector< float > &x, const std::vector< float > &y, const std::vector< float > &v) | |
Constructs a new Cloud object from lists of x and y coordinates with assigned values. | |
| void | add_point (const Point &p) |
| Add a new point to the cloud. | |
| void | clear () |
| Clear all data from the cloud. | |
| bool | from_csv (const std::string &fname) |
| Loads point data from a CSV file into the Cloud object. | |
| glm::vec4 | get_bbox () const |
| Get the bounding box of the cloud. | |
| Point | get_center () const |
| Calculates the centroid of a set of points. | |
| std::vector< int > | get_convex_hull_point_indices () const |
| Computes the indices of the points that form the convex hull of a set of points. | |
| size_t | get_npoints () const |
| Get the number of points in the cloud. | |
| std::vector< float > | get_values () const |
| Get the values assigned to the points in the cloud. | |
| float | get_values_max () const |
| Get the maximum value among the points in the cloud. | |
| float | get_values_min () const |
| Get the minimum value among the points in the cloud. | |
| std::vector< float > | interpolate_values_from_array (const Array &array, glm::vec4 bbox) |
Interpolate values from an array at the points' (x, y) locations. | |
| void | print () |
| Print information about the cloud's points. | |
| void | randomize (uint seed, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Randomize the positions and values of the cloud points. | |
| void | rejection_filter_density (const Array &density_mask, uint seed, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Filter a point cloud using rejection sampling based on a density mask. | |
| void | remap_values (float vmin, float vmax) |
| Remap the values of the cloud points to a target range. | |
| void | remove_point (int point_idx) |
| Remove a point from the cloud. | |
| void | set_points (const std::vector< float > &x, const std::vector< float > &y) |
| Set points of the using x, y coordinates. | |
| void | set_values (const std::vector< float > &new_values) |
| Set new values for the cloud points. | |
| void | set_values (float new_value) |
| Set a single value for all cloud points. | |
| void | set_values_from_array (const Array &array, const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Set the values of the cloud points using values from an underlying array. | |
| void | set_values_from_border_distance (const glm::vec4 &bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) |
| Sets point values based on their distance to the bounding box border. | |
| void | set_values_from_chull_distance () |
| Set the values of the cloud points based on the distance to the convex hull of the cloud. | |
| void | set_values_from_min_distance () |
| Sets point values based on the distance to their nearest neighbor. | |
| void | shuffle (float dx, float dy, uint seed, float dv=0.f) |
| Randomly perturbs the positions and values of all points in the cloud. | |
| void | to_array (Array &array, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) const |
| Project the cloud points onto an array. | |
| Array | to_array_sdf (glm::ivec2 shape, glm::vec4 bbox, Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox_array={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) const |
| Generate an array filled with the signed distance function (SDF) to the cloud points. | |
| void | to_array_interp (Array &array, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, InterpolationMethod2D interpolation_method=InterpolationMethod2D::DELAUNAY, Array *p_noise_x=nullptr, Array *p_noise_y=nullptr, glm::vec4 bbox_array={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}) const |
| Interpolate the values of an array using the cloud points. | |
| void | to_csv (const std::string &fname) const |
| Export the cloud data to a CSV file. | |
| Graph | to_graph_delaunay () |
| Convert the cloud to a graph using Delaunay triangulation. | |
| void | to_png (const std::string &fname, int cmap, glm::vec4 bbox={0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, int depth=CV_8U, glm::ivec2 shape={512, 512}) |
| Saves the current data as a PNG image file. | |
Public Attributes | |
| bool | closed |
Defines whether the path is closed or open. If true, the path is closed, forming a loop. If false, the path is open. | |
 Public Attributes inherited from hmap::Cloud Public Attributes inherited from hmap::Cloud | |
| std::vector< Point > | points = {} |
| Points of the cloud. | |
Detailed Description
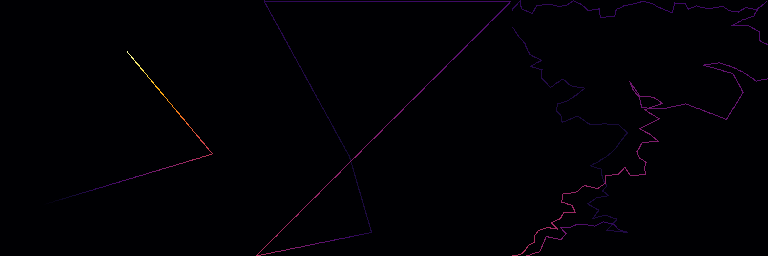
Represents an ordered set of points in 2D, forming a polyline (open or closed).
The Path class extends the Cloud class to represent a sequence of points in 2D space that are connected in a specific order, forming a polyline. The polyline can be either open or closed, depending on whether the first and last points are connected. This class provides methods for various geometric operations, including path length calculation, point insertion, and more.
Example
Result
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
◆ Path() [1/5]
|
inline |
Construct a new Path object with default properties. Initializes an empty path with the closed property set to false.
- Parameters
-
closed Open/close path flag.
◆ Path() [2/5]
|
inline |
Construct a new Path object with random positions and values. Initializes a path with a specified number of points, random values, and the option to be open or closed.
- Parameters
-
npoints Number of points to generate. seed Random seed number for generating random values. bbox Bounding box for random point generation. closed Open/close path flag.
◆ Path() [3/5]
|
inline |
Construct a new Path object based on a list of points. Initializes a path with the specified points and an option to be open or closed.
- Parameters
-
points List of points defining the path. closed Open/close path flag.
◆ Path() [4/5]
|
inline |
Construct a new Path object based on x and y coordinates. Initializes a path with the specified x and y coordinates and an option to be open or closed.
- Parameters
-
x List of xcoordinates for the points.y List of ycoordinates for the points.closed Open/close path flag.
◆ Path() [5/5]
|
inline |
Construct a new Path object based on x, y coordinates, and values. Initializes a path with the specified x and y coordinates, associated values, and an option to be open or closed.
- Parameters
-
x List of xcoordinates for the points.y List of ycoordinates for the points.v List of values associated with the points. closed Open/close path flag.
Member Function Documentation
◆ bezier()
| void hmap::Path::bezier | ( | float | curvature_ratio = 0.3f, |
| int | edge_divisions = 10 |
||
| ) |
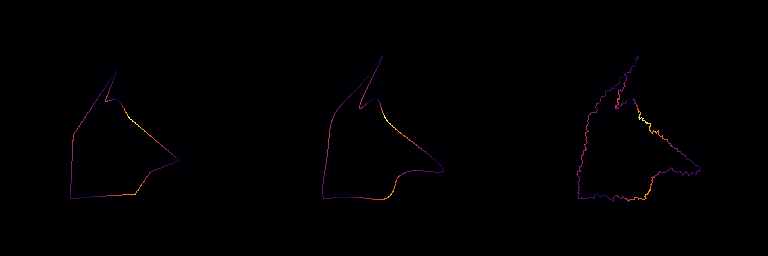
Smooth the path using Bezier curves.
This method applies Bezier curve smoothing to the path. The curvature_ratio controls the amount of curvature applied, with typical values in the range of [-1, 1], where positive values generally result in more pronounced curvature. The edge_divisions parameter determines the number of subdivisions per edge to create a smoother curve.
Example
Result
- Parameters
-
curvature_ratio Amount of curvature, usually in the range [-1, 1], with positive values resulting in more curvature. edge_divisions Number of subdivisions per edge to achieve smooth curves.
◆ bezier_round()
| void hmap::Path::bezier_round | ( | float | curvature_ratio = 0.3f, |
| int | edge_divisions = 10 |
||
| ) |
Smooth the path using Bezier curves (alternative method).
This alternative method applies Bezier curve smoothing to the path. The curvature_ratio parameter affects the curvature amount, similar to the bezier method. The edge_divisions parameter specifies how finely each edge is divided to create a smoother curve.
Example
Result
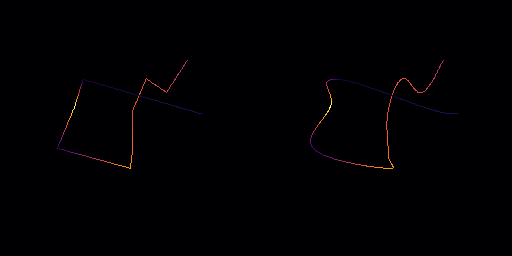
- Parameters
-
curvature_ratio Amount of curvature, typically within [-1, 1], with positive values for increased curvature. edge_divisions Number of edge subdivisions for smoothness.
◆ bspline()
| void hmap::Path::bspline | ( | int | edge_divisions = 10 | ) |
Smooth the path using B-Spline curves.
This method smooths the path using B-Spline curves, which provide a smooth curve that passes through the control points. The edge_divisions parameter defines the number of subdivisions per edge for achieving smooth curves.
Important: This function does not correctly handle closed polylines (circular contours). If the path is closed, the smoothing may not correctly close the loop, potentially leaving a gap between the start and end points.
Example
Result
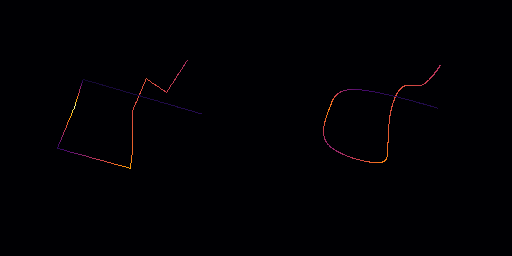
- Parameters
-
edge_divisions Number of subdivisions per edge to achieve a smooth B-Spline curve.
- Warning
- This function does not correctly handle closed polylines.
◆ catmullrom()
| void hmap::Path::catmullrom | ( | int | edge_divisions = 10 | ) |
Smooth the path using Catmull-Rom curves.
This method applies Catmull-Rom curve smoothing to the path. Catmull-Rom splines are interpolating splines that pass through each control point. The edge_divisions parameter determines the number of subdivisions per edge for smoothing.
Important: This function does not correctly handle closed polylines (circular contours). If the path is closed, the smoothing may not correctly close the loop, potentially leaving a gap between the start and end points.
Example
Result
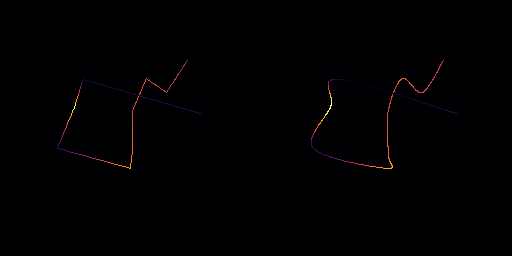
- Parameters
-
edge_divisions Number of edge subdivisions to create a smooth Catmull-Rom curve.
- Warning
- This function does not correctly handle closed polylines.
◆ clear()
| void hmap::Path::clear | ( | ) |
Clear the path data.
This method removes all points and associated data from the path, effectively resetting it to an empty state.
◆ decasteljau()
| void hmap::Path::decasteljau | ( | int | edge_divisions = 10 | ) |
Smooth the path using De Casteljau curves.
This function smooths a path by applying De Casteljau's algorithm to generate intermediate points along the path, effectively creating a Bézier curve that approximates the original path. The path is divided into segments, and the De Casteljau algorithm is applied to each segment, resulting in a smooth curve.
The parameter edge_divisions controls the number of divisions (sub-segments) created along each segment of the path. A higher number of divisions will result in a smoother curve, but will also increase the computational cost.
- Parameters
-
edge_divisions The number of divisions for each edge of the path. Default is 10, which provides a balanced level of smoothing.
Example
Result
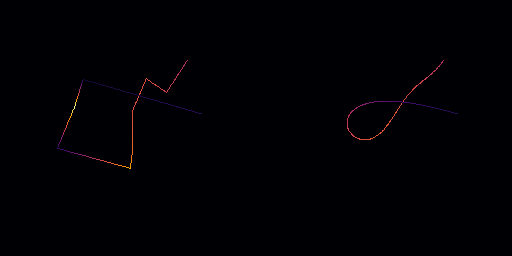
◆ decimate_cfit()
| void hmap::Path::decimate_cfit | ( | int | n_points_target = 3 | ) |
Simplifies the current path using a curvature preserving algorithm.
- Parameters
-
n_points_target The desired number of points to retain in the path. If the current number of points is less than n_points_targetor the path contains fewer than 3 points, the method returns without modifying the path.
- Note
- Does not well behave when n_points_target is significantly lower than the initial number of points.
Example
Result
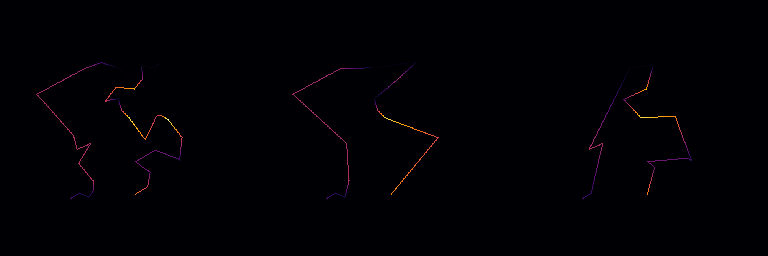
◆ decimate_vw()
| void hmap::Path::decimate_vw | ( | int | n_points_target = 3 | ) |
Simplifies the current path using the Visvalingam-Whyatt algorithm.
This method reduces the number of points in the path to the specified target, n_points_target, while preserving the overall shape. It calculates the area of triangles formed by consecutive points and removes points corresponding to the smallest areas iteratively.
- Parameters
-
n_points_target The desired number of points to retain in the path. If the current number of points is less than n_points_targetor the path contains fewer than 3 points, the method returns without modifying the path.
- Note
- Does not well behave when n_points_target is significantly lower than the initial number of points.
Example
Result
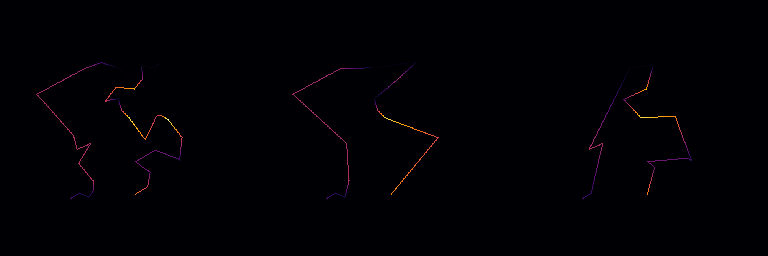
◆ dijkstra()
| void hmap::Path::dijkstra | ( | Array & | array, |
| glm::vec4 | bbox, | ||
| float | elevation_ratio = 0.f, |
||
| float | distance_exponent = 0.5f, |
||
| float | upward_penalization = 1.f, |
||
| Array * | p_mask_nogo = nullptr |
||
| ) |
Divide the path by adding points based on the lowest elevation difference between each pair of edge endpoints.
This method uses the elevation map to subdivide the path by adding intermediate points where the elevation difference between edges is minimal. The elevation_ratio parameter balances the influence of absolute elevation versus elevation difference in the cost function used for path finding. The distance_exponent affects the weight function used in Dijkstra's algorithm. Areas defined by the p_mask_nogo mask are avoided.
Example
Result
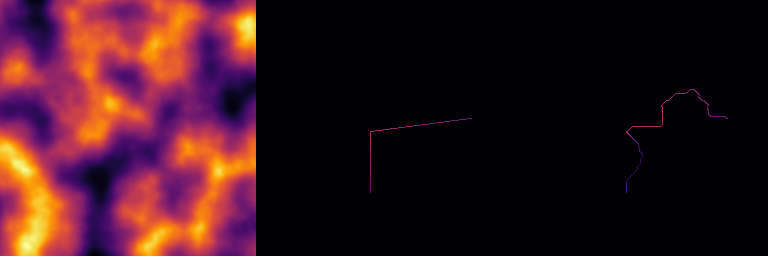
- Parameters
-
array Elevation map used to determine elevation differences along the path. bbox Bounding box of the domain, defining the area where elevation data is valid. edge_divisions Number of subdivisions per edge; set to 0 for automatic division based on array shape. elevation_ratio Ratio used to balance absolute elevation and elevation difference in the cost function. distance_exponent Exponent used in the Dijkstra weight function to adjust the influence of distance. p_mask_nogo Optional mask array defining areas to avoid; points in these areas will not be considered.
- See also
- Array::find_path_dijkstra
◆ divide()
| void hmap::Path::divide | ( | ) |
Divide the path by adding a point between each pair of consecutive points.
This method adds new points in the middle of each segment of the path to create a denser set of points along the path. This is useful for increasing the resolution of the path.
◆ fractalize()
| void hmap::Path::fractalize | ( | int | iterations, |
| uint | seed, | ||
| float | sigma = 0.3f, |
||
| int | orientation = 0, |
||
| float | persistence = 1.f, |
||
| Array * | p_control_field = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Applies fractalization to the path by adding points and randomly displacing their positions.
This method enhances the complexity of a path by iteratively adding new points between existing ones and displacing them using Gaussian noise. The process can simulate natural phenomena like terrain generation or random walk paths. The number of iterations determines the level of detail added to the path.
sigmacontrols the magnitude of the displacement, normalized by the distance between points.orientationdirects the displacement:0for random directions,1for inflation (outward displacement),-1for deflation (inward displacement).
persistencegoverns how the noise strength evolves over iterations, typically reducing it gradually.- An optional
control_fieldarray allows for local adjustments of displacement amplitude, guided by thebbox(bounding box), which defines the spatial extent within which the control field is applied.
Example
Result

- Parameters
-
iterations Number of iterations to apply the fractalization process. seed Seed value for random number generation, ensuring reproducibility. sigma Standard deviation of the Gaussian displacement, relative to the distance between points. orientation Determines the displacement direction: 0for random,1for inflation,-1for deflation.persistence Factor that adjusts the noise intensity across iterations. control_field Optional pointer to an array that locally modifies the displacement amplitude. bbox Bounding box that defines the valid area for the control field's influence.
◆ get_arc_length()
| std::vector< float > hmap::Path::get_arc_length | ( | ) |
Get the arc length of the path.
The arc length is the cumulative distance along the path, normalized to the range [0, 1]. This represents the distance traveled from the start to each point along the path as a fraction of the total path length.
- Returns
- std::vector<float> Vector of arc length values, where each entry corresponds to a point on the path and represents the normalized distance from the start of the path to that point.
◆ get_cumulative_distance()
| std::vector< float > hmap::Path::get_cumulative_distance | ( | ) |
Get the cumulative distance of the path.
This method computes the cumulative distance along the path, which is the total distance traveled up to each point on the path. It accumulates the distances from the start of the path to each point.
- Returns
- std::vector<float> Vector of cumulative distance values, where each entry represents the distance from the start of the path to the respective point.
◆ get_values()
| std::vector< float > hmap::Path::get_values | ( | ) | const |
Get the values assigned to the points on the path.
This method retrieves the values assigned to each point on the path. These values can represent any attribute associated with the points, such as color, intensity, or other metrics.
- Returns
- std::vector<float> Vector of values assigned to the points on the path.
◆ get_x()
|
virtual |
Get the x coordinates of the points on the path.
This method retrieves the x coordinates of all points in the path. Each value in the returned vector corresponds to the x coordinate of a point along the path.
- Returns
- std::vector<float> Vector of
xvalues of the points on the path.
Reimplemented from hmap::Cloud.
◆ get_xy()
|
virtual |
Get the coordinates of the points as a single vector.
This method returns the coordinates of the points in the path as a single vector, where the coordinates are interleaved: (x0, y0, x1, y1, ...). This format is useful for operations that require a flat representation of the coordinates.
- Returns
- std::vector<float> Vector of interleaved
xandycoordinates of the points on the path.
Reimplemented from hmap::Cloud.
◆ get_y()
|
virtual |
Get the y coordinates of the points on the path.
This method retrieves the y coordinates of all points in the path. Each value in the returned vector corresponds to the y coordinate of a point along the path.
- Returns
- std::vector<float> Vector of
yvalues of the points on the path.
Reimplemented from hmap::Cloud.
◆ enforce_monotonic_values()
| void hmap::Path::enforce_monotonic_values | ( | bool | decreasing = true | ) |
Enforces monotonicity on the values of the points in the path.
This method adjusts the v values of the points in the path to ensure that they are either monotonically decreasing or increasing, based on the input parameter.
- Parameters
-
decreasing If true, enforces a monotonically decreasing order for the values. If false, enforces a monotonically increasing order for the values.
- Note
- This method modifies the path in place.
◆ meanderize()
| void hmap::Path::meanderize | ( | float | ratio, |
| float | noise_ratio = 0.1f, |
||
| uint | seed = 1, |
||
| int | iterations = 1, |
||
| int | edge_divisions = 10 |
||
| ) |
Add "meanders" to the path.
This method introduces meandering effects to the path by adding random deviations. The amplitude of the meanders is controlled by the ratio parameter, while the noise_ratio controls the amount of randomness. The seed parameter is used to initialize the random number generator, ensuring reproducibility. The iterations parameter defines how many times the meandering process is applied, and edge_divisions controls how finely each edge is subdivided during the meandering.
Example
Result

- Parameters
-
ratio Amplitude ratio of the meanders. Typically a positive value. noise_ratio Ratio of randomness introduced during meandering. Default is 0.1. seed Seed for random number generation. Default is 1. iterations Number of iterations to apply meandering. Default is 1. edge_divisions Number of sub-divisions of each edge. Default is 10.
◆ reorder_nns()
| void hmap::Path::reorder_nns | ( | int | start_index = 0 | ) |
Reorder points using a nearest neighbor search.
This method reorders the points in the path to minimize the total distance by performing a nearest neighbor search starting from the specified start_index. This approach is useful for optimizing the path or improving its order.
- Parameters
-
start_index Index of the starting point for the nearest neighbor search. Default is 0.
◆ resample()
| void hmap::Path::resample | ( | float | delta | ) |
Resample the path to achieve an approximately constant distance between points.
This method adjusts the points in the path to ensure that the distance between each consecutive point is approximately equal to the specified delta. This is useful for creating a path with evenly spaced points.
- Parameters
-
delta Target distance between consecutive points.
◆ resample_uniform()
| void hmap::Path::resample_uniform | ( | ) |
Resample the path to achieve fairly uniform distance between consecutive points.
This method adjusts the path so that the distance between each consecutive point is as uniform as possible. It redistributes the points to ensure more even spacing along the path.
◆ reverse()
| void hmap::Path::reverse | ( | ) |
Reverse the order of points in the path.
This method reverses the sequence of points in the path, which can be useful for various applications, such as changing the direction of the path traversal.
◆ sdf_angle_closed()
| float hmap::Path::sdf_angle_closed | ( | float | x, |
| float | y | ||
| ) |
Return the angle of the closest edge to the point (x, y), assuming a closed path.
This method calculates the angle of the edge closest to the specified point (x, y) on a path that is closed. The angle is returned in radians. The path is assumed to form a continuous loop, and the closest edge is determined accordingly.
Example
Result



- Parameters
-
x x coordinate of the point. y y coordinate of the point.
- Returns
- float Angle of the closest edge in radians.
◆ sdf_angle_open()
| float hmap::Path::sdf_angle_open | ( | float | x, |
| float | y | ||
| ) |
Return the angle of the closest edge to the point (x, y), assuming an open path.
This method calculates the angle of the edge closest to the specified point (x, y) on a path that is open. The angle is returned in radians. The path is assumed to have distinct start and end points, and the closest edge is determined based on this open structure.
Example
Result



- Parameters
-
x x coordinate of the point. y y coordinate of the point.
- Returns
- float Angle of the closest edge in radians.
◆ sdf_closed()
| float hmap::Path::sdf_closed | ( | float | x, |
| float | y | ||
| ) |
Return the signed distance function value at (x, y), assuming a closed path.
This method computes the signed distance from the point (x, y) to the nearest edge of a closed path. The distance is signed, meaning it indicates whether the point is inside or outside the path, with negative values typically indicating that the point is inside the path.
Example
Result



- Parameters
-
x x coordinate of the point. y y coordinate of the point.
- Returns
- float Signed distance to the nearest edge.
◆ sdf_elevation_closed()
| float hmap::Path::sdf_elevation_closed | ( | float | x, |
| float | y, | ||
| float | slope | ||
| ) |
Return the elevation value at (x, y) away from the path based on a downslope slope, assuming a closed path.
This method calculates the elevation value at a point (x, y) based on its distance from the closed path, adjusted by a downslope factor. The downslope determines how quickly the elevation decreases as you move away from the path.
Example
Result



- Parameters
-
x x coordinate of the point. y y coordinate of the point. slope Downslope factor influencing the elevation decrease.
- Returns
- float Adjusted elevation value based on the downslope.
◆ sdf_elevation_open()
| float hmap::Path::sdf_elevation_open | ( | float | x, |
| float | y, | ||
| float | slope | ||
| ) |
Return the elevation value at (x, y) away from the path based on a downslope slope, assuming an open path.
This method calculates the elevation value at a point (x, y) considering its distance from an open path and adjusting it based on a downslope factor. The downslope determines how the elevation decreases as you move away from the path.
Example
Result



- Parameters
-
x x coordinate of the point. y y coordinate of the point. slope Downslope factor affecting the elevation decrease.
- Returns
- float Adjusted elevation value based on the downslope.
◆ sdf_open()
| float hmap::Path::sdf_open | ( | float | x, |
| float | y | ||
| ) |
Return the value of the signed distance function at (x, y), assuming an open path.
This method computes the signed distance from the point (x, y) to the nearest edge of an open path. The signed distance indicates how far the point is from the path, with positive values typically representing the outside of the path and negative values indicating the inside.
Example
Result



- Parameters
-
x x coordinate of the point. y y coordinate of the point.
- Returns
- float Signed distance to the nearest edge of the open path.
◆ smooth()
Applies a smoothing operation to the path points using a moving average filter.
This method smooths the path points based on a specified number of neighboring points, an averaging intensity, and an inertia factor. The smoothing involves calculating the average of neighboring points within a range defined by navg, and then applying an intensity-based weighted average to blend the original and smoothed values. Additionally, an inertia effect can be applied to gradually adjust point positions based on previous points.
- Parameters
-
navg Number of neighboring points to consider on each side of the current point during the smoothing process. Higher values result in broader smoothing. averaging_intensity The weight given to the averaged points. A value of 1.0 applies full intensity, resulting in a complete averaging of the neighboring points. Lower values retain more of the original point's position. inertia The factor by which each point is influenced by its previous point after the initial smoothing pass. A value of 0 has no inertia effect, while a higher value blends the current point's position with that of the preceding point, creating a trailing effect.
Example
Result
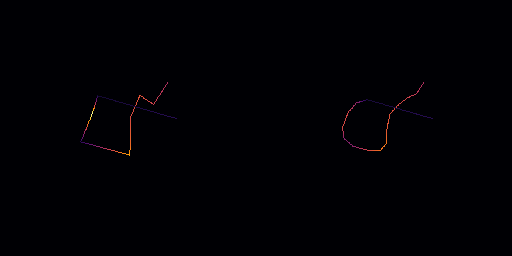
◆ subsample()
| void hmap::Path::subsample | ( | int | step | ) |
Subsample the path by keeping only every n-th point.
This method reduces the number of points in the path by retaining only every 'step'-th point, effectively subsampling the path. This can be useful for simplifying the path or reducing data size.
- Parameters
-
step The interval of points to keep. For example, a step of 2 will keep every second point.
◆ to_array()
| void hmap::Path::to_array | ( | Array & | array, |
| glm::vec4 | bbox = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f}, |
||
| bool | filled = false |
||
| ) | const |
Project path points to an array.
This method projects the points of the path onto a 2D array, filling the array based on the path's points. Optionally, the contour of the path can be filled using flood fill if the filled parameter is set to true.
Example
- Parameters
-
array The array to which the path points will be projected. bbox Bounding box defining the domain of the array. filled Boolean flag indicating whether to perform flood filling of the path's contour.
◆ to_array_sdf()
| Array hmap::Path::to_array_sdf | ( | glm::ivec2 | shape, |
| glm::vec4 | bbox, | ||
| Array * | p_noise_x = nullptr, |
||
| Array * | p_noise_y = nullptr, |
||
| glm::vec4 | bbox_array = {0.f, 1.f, 0.f, 1.f} |
||
| ) |
Return an array filled with the signed distance function to the path.
This method computes the signed distance function (SDF) from the path and fills an output array with the calculated values. The SDF represents the distance from each point in the array to the nearest point on the path, with positive values indicating distances outside the path and negative values indicating distances inside the path.
Example
Result
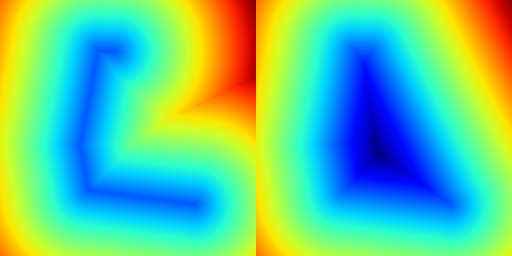
- Parameters
-
shape Shape of the output array, defining its dimensions. bbox Bounding box specifying the region to consider for the SDF calculation. p_noise_x Optional reference to an array of noise values in the x-direction used for domain warping. If not provided, no noise is applied. p_noise_y Optional reference to an array of noise values in the y-direction used for domain warping. If not provided, no noise is applied. bbox_array Bounding box of the destination array, used to map the output array coordinates to the path coordinates.
- Returns
- Array The resulting array filled with the signed distance function values.
◆ to_png()
| void hmap::Path::to_png | ( | std::string | fname, |
| glm::ivec2 | shape = {512, 512} |
||
| ) |
Export path as PNG image file.
This method generates a PNG image representing the path and saves it to the specified file. The resolution of the image can be adjusted using the shape parameter.
Example
- Parameters
-
fname The filename for the output PNG image. shape Resolution of the image, specified as width and height.
Member Data Documentation
◆ closed
| bool hmap::Path::closed |
Defines whether the path is closed or open. If true, the path is closed, forming a loop. If false, the path is open.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files: